Activity 14 1 Glass Fracture Patterns Answer Key
Onlines
Apr 01, 2025 · 6 min read
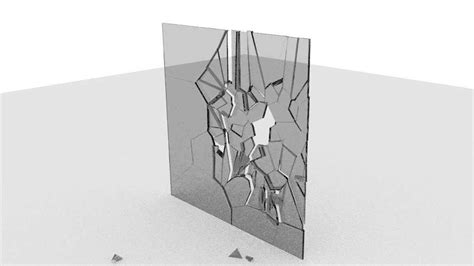
Table of Contents
Activity 14: 1 Glass Fracture Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding glass fracture patterns is crucial in various fields, from forensic science to material engineering. This detailed guide delves into Activity 14, focusing on the analysis and interpretation of glass fracture patterns, providing a comprehensive understanding of the subject matter. We'll cover radial fractures, concentric fractures, the 3R rule, sequence of impact, and more, offering a complete answer key to help you master this critical skill.
Understanding Glass Fracture: The Basics
Before diving into the intricacies of Activity 14, let's establish a foundational understanding of glass fracture. When subjected to force, glass, a brittle material, doesn't deform plastically; instead, it fractures. These fractures provide invaluable clues about the nature of the impact, its direction, and even the sequence of multiple impacts. The key to interpreting these fractures lies in identifying the distinct patterns they form.
Radial Fractures vs. Concentric Fractures: The Defining Characteristics
Two primary types of fractures define the pattern on a shattered glass pane:
-
Radial Fractures: These fractures radiate outwards from the point of impact, like spokes on a wheel. They are formed by the initial stress wave propagating through the glass. The direction of the stress wave dictates the direction of these fractures. Observing the direction of the radial fractures is vital in determining the point of origin of the impact.
-
Concentric Fractures: These fractures form circular rings around the point of impact. They arise after the initial radial fractures, often forming later as the glass continues to expand and contract under stress. The concentric fractures are typically less numerous than radial fractures and often appear less defined.
Understanding the difference between these fracture types is crucial for accurately reconstructing the event that caused the glass breakage. Activity 14 will rigorously test your understanding of these differences.
Activity 14: A Deeper Dive into Glass Fracture Analysis
Activity 14 likely presents you with various scenarios involving shattered glass. You are tasked with analyzing images or descriptions of the fractures to determine:
-
Point of Impact: Pinpointing the exact location where the initial force struck the glass. This is often the center of the concentric fractures and the origin point of the radiating radial fractures.
-
Direction of Force: Establishing the direction from which the impact occurred. This is determined by the orientation and direction of the radial and concentric fractures. We'll examine the 3R rule shortly.
-
Sequence of Impacts (if multiple): Identifying whether multiple impacts occurred and establishing their order. Understanding fracture patterns allows you to determine the chronology of events.
-
Type of Impact: Determining whether the impact was a low-energy impact (e.g., a small rock) or a high-energy impact (e.g., a bullet). The extent of the fracture network, the size of the radial and concentric fractures, and the overall damage to the glass will indicate the impact energy level.
The 3R Rule: A Cornerstone of Glass Fracture Analysis
The 3R rule is a critical principle in forensic glass analysis. It provides a simple yet effective method for determining the direction of force in a single fracture:
Right angle Rule: On the reverse side of the glass from where the impact occurred, the radial fracture terminates at a right angle to the concentric fracture. This principle allows investigators to conclusively determine the side of impact.
Mastering the 3R rule is paramount for successful completion of Activity 14. Practice applying this rule to various fracture patterns to ensure a solid understanding. Remember, the 3R rule is only applicable to the analysis of a single fracture line.
Analyzing Multiple Impacts: Deciphering the Sequence
When multiple impacts have occurred, the analysis becomes more complex. However, careful observation of the fracture patterns can still reveal the sequence of events. Later impacts will generally disrupt and interrupt existing fracture patterns.
-
Overlapping Fractures: Fractures from later impacts will often overlap or terminate at the fractures created by earlier impacts. This overlapping provides clear evidence for determining the sequence.
