7-2 Project Company Accounting Workbook And Summary Report
Onlines
Mar 24, 2025 · 7 min read
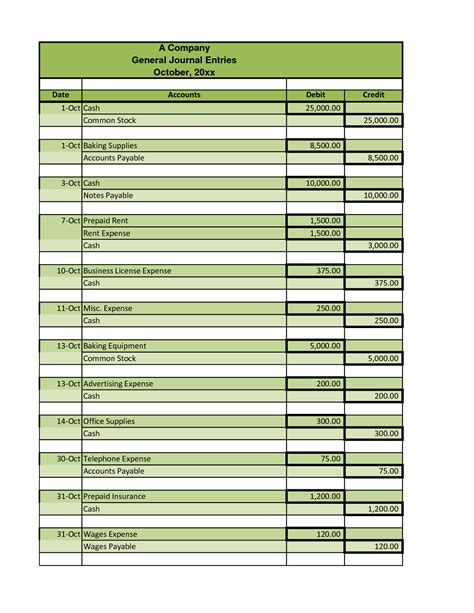
Table of Contents
7-2 Project: Company Accounting Workbook and Summary Report: A Comprehensive Guide
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of the 7-2 Project, focusing on the creation of a company accounting workbook and its accompanying summary report. We'll explore the essential components, provide practical examples, and offer valuable insights to ensure accuracy and efficiency in your financial reporting. This guide is designed to be a valuable resource for students, entrepreneurs, and anyone seeking a deeper understanding of company accounting practices.
Understanding the 7-2 Project: Scope and Objectives
The 7-2 Project, typically encountered in accounting courses or professional training, aims to solidify understanding of core accounting principles through hands-on application. It involves creating a complete accounting system for a hypothetical (or real) company, including recording transactions, preparing financial statements, and analyzing the results. The project necessitates meticulous record-keeping and a strong grasp of fundamental accounting concepts like debits and credits, the accounting equation (Assets = Liabilities + Equity), and the preparation of financial statements (income statement, balance sheet, statement of cash flows).
Part 1: The Company Accounting Workbook – A Detailed Breakdown
The workbook forms the backbone of the 7-2 Project. It's where all transactions are meticulously recorded and processed. A well-structured workbook ensures accuracy and facilitates efficient financial statement preparation. Here's a breakdown of its key components:
1. Chart of Accounts: The Foundation of Your Workbook
The chart of accounts is the very first step and arguably the most crucial. It's a comprehensive list of all the accounts used by the company to record its financial transactions. Each account has a unique number for easy identification and organization. A typical chart of accounts includes:
- Assets: Current Assets (Cash, Accounts Receivable, Inventory, Prepaid Expenses), and Non-Current Assets (Property, Plant, and Equipment, Intangible Assets).
- Liabilities: Current Liabilities (Accounts Payable, Salaries Payable, Short-Term Loans), and Non-Current Liabilities (Long-Term Loans, Bonds Payable).
- Equity: Capital Stock, Retained Earnings.
- Revenue: Sales Revenue, Service Revenue.
- Expenses: Cost of Goods Sold, Salaries Expense, Rent Expense, Utilities Expense, Depreciation Expense.
Example:
| Account Number | Account Name | Account Type |
|---|---|---|
| 101 | Cash | Asset |
| 106 | Accounts Receivable | Asset |
| 201 | Accounts Payable | Liability |
| 301 | Common Stock | Equity |
| 401 | Sales Revenue | Revenue |
| 501 | Cost of Goods Sold | Expense |
2. General Journal: Recording Transactions
The general journal is where all transactions are initially recorded. Each entry includes the date, accounts affected (debits and credits), a brief description of the transaction, and a reference number. The fundamental accounting equation must always remain balanced (Debits = Credits).
Example Transaction: Purchase of office supplies for $50 cash.
| Date | Account Name | Debit | Credit | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oct 26, 2024 | Office Supplies Expense | $50 | Purchased office supplies with cash | |
| Cash | $50 |
3. General Ledger: Summarizing Account Balances
The general ledger organizes transactions by account. It summarizes all debits and credits for each account, providing a running balance. This allows for easy monitoring of account balances throughout the accounting period. The general ledger is essentially a collection of individual account ledgers.
Example: Cash Account in the General Ledger
| Date | Description | Debit | Credit | Balance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oct 1, 2024 | Beginning Balance | $1000 | ||
| Oct 26, 2024 | Purchase of Supplies | $50 | $950 | |
| Oct 27, 2024 | Sales Revenue | $200 | $1150 |
4. Trial Balance: Verifying the Accounting Equation
The trial balance is a crucial step in the accounting cycle. It summarizes the balances of all general ledger accounts. The total debits must equal the total credits, verifying that the accounting equation remains balanced. Discrepancies indicate errors that need to be corrected.
