3.04 Quiz: Tables And Graphs 2
Onlines
Apr 04, 2025 · 6 min read
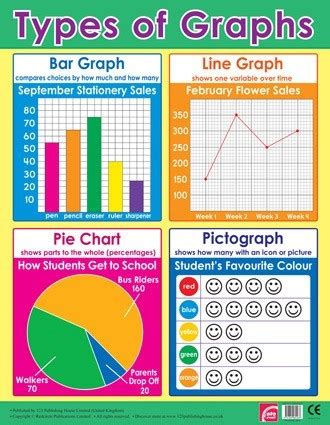
Table of Contents
3.04 Quiz: Tables and Graphs 2: Mastering Data Representation and Analysis
This comprehensive guide dives deep into the intricacies of tables and graphs, equipping you with the knowledge and skills to ace your 3.04 quiz and beyond. We'll explore various types of tables and graphs, their applications, and crucial analysis techniques. Remember, understanding data representation is fundamental to effective communication and decision-making in countless fields.
H2: Understanding the Importance of Tables and Graphs
Before we delve into the specifics of different table and graph types, let's establish why mastering their creation and interpretation is crucial. Tables and graphs are powerful tools for:
- Data Summarization: They condense large datasets into easily digestible formats, revealing patterns and trends at a glance. Imagine trying to analyze thousands of individual data points – impossible without a well-structured table or graph.
- Effective Communication: They communicate complex information clearly and concisely, making it accessible to a wider audience, regardless of their statistical background. A picture, they say, is worth a thousand words, and this holds true for data visualization.
- Identifying Trends and Patterns: Visual representation allows for rapid identification of trends, outliers, and correlations that might be missed when examining raw data. This is crucial for informed decision-making.
- Supporting Arguments and Conclusions: In research papers, presentations, and reports, tables and graphs provide compelling visual evidence to support claims and conclusions.
H2: Types of Tables: Organizing Your Data Effectively
Tables are the foundation for data organization. Understanding the different types of tables helps you choose the most appropriate format for your specific needs.
H3: Frequency Distribution Tables:
These tables summarize the frequency of occurrences for different values or categories within a dataset. They're especially useful for categorical data (e.g., colors, types of fruit) and discrete numerical data (e.g., number of siblings). Key elements include:
- Classes/Categories: The distinct values or groups being counted.
- Frequency: The number of times each class or category appears in the dataset.
- Relative Frequency: The proportion of each class or category relative to the total number of observations (often expressed as a percentage).
- Cumulative Frequency: The running total of frequencies for all classes up to a given point.
H3: Contingency Tables:
Also known as cross-tabulation tables, these tables display the relationship between two or more categorical variables. They're useful for understanding the association between variables and identifying potential correlations. For example, you could use a contingency table to analyze the relationship between gender and preference for a particular product.
H3: Data Tables (General Purpose):
These are versatile tables used to organize numerical data in rows and columns, often used as a foundation for creating graphs. They are fundamental for any quantitative analysis.
H2: Types of Graphs: Visualizing Your Data Insights
Graphs transform numerical data into visual representations, facilitating quick understanding and identification of trends. Let's explore several common graph types:
H3: Bar Graphs (and Histograms):
- Bar Graphs: Use rectangular bars to represent the frequency or magnitude of different categories. They're excellent for comparing values across categories.
- Histograms: Similar to bar graphs, but used for numerical data that is grouped into intervals (bins). The bars are adjacent, unlike in bar graphs, indicating continuous data. Histograms are effective in showing data distributions.
H3: Line Graphs:
These graphs connect data points with lines, revealing trends and changes over time or across continuous variables. They are ideal for illustrating trends, growth, or decay. Multiple lines can be used to compare different variables simultaneously.
H3: Pie Charts:
Pie charts represent proportions or percentages of a whole. Each slice of the pie corresponds to a category, with its size representing its relative proportion. They are visually appealing but can become cluttered with many categories.
