1.the Five Common Types Of Expressway Interchanges Are _________________.
Onlines
Mar 14, 2025 · 6 min read
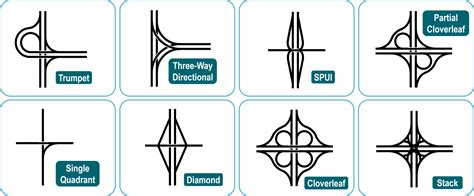
Table of Contents
Five Common Types of Expressway Interchanges: A Deep Dive into Design and Functionality
Expressways, the lifelines of modern transportation networks, wouldn't be nearly as efficient without well-designed interchanges. These crucial junctions allow vehicles to seamlessly transition between expressways and other roadways, minimizing congestion and maximizing traffic flow. Understanding the different types of interchanges is key to appreciating the complexity and ingenuity behind modern highway engineering. This article will explore five common types of expressway interchanges, detailing their design, advantages, disadvantages, and optimal applications.
1. Diamond Interchange
The diamond interchange, arguably the most common type, is characterized by its simplicity and cost-effectiveness. Its design features two pairs of ramps: one pair for entering the expressway and another for exiting. These ramps cross over or under the expressway's main lanes, forming a diamond shape.
Advantages of Diamond Interchanges:
- Cost-effective: Diamond interchanges are relatively inexpensive to construct compared to other interchange types, making them ideal for areas with limited budgets.
- Simple design: Their straightforward design simplifies construction and maintenance.
- Suitable for low-volume traffic: They function efficiently for lower traffic volumes.
Disadvantages of Diamond Interchanges:
- Weaving conflicts: Drivers merging onto and exiting the expressway often create weaving conflicts, potentially leading to accidents, especially at higher traffic volumes.
- Inefficient for high-volume traffic: Diamond interchanges can become significantly congested during peak hours due to the merging and diverging maneuvers.
- Limited capacity: Their capacity is limited, making them unsuitable for areas with high traffic demands.
2. Cloverleaf Interchange
The cloverleaf interchange offers a more complex design, featuring a continuous loop ramp system for both entering and exiting the expressway. This design eliminates some of the weaving conflicts found in diamond interchanges, but at the cost of increased complexity and land requirements.
Advantages of Cloverleaf Interchanges:
- Reduced weaving conflicts: Compared to diamond interchanges, cloverleafs minimize weaving maneuvers, improving safety and traffic flow.
- Improved capacity: They offer a higher capacity than diamond interchanges, accommodating larger traffic volumes.
Disadvantages of Cloverleaf Interchanges:
- High construction costs: Cloverleaf interchanges are considerably more expensive to build than diamond interchanges due to their complex ramp system and greater land usage.
- High land requirements: Their design necessitates a significant amount of land, making them unsuitable for areas with limited space.
- Potential for high speeds on ramps: The continuous curves can encourage higher speeds on the ramps, increasing the risk of accidents.
3. Trumpet Interchange
The trumpet interchange, also known as a partial cloverleaf, is a hybrid design combining elements of both diamond and cloverleaf interchanges. It usually accommodates traffic moving from one direction of the expressway to one direction of the intersecting road. It's essentially half a cloverleaf.
Advantages of Trumpet Interchanges:
- Cost-effective alternative to cloverleaf: It offers a more cost-effective option compared to a full cloverleaf interchange.
- Reduced land requirements: It needs less land than a full cloverleaf, but more than a diamond.
- Improved safety over a simple diamond: It offers better safety features compared to a diamond interchange, particularly in situations with higher traffic volumes.
Disadvantages of Trumpet Interchanges:
- Limited capacity: The capacity is still limited compared to a full cloverleaf.
- Potential for congestion: Congestion can occur during peak hours.
- Not suitable for all situations: It’s not ideal for all traffic scenarios, as it only caters to traffic flows in one direction.
