10.3.5 Packet Tracer - Troubleshoot Default Gateway Issues
Onlines
Apr 05, 2025 · 7 min read
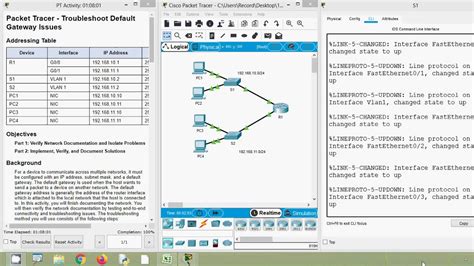
Table of Contents
10.3.5 Packet Tracer: Troubleshooting Default Gateway Issues – A Comprehensive Guide
Troubleshooting network connectivity problems can be a daunting task, but understanding the fundamentals, particularly the role of the default gateway, is crucial for effective problem-solving. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of default gateway issues within the context of Packet Tracer 10.3.5, providing you with a step-by-step approach to identify and resolve common problems. We'll cover various scenarios and techniques to help you master this essential networking skill.
Understanding the Default Gateway
Before diving into troubleshooting, let's solidify our understanding of the default gateway. The default gateway acts as the bridge between your local network and the wider internet or other networks. Think of it as the address your computer consults when it needs to send data outside its immediate network. If the default gateway is incorrectly configured or unavailable, your devices won't be able to communicate with the outside world.
Key Considerations Regarding Default Gateways:
- IP Address: The default gateway is identified by its IP address. This IP address must be reachable from your device.
- Subnet Mask: The subnet mask determines which network a device belongs to. It's essential that both the device and the gateway share the same network segment.
- Connectivity: The gateway itself must have a valid connection to the internet or other destination network.
- Routing Table: The device's routing table must correctly point to the default gateway's IP address for routes outside the local network.
Common Default Gateway Problems in Packet Tracer 10.3.5
In Packet Tracer, simulating network issues helps build practical troubleshooting experience. Here are some common default gateway problems you might encounter:
1. Incorrectly Configured Default Gateway IP Address:
This is the most frequent error. The device might have an incorrect gateway IP address entered in its configuration. For example, a typo in the IP address or using an IP address that doesn't belong to the gateway device will lead to connectivity failures.
2. Gateway Device Offline or Unreachable:
The default gateway device (typically a router) might be powered off, experiencing connectivity issues, or having a configuration problem itself. This will directly impact the ability of devices on the local network to communicate with external networks.
3. Incorrect Subnet Mask Configuration:
An incorrect subnet mask will prevent the device from identifying the network it belongs to and therefore won't be able to correctly route traffic to the default gateway.
4. Cable Disconnections:
Physical connectivity issues, such as loose or disconnected cables between the device and the default gateway, are common causes of network problems. In Packet Tracer, this is easily simulated by disconnecting the virtual cables.
5. Firewall Issues:
While less common in basic Packet Tracer setups, firewalls on the gateway or the device itself could be blocking necessary traffic. This can manifest as a failure to reach the default gateway, even if it's correctly configured.
Troubleshooting Methodology: A Step-by-Step Approach
Let's outline a structured approach to troubleshooting default gateway issues in Packet Tracer 10.3.5:
Step 1: Verify Physical Connections
Begin by visually inspecting all physical connections in your Packet Tracer network. Are all cables correctly plugged in? Are all devices powered on? This seemingly simple step often resolves a surprising number of problems.
Step 2: Check Device IP Configuration
- IP Address: Ensure each device has a valid IP address within the correct subnet.
- Subnet Mask: Verify that the subnet mask is correctly configured on all devices.
- Default Gateway: Check that the default gateway IP address is accurately set on each device. This should match the IP address of the interface on the router or gateway device facing the local network.
Note: Use the command-line interface (CLI) of each device (e.g., typing show ip interface brief on a Cisco router) to verify IP configuration.
Step 3: Ping the Default Gateway
From the device experiencing connectivity issues, use the ping command to test connectivity to the default gateway. For example: ping <default_gateway_ip_address>. If the ping is successful, the connection to the gateway is established; otherwise, proceed to the next steps.
