4-2 Skills Practice Writing Equations In Slope-intercept Form
Onlines
Mar 25, 2025 · 7 min read
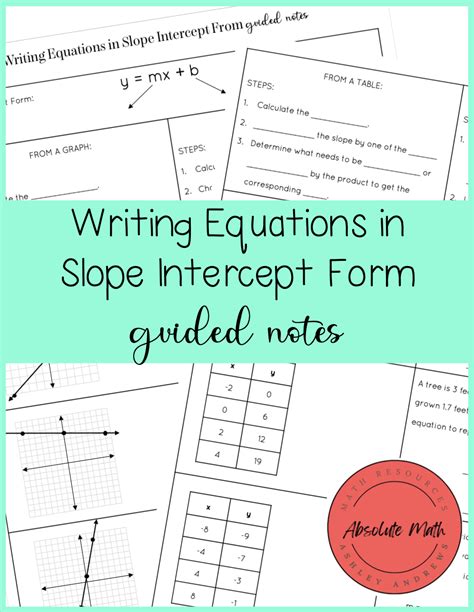
Table of Contents
Mastering the Slope-Intercept Form: A Deep Dive into 4-2 Skills Practice
The slope-intercept form, arguably the most fundamental equation in algebra, provides a powerful tool for understanding and representing linear relationships. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of writing equations in slope-intercept form (y = mx + b), focusing on the essential 4-2 skills practice, ensuring a solid foundation for more advanced algebraic concepts. We’ll explore various scenarios, offering practical examples and troubleshooting tips to solidify your understanding.
Understanding the Building Blocks: Slope (m) and y-intercept (b)
Before diving into equation writing, let's refresh our understanding of the key components:
Slope (m): The Steeper the Better (or Worse, Depending on the Context!)
The slope, denoted by 'm', represents the rate of change or steepness of a line. It's calculated as the ratio of the vertical change (rise) to the horizontal change (run) between any two points on the line. A positive slope indicates an upward trend (from left to right), while a negative slope indicates a downward trend. A slope of zero means the line is horizontal, and an undefined slope signifies a vertical line.
Formula for Slope:
m = (y₂ - y₁) / (x₂ - x₁)
where (x₁, y₁) and (x₂, y₂) are any two points on the line.
Example: Find the slope of the line passing through points (2, 4) and (6, 10).
m = (10 - 4) / (6 - 2) = 6 / 4 = 3/2
y-intercept (b): Where the Line Crosses the y-axis
The y-intercept, denoted by 'b', represents the point where the line intersects the y-axis. In other words, it's the value of 'y' when 'x' is equal to zero.
Finding the y-intercept:
You can find the y-intercept using a graph (where the line intersects the y-axis) or by substituting the slope and coordinates of a known point into the slope-intercept equation (y = mx + b) and solving for 'b'.
Writing Equations in Slope-Intercept Form: A Step-by-Step Guide
Now, let's apply our knowledge to write equations in slope-intercept form (y = mx + b). The process typically involves these steps:
-
Find the slope (m): Use the slope formula if given two points. If the slope is provided directly, proceed to step 2.
-
Find the y-intercept (b): If the y-intercept is given directly, proceed to step 3. Otherwise, use the slope (m), the coordinates of a point (x, y) on the line, and substitute these values into the slope-intercept equation (y = mx + b) to solve for 'b'.
-
Write the equation: Substitute the values of 'm' and 'b' into the slope-intercept form (y = mx + b) to obtain the equation of the line.
4-2 Skills Practice: Diverse Scenarios and Examples
Let's tackle various scenarios, enhancing our understanding of writing equations in slope-intercept form through practical examples. These examples cover the spectrum of possibilities encountered in 4-2 skill practice exercises.
Scenario 1: Given two points
Problem: Write the equation of the line passing through points (1, 3) and (4, 9).
Solution:
-
Find the slope (m):
m = (9 - 3) / (4 - 1) = 6 / 3 = 2
-
Find the y-intercept (b): Use the point-slope form first, then convert to slope-intercept form:
y - y₁ = m(x - x₁) (Point-slope form)
Substitute one of the points (let's use (1, 3)) and the slope (m = 2):
y - 3 = 2(x - 1)
y - 3 = 2x - 2
y = 2x + 1 (Slope-intercept form) Therefore, b = 1.
-
Write the equation: y = 2x + 1
Scenario 2: Given the slope and a point
Problem: Write the equation of the line with a slope of -1/2 passing through the point (2, -1).
