Activity-based Management Is Focused On Blank______.
Onlines
Mar 19, 2025 · 7 min read
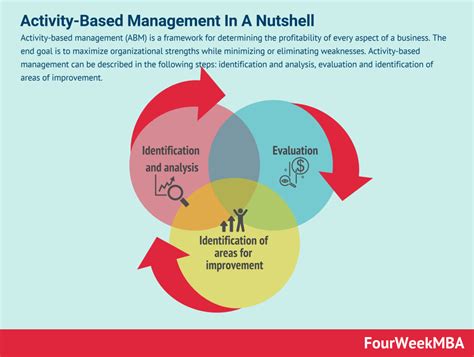
Table of Contents
Activity-Based Management is Focused on Activities
Activity-based management (ABM) is a management accounting approach that focuses on the activities performed within an organization. Unlike traditional cost accounting methods which often allocate overhead costs arbitrarily, ABM meticulously traces costs to specific activities and then assigns those costs to products or services based on their consumption of those activities. This granular level of cost analysis allows businesses to gain a much deeper understanding of their cost structure, pinpoint areas for improvement, and ultimately make more informed business decisions.
Understanding the Core of ABM: Activities
The fundamental principle underpinning ABM is the identification and analysis of individual activities. These activities are the basic building blocks of an organization's operations. They represent the work performed to create and deliver products or services. This could encompass anything from designing a product to answering customer inquiries, from manufacturing components to marketing campaigns. The key is to break down operations into discrete, measurable activities.
Identifying Key Activities
Identifying the right activities is crucial for the success of an ABM implementation. This requires a thorough understanding of the organization's processes and workflows. Several techniques can assist in this identification:
- Process Mapping: Visually mapping out the steps involved in each process helps to identify the individual activities involved.
- Workflow Analysis: Analyzing the flow of work through the organization reveals key activities and their interdependencies.
- Observation and Interviews: Directly observing employees and interviewing them can provide valuable insights into the activities they perform.
- Data Analysis: Reviewing existing data on time spent on various tasks can help identify significant activities.
The identified activities must be:
- Specific: Clearly defined and easily understood.
- Measurable: Quantifiable in terms of time, resources, or output.
- Achievable: Realistic and within the organization's capacity.
- Relevant: Directly related to the organization's goals and objectives.
- Time-Bound: Associated with a specific timeframe.
Once activities are identified, the next step involves cost allocation.
Cost Allocation in ABM: Linking Costs to Activities
A significant difference between ABM and traditional costing methods lies in the way costs are allocated. Traditional systems often allocate overhead costs using arbitrary allocation bases, such as direct labor hours or machine hours. This can lead to inaccurate cost estimations and flawed decision-making. In contrast, ABM meticulously traces costs to specific activities.
Cost Drivers in ABM
To allocate costs effectively, ABM identifies cost drivers. These are factors that cause costs to increase or decrease. Understanding cost drivers allows for a more accurate assignment of costs to activities. Examples of cost drivers include:
- Number of orders: The cost of order processing increases as the number of orders increases.
- Number of machine setups: The cost of machine maintenance increases with the number of setups.
- Number of customer inquiries: The cost of customer service increases with the number of inquiries.
- Number of design changes: The cost of product design increases with the number of design changes.
- Direct Labor Hours: Time spent by direct labor on a specific activity.
The choice of cost driver depends on the specific activity being analyzed. It’s crucial to select cost drivers that accurately reflect the relationship between the activity and the costs incurred.
Cost Pooling and Allocation
Once cost drivers are identified, costs are grouped into cost pools. A cost pool is a collection of costs associated with a specific activity. For example, a cost pool might include the salaries of customer service representatives, the cost of phone lines, and the cost of software used for managing customer inquiries.
Costs are then allocated from the cost pools to individual activities based on the consumption of the cost driver. For instance, if the cost driver for customer service is the number of customer inquiries, the cost of customer service will be allocated to each product or service based on the number of inquiries generated by that product or service.
The Benefits of Activity-Based Management
ABM offers a multitude of benefits for organizations seeking to optimize their operations and improve profitability:
- More Accurate Costing: ABM provides a more precise understanding of the costs associated with each product, service, or activity. This improved accuracy eliminates the distortions caused by arbitrary cost allocation methods.