Step 4: Ping an External Website
If the ping to the default gateway succeeded, attempt to ping an external website, such as google.com or 8.8.8.8. A successful ping indicates that the gateway is correctly functioning and has internet connectivity. If it fails, the problem might lie with the gateway's internet connection or its routing configuration.
Step 5: Investigate the Default Gateway Device
If previous steps failed, the problem likely resides within the default gateway itself. Examine its configuration:
- IP Address: Is the gateway's IP address correctly assigned and reachable?
- Routing Table: Check the gateway's routing table (using commands like
show ip routeon Cisco devices) to ensure it has a route to the external network. - Connectivity: Is the gateway properly connected to the internet? This might involve inspecting the uplink interface and its configuration.
Step 6: Check for Firewall Interference
Although less common in basic scenarios, firewalls can sometimes block network traffic. Temporarily disable firewalls on both the client device and the gateway to rule out this possibility. Remember to re-enable the firewalls after troubleshooting.
Step 7: Utilize Packet Tracer's Diagnostic Tools
Packet Tracer 10.3.5 offers powerful diagnostic tools. Use these tools to visualize the network traffic and identify potential bottlenecks or errors. This includes features like the "Simulation" tab and the ability to inspect individual packets.
Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques
For more complex scenarios, consider these advanced approaches:
- Traceroute: Use the
traceroutecommand to trace the path packets take to reach a destination. This helps identify potential points of failure along the network path. - ARP Table Inspection: Examine the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) table on the device to ensure that IP addresses are correctly mapped to MAC addresses. A faulty ARP table can cause connectivity problems.
- Network Topology Review: Carefully examine the entire network topology. Check for any misconfigurations, such as incorrect VLAN assignments or improperly configured switches.
Common Errors and Their Solutions: Real-World Examples
Let's examine some common scenarios and their solutions within the context of Packet Tracer 10.3.5:
Scenario 1: PC Cannot Access the Internet
- Problem: A PC is unable to access the internet. Pinging the default gateway fails.
- Possible Causes: Incorrect default gateway IP address on the PC, gateway device offline, or cable disconnection between the PC and the gateway.
- Solution: Verify PC IP configuration, check if the gateway is active, and inspect the cable connection.
Scenario 2: PC Can Ping the Gateway but Not the Internet
- Problem: A PC can ping the default gateway but fails to ping external websites.
- Possible Causes: The gateway has no internet connectivity (e.g., an issue with its WAN connection), the gateway's routing is incorrectly configured, or a firewall is blocking access.
- Solution: Verify the gateway's internet connection, check its routing table, and temporarily disable firewalls.
Scenario 3: Multiple PCs on the Same Network Have Connectivity Issues
- Problem: Multiple PCs on the same network share the same problem: they cannot access the internet.
- Possible Causes: A problem with the default gateway itself (e.g., router malfunction, WAN connection issue), a network cable problem affecting the entire network's connection to the gateway, or a problem with the ISP service.
- Solution: Investigate the default gateway's configuration and connectivity, check all network cables, and consider contacting the internet service provider.
Conclusion: Mastering Default Gateway Troubleshooting
Mastering default gateway troubleshooting is a vital skill for any network administrator. By understanding the fundamental concepts and applying a structured troubleshooting methodology, you can efficiently identify and resolve a wide range of connectivity problems. Packet Tracer 10.3.5 provides an excellent platform for practicing these skills in a safe and controlled environment. Remember to systematically work through each step, leveraging Packet Tracer's diagnostic tools and utilizing advanced techniques when necessary. This approach ensures you can effectively diagnose and resolve default gateway issues, building your confidence and expertise in network troubleshooting. Remember to practice regularly, experimenting with different scenarios and network configurations to strengthen your understanding and build your problem-solving skills.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Unit 2 Test Study Guide Linear Functions And Systems
Apr 05, 2025
-
Did You Get It Level 2 Pp 204 205 Answers
Apr 05, 2025
-
El Futbol En Espana Tiene Una Muy Grande
Apr 05, 2025
-
Describe The Location Of The Wounds On Figure 1 18
Apr 05, 2025
-
Letrs Unit 6 Session 3 Check For Understanding
Apr 05, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 10.3.5 Packet Tracer - Troubleshoot Default Gateway Issues . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