Solution:
-
Slope (m): m = -1/2
-
Find the y-intercept (b): Use the point-slope form:
y - (-1) = (-1/2)(x - 2)
y + 1 = (-1/2)x + 1
y = (-1/2)x
-
Write the equation: y = (-1/2)x
Scenario 3: Given the slope and the y-intercept
Problem: Write the equation of the line with a slope of 3 and a y-intercept of -5.
Solution:
This is the simplest scenario. We directly substitute into the slope-intercept form:
-
Slope (m): m = 3
-
y-intercept (b): b = -5
-
Write the equation: y = 3x - 5
Scenario 4: Given a graph
Problem: Write the equation of the line shown in the graph (imagine a graph with a line passing through (0, 2) and (1, 5)).
Solution:
-
Find the slope (m): Using the points (0, 2) and (1, 5):
m = (5 - 2) / (1 - 0) = 3
-
Find the y-intercept (b): The line intersects the y-axis at (0, 2). Therefore, b = 2
-
Write the equation: y = 3x + 2
Scenario 5: Parallel and Perpendicular Lines
Problem: Write the equation of the line parallel to y = 2x + 4 and passing through (1, 3).
Solution:
Parallel lines have the same slope.
-
Slope (m): The slope of y = 2x + 4 is 2. Therefore, m = 2
-
Find the y-intercept (b): Use the point-slope form with the point (1, 3):
y - 3 = 2(x - 1)
y - 3 = 2x - 2
y = 2x + 1
-
Write the equation: y = 2x + 1
Problem: Write the equation of the line perpendicular to y = 2x + 4 and passing through (1, 3).
Solution:
Perpendicular lines have slopes that are negative reciprocals of each other.
-
Slope (m): The slope of y = 2x + 4 is 2. The negative reciprocal is -1/2. Therefore, m = -1/2
-
Find the y-intercept (b): Use the point-slope form with the point (1, 3):
y - 3 = (-1/2)(x - 1)
y - 3 = (-1/2)x + 1/2
y = (-1/2)x + 7/2
-
Write the equation: y = (-1/2)x + 7/2
Troubleshooting Common Mistakes
Several common errors can hinder your progress. Let's address them proactively:
-
Incorrect Slope Calculation: Double-check your calculations when finding the slope using the slope formula. Ensure you subtract the y-coordinates and x-coordinates in the correct order.
-
Confusion with Point-Slope Form: Remember that the point-slope form (y - y₁ = m(x - x₁)) is a valuable intermediary step, especially when you don't have the y-intercept directly.
-
Algebraic Errors: Carefully execute algebraic manipulations when solving for 'b'. Simple mistakes can lead to an incorrect equation.
-
Misinterpreting Parallel and Perpendicular Lines: Understand that parallel lines have equal slopes, while perpendicular lines have slopes that are negative reciprocals.
Expanding Your Skills: Advanced Applications
The slope-intercept form isn't just a theoretical concept; it's a practical tool applicable across diverse fields. Consider these advanced applications:
-
Data Analysis: Analyzing trends in data sets by finding the line of best fit (linear regression) and interpreting its slope and y-intercept.
-
Modeling Real-world Phenomena: Representing linear relationships in real-world scenarios, such as distance-time relationships, cost-quantity relationships, and more.
-
Solving Systems of Equations: Using the slope-intercept form to graphically solve systems of linear equations by identifying the point of intersection.
-
Calculus: The slope-intercept form is foundational to understanding derivatives and tangents in calculus.
Conclusion: Mastering the Slope-Intercept Form
This comprehensive guide has provided a thorough exploration of writing equations in slope-intercept form, addressing the essential 4-2 skills practice. By understanding the fundamental concepts of slope and y-intercept, mastering the step-by-step process, and working through diverse scenarios, you are now well-equipped to tackle a wide range of problems and applications. Remember that practice is key. Consistent effort will solidify your understanding and empower you to confidently apply this crucial algebraic tool in various contexts. Keep practicing, and your mastery of the slope-intercept form will undoubtedly enhance your overall algebraic proficiency.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
1 1 5 Gears Pulley Drives And Sprockets
Mar 28, 2025
-
Chapter 11 Summary Lord Of The Flies
Mar 28, 2025
-
Final Exam For Is 100 C Answers
Mar 28, 2025
-
James Stewart Calculus 8th Edition Solutions Pdf
Mar 28, 2025
-
Summary Chapter 2 To Kill A Mockingbird
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 4-2 Skills Practice Writing Equations In Slope-intercept Form . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