4. Directional Interchange
A directional interchange is a more advanced design that separates traffic movements based on their desired directions. This separation helps minimize weaving and improve traffic flow, particularly beneficial for high-volume expressways. Directional interchanges are often complex and expensive to build, but they significantly improve safety and efficiency.
Advantages of Directional Interchanges:
- Optimal traffic flow: The separated movements result in significantly improved traffic flow and reduced congestion.
- Enhanced safety: Minimizing weaving conflicts dramatically reduces the risk of accidents.
- Suitable for high-volume traffic: Directional interchanges are well-suited for expressways with exceptionally high traffic volumes.
Disadvantages of Directional Interchanges:
- High construction costs: These are among the most expensive interchange types to construct.
- Complex design: Their intricate design increases complexity in planning, construction, and maintenance.
- Large land requirements: They require substantial land areas, limiting their suitability for constrained urban environments.
5. Turbine Interchange
The turbine interchange is a complex and efficient design, particularly effective for handling large volumes of traffic between two expressways intersecting at approximately a 90-degree angle. It's characterized by its circular or spiral ramp design, enabling smooth transitions between the expressways and minimizing weaving.
Advantages of Turbine Interchanges:
- Exceptional capacity: They can handle exceptionally high traffic volumes with relative ease.
- High efficiency: The design optimizes traffic flow, reducing congestion and delays.
- Superior safety: The smooth ramp transitions significantly enhance safety compared to simpler interchange types.
Disadvantages of Turbine Interchanges:
- Extremely high construction costs: These are among the most expensive interchanges to build and maintain.
- Extensive land requirements: Their complex design demands a large amount of land.
- Complex design and construction: Planning, construction, and maintenance are complex and require high levels of engineering expertise.
Choosing the Right Interchange Type: Factors to Consider
The selection of an appropriate interchange type depends on several crucial factors:
- Traffic volume: Interchanges must be designed to handle the expected traffic load, both current and projected future volumes. High-volume areas necessitate interchanges with higher capacities, such as directional or turbine interchanges.
- Available land: The amount of available land significantly impacts the choice of interchange type. Limited space might restrict the options to simpler, less land-intensive designs like diamond interchanges.
- Budget: Construction costs vary dramatically between interchange types. Diamond interchanges are the most cost-effective, while turbine interchanges are the most expensive. Budget constraints will heavily influence the selection process.
- Safety: Safety considerations are paramount. Interchange designs minimizing weaving and high-speed maneuvers are crucial for reducing accident rates.
- Environmental impact: Environmental factors, such as the impact on surrounding ecosystems and noise pollution, must also be considered. This can influence the placement and design of the ramps and other elements of the interchange.
- Future expansion: The interchange should be designed to accommodate future traffic growth and potential expansions of the highway system.
Conclusion: Balancing Efficiency, Safety, and Cost
The selection of an expressway interchange type is a complex decision, demanding careful consideration of numerous factors. While diamond interchanges represent a cost-effective solution for low-traffic areas, more intricate designs like directional and turbine interchanges are necessary for high-volume areas where safety and efficiency are paramount. The optimal choice involves a careful balancing act between cost, efficiency, safety, and the specific constraints of the project site. Understanding the characteristics of each type is critical for highway engineers, urban planners, and anyone interested in the intricacies of efficient transportation systems. Through careful planning and the selection of the appropriate interchange type, we can create highway networks that efficiently move people and goods while prioritizing safety and sustainability.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Would Represent A Referendum
Mar 14, 2025
-
Measured Progress Maryland Mathematics Performance Task Unstructured Answers
Mar 14, 2025
-
Advance Study Assignment The Geometrical Structure Of Molecules
Mar 14, 2025
-
Letrs Unit 6 Session 1 Check For Understanding
Mar 14, 2025
-
Pre Lab Exercise 20 2 Formed Elements
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 1.the Five Common Types Of Expressway Interchanges Are _________________. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