-
Fracture Termination: A fracture line that stops at another fracture indicates that the first fracture happened before the second. This principle is crucial in reconstructing a multi-impact scenario.
-
Secondary Fractures: Look for fractures that are significantly smaller or less defined than the primary fracture pattern. These often result from a secondary or weaker impact.
Activity 14 will likely test your ability to correctly identify and interpret scenarios with multiple impacts. Thorough observation and application of the principles mentioned above will be key to success.
Beyond the Basics: Factors Influencing Fracture Patterns
Several factors can influence the patterns of glass fractures. These factors are critical to consider for accurate interpretation:
-
Type of Glass: The type of glass (e.g., tempered glass, laminated glass) significantly impacts its fracture behavior. Tempered glass, for instance, shatters into numerous small pieces, making analysis more challenging.
-
Thickness of Glass: Thicker glass will generally exhibit different fracture patterns compared to thinner glass. The energy required to fracture thicker glass is higher and the fracture patterns are likely to be more complex.
-
Angle of Impact: The angle at which the force impacts the glass influences the shape and direction of the resulting fractures. An oblique impact will produce different patterns compared to a perpendicular impact.
-
Type of Force: The nature of the force (e.g., blunt force, sharp force, explosive force) alters the resulting fracture patterns. This aspect is particularly important in forensic investigations.
Activity 14 Answer Key: A Step-by-Step Approach
While I cannot provide a specific answer key for a hypothetical "Activity 14," I can offer a general approach for analyzing glass fracture patterns that will aid in answering any specific questions posed within the activity.
Step 1: Careful Observation: Examine the glass fracture patterns meticulously. Take your time. The more detailed your observation, the more accurate your analysis.
Step 2: Identify Radial and Concentric Fractures: Clearly distinguish between the radial and concentric fractures. Count the number of each type, note their direction, and measure their extent.
Step 3: Apply the 3R Rule: For single-impact scenarios, use the 3R rule to determine the direction of force. Carefully examine each fracture line to ensure its application.
Step 4: Analyze Multiple Impacts (if applicable): If multiple impacts occurred, look for overlapping fractures, fracture termination points, and secondary fractures to establish the sequence of impacts.
Step 5: Consider Additional Factors: Take into account the type of glass, its thickness, the angle of impact, and the type of force when making your interpretation. This will enhance the accuracy and completeness of your analysis.
Step 6: Draw Conclusions: Based on your observations and analysis, draw clear and concise conclusions regarding the point of impact, direction of force, sequence of impacts, and the likely type of impact.
Expanding Your Knowledge: Further Exploration
Understanding glass fracture patterns is a continually evolving field. To enhance your expertise beyond the scope of Activity 14, consider exploring these areas:
-
Forensic Glass Analysis: Delve into the forensic applications of glass fracture analysis, exploring case studies and investigative techniques.
-
Material Science of Glass: Gain a deeper understanding of the physical and chemical properties of glass and how these properties affect its fracture behavior.
-
Advanced Imaging Techniques: Explore advanced imaging techniques, such as microscopic analysis, that can provide a more detailed examination of fracture patterns.
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Glass Fracture Analysis
Activity 14 presents a valuable opportunity to hone your skills in analyzing glass fracture patterns. By mastering the principles outlined in this guide – understanding radial and concentric fractures, applying the 3R rule effectively, and analyzing multiple impacts – you can confidently approach any glass fracture analysis challenge. Remember, meticulous observation, systematic analysis, and consideration of all influencing factors are crucial for achieving accurate and insightful results. With dedication and practice, you will become proficient in this critical area of study.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Summary Of Julius Caesar Act 2 Scene 2
Apr 02, 2025
-
Quotes And Then There Were None
Apr 02, 2025
-
What Strategies Did You Use To Hunt For Moths
Apr 02, 2025
-
Characters In The Time Of The Butterflies
Apr 02, 2025
-
Ac Theory Level 3 Lesson 3
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Activity 14 1 Glass Fracture Patterns Answer Key . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