- Improved Decision-Making: With more accurate cost data, management can make more informed decisions regarding pricing, product mix, and resource allocation. Understanding which activities are profitable and which are not allows for strategic resource deployment.
- Enhanced Process Improvement: ABM highlights inefficiencies and bottlenecks within the organization's processes. By identifying activities that consume excessive resources, companies can focus improvement efforts on the areas with the greatest potential for cost savings.
- Better Product Pricing: Accurate cost information allows for more effective pricing strategies. Products and services can be priced to reflect their true cost, ensuring profitability and competitiveness.
- Increased Profitability: By improving efficiency and optimizing resource allocation, ABM contributes to increased profitability. This is achieved through reduced costs, improved pricing, and increased operational efficiency.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: By understanding the cost of providing different levels of customer service, organizations can tailor their service offerings to meet customer needs while remaining profitable.
Implementing Activity-Based Management: A Step-by-Step Approach
Implementing ABM effectively requires a systematic approach. The process typically involves the following steps:
- Define the Scope: Identify the specific areas of the business that will be included in the ABM implementation.
- Identify Activities: Use process mapping, workflow analysis, and other techniques to identify all activities within the chosen scope.
- Determine Cost Drivers: Identify the factors that drive the cost of each activity.
- Assign Costs to Activities: Allocate costs to activities based on the consumption of the cost drivers.
- Develop a Cost Model: Create a model that accurately reflects the relationship between activities, costs, and products or services.
- Implement and Monitor: Implement the ABM system and continuously monitor its performance to ensure accuracy and effectiveness.
- Regular Review and Adjustment: ABM is not a static system. Regularly review and adjust the system to reflect changes in the business environment and processes.
Comparing ABM with Traditional Costing Methods
Traditional costing methods, such as absorption costing, often rely on simplistic cost allocation bases, leading to inaccuracies in cost assignment. ABM, however, provides a far more detailed and precise understanding of cost behavior. Here’s a comparative table highlighting the key differences:
| Feature | Traditional Costing (e.g., Absorption Costing) | Activity-Based Management (ABM) |
|---|---|---|
| Cost Allocation Basis | Arbitrary allocation bases (e.g., direct labor hours, machine hours) | Cost drivers directly related to activities |
| Cost Accuracy | Less accurate, prone to distortions | More accurate, reflects actual cost behavior |
| Overhead Cost Allocation | Overhead costs are allocated broadly | Overhead costs are allocated to specific activities |
| Complexity | Relatively simple to implement | More complex to implement |
| Cost of Implementation | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost |
| Data Requirements | Less data required | More data required |
| Decision-Making | Limited insights for decision-making | Provides detailed insights for better decision-making |
Overcoming Challenges in ABM Implementation
Implementing ABM presents certain challenges that organizations need to address:
- High Implementation Costs: Implementing ABM can be expensive, requiring significant upfront investment in time, resources, and technology.
- Data Collection Challenges: Gathering accurate and reliable data for cost allocation can be time-consuming and challenging.
- Complexity: Understanding and implementing the system's complexities can be daunting for some organizations.
- Resistance to Change: Employees may resist changes to established processes and workflows.
- Maintaining Data Accuracy: Ensuring data accuracy over time requires ongoing monitoring and adjustments.
Despite these challenges, the benefits of improved cost accuracy, enhanced decision-making, and increased profitability far outweigh the initial investment and effort required.
Conclusion: Activity-Based Management for a Data-Driven Future
Activity-based management is a powerful tool for organizations seeking to gain a deeper understanding of their cost structure and improve operational efficiency. By focusing on activities as the fundamental building blocks of operations and meticulously tracing costs to these activities, ABM provides a far more accurate and insightful view of cost behavior than traditional methods. While the implementation requires significant investment and effort, the resulting benefits – improved decision-making, enhanced profitability, and a more data-driven approach to management – are invaluable in today's competitive business landscape. By embracing ABM, organizations can position themselves for sustainable success in the future.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Landscapes Of New York State Lab Answer Key
Mar 19, 2025
-
The Earnings Spread For A Bank Is Equal To
Mar 19, 2025
-
Which Is A Trait Of Readers Theater
Mar 19, 2025
-
Animal Farm Summary Of Chapter 8
Mar 19, 2025
-
Annotations For A Raisin In The Sun
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Activity-based Management Is Focused On Blank______. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