H3: Scatter Plots:
Scatter plots show the relationship between two numerical variables. Each point on the graph represents a pair of data values. Scatter plots help identify correlations (positive, negative, or no correlation). Trend lines can be added to visualize the overall relationship.
H3: Box Plots (Box-and-Whisker Plots):
Box plots summarize the distribution of a numerical dataset, highlighting key statistics like the median, quartiles, and outliers. They are excellent for comparing distributions across different groups.
H2: Choosing the Right Table and Graph:
Selecting the appropriate table or graph is crucial for effective data representation. Consider the following factors:
- Type of Data: Categorical, numerical, or a combination of both.
- Purpose of Visualization: To compare values, show trends, identify correlations, or summarize distributions.
- Audience: The level of statistical knowledge of the intended audience. A complex graph might be inappropriate for a non-technical audience.
- Number of Data Points: Some graph types are better suited to smaller datasets than others.
H2: Advanced Techniques and Considerations:
H3: Data Cleaning and Preprocessing:
Before creating tables and graphs, it’s essential to clean and preprocess your data. This includes handling missing values, identifying and correcting errors, and potentially transforming variables (e.g., standardizing or normalizing). Clean data leads to accurate and meaningful visualizations.
H3: Data Interpretation:
Once you have created your tables and graphs, carefully interpret the results. Look for trends, patterns, outliers, and relationships between variables. Avoid over-interpreting results; focus on drawing conclusions supported by the data.
H3: Ethical Considerations:
Always present data accurately and ethically. Avoid manipulating the visuals to mislead the audience. Clearly label axes, provide a legend, and include relevant context.
H3: Using Software for Data Visualization:
Numerous software packages simplify the process of creating tables and graphs. Spreadsheet software (like Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets), statistical software (like R or SPSS), and data visualization tools (like Tableau or Power BI) offer advanced features for creating high-quality visuals.
H2: Practice Problems and Examples:
Let's solidify your understanding with some example problems.
Problem 1: You have collected data on the number of hours students spend studying per week and their corresponding exam scores. What type of graph would be most appropriate to visualize the relationship between these two variables? Why?
Solution: A scatter plot would be most appropriate. It allows visualization of the relationship between two numerical variables (study hours and exam scores), helping to identify any correlation.
Problem 2: You have data on the different types of pets owned by students in a class. Which type of graph would best represent the distribution of pet types?
Solution: A bar graph would be most effective. It clearly shows the frequency of each pet type.
Problem 3: You need to present data on the proportions of different budget categories in a household budget. What type of graph is ideal for this task?
Solution: A pie chart would be suitable. It visually represents the proportions of the different budget categories as slices of a pie.
H2: Beyond the Quiz: Real-World Applications
The skills you learn in analyzing tables and graphs extend far beyond the classroom. Understanding data visualization is essential in various professions, including:
- Business Analytics: Analyzing sales trends, customer behavior, and market performance.
- Science and Research: Presenting experimental results, analyzing statistical data, and communicating findings.
- Finance: Tracking investment performance, analyzing market trends, and managing risk.
- Healthcare: Monitoring patient outcomes, analyzing disease trends, and improving healthcare delivery.
- Education: Assessing student performance, tracking educational trends, and improving teaching methods.
Mastering the creation and interpretation of tables and graphs is a valuable skill applicable across numerous disciplines. By understanding the various types of tables and graphs, choosing the most appropriate visualization, and interpreting results effectively, you are well-equipped to navigate data-driven environments and contribute effectively to various fields. Remember to practice regularly and utilize available software tools to enhance your skills further. Good luck with your 3.04 quiz!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Lord Of The Flies Chapter Notes
Apr 04, 2025
-
Which Of These Are Examples Of Business Analytics
Apr 04, 2025
-
Unit 3 Progress Check Frq Part A Answers
Apr 04, 2025
-
Select Reagents From The Table To Perform The Following Conversions
Apr 04, 2025
-
Theme For Dulce Et Decorum Est
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 3.04 Quiz: Tables And Graphs 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
