10-8 Study Guide And Intervention Equations Of Circles
Onlines
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
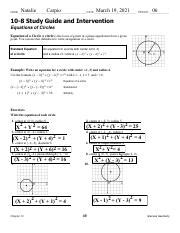
Table of Contents
10-8 Study Guide and Intervention: Equations of Circles
This comprehensive guide delves into the fascinating world of circle equations, providing a thorough understanding of their derivation, properties, and applications. We'll explore various forms of the equation, tackle practice problems, and unravel the intricacies of identifying key characteristics of a circle directly from its equation. This guide is designed to be a valuable resource for students aiming to master this crucial topic in geometry and algebra.
Understanding the Equation of a Circle: A Foundation
A circle, in its simplest form, is defined as the set of all points equidistant from a central point. This central point is the center of the circle, and the constant distance from the center to any point on the circle is the radius.
The standard equation of a circle is derived using the distance formula. Consider a circle with center (h, k) and radius r. Let (x, y) be any point on the circle. The distance between (x, y) and (h, k) is given by:
√((x - h)² + (y - k)²)
Since this distance must always be equal to the radius r, we can write the equation:
(x - h)² + (y - k)² = r²
This is the standard form of the equation of a circle. It clearly reveals the circle's center and radius.
Identifying Key Features from the Standard Equation
The standard form provides a direct pathway to understanding the circle's characteristics:
- Center: The coordinates of the center are (h, k).
- Radius: The radius is the square root of the constant term on the right-hand side, √r².
Example:
The equation (x - 3)² + (y + 2)² = 25 represents a circle with center (3, -2) and radius √25 = 5.
Beyond the Standard Form: General Form and its Conversion
While the standard form is intuitive, circle equations often appear in a less straightforward format known as the general form. This form is written as:
x² + y² + Dx + Ey + F = 0
Converting the general form to the standard form involves a process called completing the square. This process allows us to rewrite the equation in a form that clearly identifies the center and radius.
Completing the Square: A Step-by-Step Guide
Let's break down the process of completing the square with an example:
Example: Convert the equation x² + y² + 6x - 4y - 3 = 0 to standard form.
-
Group x and y terms: Rearrange the equation to group the x terms and y terms together:
(x² + 6x) + (y² - 4y) = 3
-
Complete the square for x terms: To complete the square for the x terms, take half of the coefficient of x (which is 6), square it ((6/2)² = 9), and add it to both sides of the equation:
(x² + 6x + 9) + (y² - 4y) = 3 + 9
-
Complete the square for y terms: Similarly, for the y terms, take half of the coefficient of y (-4), square it ((-4/2)² = 4), and add it to both sides:
(x² + 6x + 9) + (y² - 4y + 4) = 3 + 9 + 4
-
Factor and simplify: Rewrite the equation by factoring the perfect square trinomials:
(x + 3)² + (y - 2)² = 16
Now, the equation is in standard form. We can identify the center as (-3, 2) and the radius as √16 = 4.
Solving Problems: Application of Circle Equations
Numerous problems involve utilizing the equation of a circle. Let's examine a few common types:
Problem 1: Finding the Equation Given Center and Radius
Problem: Find the equation of a circle with center (2, -5) and radius 7.
Solution: Directly substitute the values into the standard form:
(x - 2)² + (y + 5)² = 7² = 49
Problem 2: Finding the Center and Radius Given the Equation
Problem: Find the center and radius of the circle represented by the equation x² + y² - 8x + 10y - 8 = 0.
Solution: Complete the square to convert to standard form:
(x² - 8x + 16) + (y² + 10y + 25) = 8 + 16 + 25
(x - 4)² + (y + 5)² = 49
Center: (4, -5); Radius: 7
Problem 3: Determining if a Point Lies on a Circle
Problem: Determine if the point (1, 3) lies on the circle (x - 2)² + (y + 1)² = 5.
Solution: Substitute the coordinates of the point into the equation:
(1 - 2)² + (3 + 1)² = (-1)² + (4)² = 1 + 16 = 17
Since 17 ≠ 5, the point (1, 3) does not lie on the circle.
Problem 4: Finding the Equation Given Three Points
Problem: Find the equation of a circle passing through points (1, 2), (3, 4), and (5, 2).
Solution: This problem requires a more involved approach. We'll use the general form of the equation: x² + y² + Dx + Ey + F = 0. Substitute the coordinates of each point into the equation, creating a system of three equations with three unknowns (D, E, F). Solve this system to find the values of D, E, and F. Then, rewrite the equation in standard form by completing the square. This often involves simultaneous equations and requires careful algebraic manipulation. This problem demonstrates a more advanced application of circle equations.
Advanced Topics and Extensions
The fundamental concepts discussed above provide a strong foundation. However, further exploration can delve into:
Circles and other Geometric Shapes
Understanding circle equations allows for the exploration of intersections between circles and lines, and other conic sections. For example, finding the points of intersection between a line and a circle often involves solving a system of equations.
Applications in Other Fields
Circle equations have widespread applications in various fields, including:
- Physics: Describing circular motion, wave propagation.
- Engineering: Designing circular structures, analyzing stress distributions.
- Computer Graphics: Creating circular objects and animations.
Conclusion: Mastering Circle Equations
A solid grasp of circle equations is crucial for success in various mathematical and scientific endeavors. By understanding the standard form, general form, and the process of completing the square, you gain the tools to analyze, manipulate, and apply these equations effectively. The examples and problem-solving techniques outlined in this guide will help you build confidence and competence in this important area of mathematics. Remember to practice regularly and explore further applications to deepen your understanding. Mastering circle equations unlocks a deeper appreciation for the elegance and utility of mathematical concepts. Through consistent practice and a dedication to understanding the underlying principles, you can confidently tackle any challenge related to the equations of circles.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Act 3 Scene 3 Hamlet Summary
Mar 23, 2025
-
Medical Surgical Lpn Rn Assessment 1 Shiftkey Quizlet
Mar 23, 2025
-
2021 Practice Exam Mcq Ap Csp
Mar 23, 2025
-
Code Standards And Practices 4 Lesson 1
Mar 23, 2025
-
The Tenors Sing The While The Strings Perform The
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 10-8 Study Guide And Intervention Equations Of Circles . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