5. Adjusting Entries: Ensuring Accuracy
Adjusting entries are made at the end of the accounting period to ensure that revenues and expenses are recognized in the correct period. Common adjusting entries include:
- Accrued Revenues: Revenues earned but not yet received.
- Accrued Expenses: Expenses incurred but not yet paid.
- Prepaid Expenses: Expenses paid in advance.
- Unearned Revenues: Revenues received in advance.
- Depreciation: Allocation of the cost of an asset over its useful life.
6. Adjusted Trial Balance: Post-Adjustment Verification
After making adjusting entries, another trial balance is prepared – the adjusted trial balance. This reflects the updated account balances after considering the adjusting entries. It’s the foundation for preparing the financial statements.
Part 2: The Summary Report – Presenting Your Findings
The summary report is a concise presentation of the company's financial performance and position. It's derived from the information meticulously recorded in the workbook. This report is crucial for stakeholders to understand the company's financial health. The summary report typically includes:
1. Income Statement: Measuring Profitability
The income statement shows the company's revenues, expenses, and net income (or net loss) over a specific period. It provides a clear picture of the company's profitability.
Example:
Income Statement for the Year Ended December 31, 2024
| Revenue | |
|---|---|
| Sales Revenue | $10,000 |
| Total Revenue | $10,000 |
| Expenses | |
| Cost of Goods Sold | $4,000 |
| Salaries Expense | $2,000 |
| Rent Expense | $1,000 |
| Utilities Expense | $500 |
| Depreciation Expense | $500 |
| Total Expenses | $8,000 |
| Net Income | $2,000 |
2. Balance Sheet: Showing Financial Position
The balance sheet presents a snapshot of the company's assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time. It illustrates the company's financial position.
Example:
Balance Sheet as of December 31, 2024
| Assets | Liabilities & Equity | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Cash | $1,500 | Accounts Payable | $1,000 |
| Accounts Receivable | $500 | Salaries Payable | $200 |
| Inventory | $2,000 | Total Liabilities | $1,200 |
| Total Assets | $4,000 | Common Stock | $2,000 |
| Retained Earnings | $800 | ||
| Total Equity | $2,800 | ||
| Total Liabilities & Equity | $4,000 |
3. Statement of Cash Flows: Tracking Cash Movement
The statement of cash flows tracks the inflow and outflow of cash during a specific period. It categorizes cash flows into operating, investing, and financing activities.
Example:
Statement of Cash Flows for the Year Ended December 31, 2024
| Cash Flows from Operating Activities | |
|---|---|
| Net Income | $2,000 |
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities | |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | $2,500 |
| Cash Flows from Investing Activities | |
|---|---|
| Purchase of equipment | ($1,000) |
| Net cash used in investing activities | ($1,000) |
| Cash Flows from Financing Activities | |
|---|---|
| Proceeds from issuance of common stock | $2,000 |
| Net cash provided by financing activities | $2,000 |
| Net increase in cash | $3,500 | | Beginning cash balance | $1,000 | | Ending cash balance | $4,500 |
4. Analysis and Interpretation: Drawing Conclusions
The summary report isn't just a presentation of numbers; it requires analysis and interpretation. This section discusses key financial ratios, trends, and insights derived from the financial statements. For example, you might analyze profitability ratios (gross profit margin, net profit margin), liquidity ratios (current ratio, quick ratio), and solvency ratios (debt-to-equity ratio). This analysis provides valuable insights into the company's financial health and performance.
Conclusion: Mastering the 7-2 Project
The 7-2 Project is a crucial exercise in developing a strong understanding of company accounting. By meticulously creating the accounting workbook and crafting a comprehensive summary report, you’ll gain practical experience in applying fundamental accounting principles. Remember, accuracy and thoroughness are paramount. A well-executed 7-2 project demonstrates a solid grasp of accounting concepts and provides a valuable foundation for future accounting endeavors. This detailed guide provides a strong starting point, but further research and practice are crucial for mastering the nuances of company accounting. Remember to consult your course materials and seek clarification when needed. Good luck!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Installation Of Production Improvement Option D
Mar 28, 2025
-
Math 1314 Lab Module 3 Answers
Mar 28, 2025
-
Rate Of Return Chapter 3 Lesson 6
Mar 28, 2025
-
Ap Csa Unit 4 Progress Check Mcq
Mar 28, 2025
-
Baked Dessert Into Garden Tool Puzzle
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 7-2 Project Company Accounting Workbook And Summary Report . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
