Atoms Vs Ions Worksheet Answers Key
Onlines
Mar 31, 2025 · 6 min read
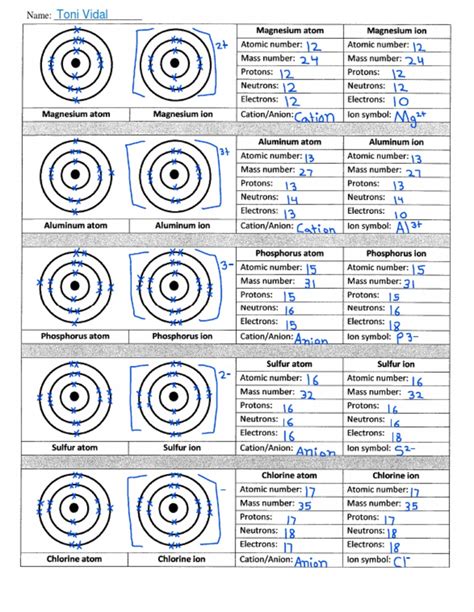
Table of Contents
- Atoms Vs Ions Worksheet Answers Key
- Table of Contents
- Atoms vs. Ions: A Comprehensive Worksheet and Answer Key
- What is an Atom?
- Subatomic Particles:
- Atomic Number and Mass Number:
- What is an Ion?
- Cations and Anions:
- The Significance of Electron Configuration:
- Atoms vs. Ions: Key Differences Summarized
- Atoms vs. Ions Worksheet
- Atoms vs. Ions Worksheet Answer Key
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Atoms vs. Ions: A Comprehensive Worksheet and Answer Key
Understanding the fundamental difference between atoms and ions is crucial for grasping core concepts in chemistry. This article provides a detailed explanation of atoms and ions, followed by a comprehensive worksheet designed to test your knowledge and a complete answer key. We'll delve into the intricacies of atomic structure, electron configurations, and the processes that lead to ion formation. By the end, you'll have a solid grasp of this essential chemistry topic.
What is an Atom?
An atom is the smallest unit of an element that retains the chemical properties of that element. It's the fundamental building block of all matter. Atoms are incredibly small, far too small to be seen with the naked eye, even with powerful microscopes. They consist of three primary subatomic particles:
Subatomic Particles:
- Protons: Positively charged particles located in the atom's nucleus. The number of protons determines the element's atomic number and identity.
- Neutrons: Neutrally charged particles also found in the nucleus. They contribute to the atom's mass but not its charge.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus in energy levels or shells. The number of electrons typically equals the number of protons in a neutral atom.
Atomic Number and Mass Number:
- Atomic Number (Z): The number of protons in an atom's nucleus. This uniquely identifies the element. For example, hydrogen (H) has an atomic number of 1, while oxygen (O) has an atomic number of 8.
- Mass Number (A): The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom's nucleus. This represents the atom's mass. For instance, a carbon-12 atom (¹²C) has a mass number of 12 (6 protons + 6 neutrons).
What is an Ion?
An ion is an atom or molecule that has gained or lost one or more electrons, resulting in a net electrical charge. This process, called ionization, alters the atom's overall neutrality. Ions can be either positively or negatively charged:
Cations and Anions:
- Cations: Positively charged ions. These are formed when an atom loses one or more electrons. Metals typically form cations because they readily lose electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration. For example, sodium (Na) readily loses one electron to form a sodium ion (Na⁺).
- Anions: Negatively charged ions. These are formed when an atom gains one or more electrons. Nonmetals often form anions because they readily gain electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration. For example, chlorine (Cl) readily gains one electron to form a chloride ion (Cl⁻).
The Significance of Electron Configuration:
The stability of an atom or ion is strongly linked to its electron configuration. Atoms tend to lose or gain electrons to achieve a full outermost electron shell, a configuration often referred to as a stable octet (eight electrons in the outermost shell). This drive for stability is a fundamental principle in chemical bonding.
Atoms vs. Ions: Key Differences Summarized
| Feature | Atom | Ion |
|---|---|---|
| Charge | Neutral (no net charge) | Positive (cation) or negative (anion) |
| Electron Number | Equal to proton number | Unequal to proton number |
| Stability | Relatively less stable (except noble gases) | More stable (achieves full outer shell) |
| Formation | Naturally occurring | Formed through ionization |
Atoms vs. Ions Worksheet
Instructions: Answer the following questions based on your understanding of atoms and ions.
Part 1: True or False
- Atoms are electrically neutral. (True/False)
- Ions are formed when atoms gain or lose neutrons. (True/False)
- Cations are positively charged ions. (True/False)
- Anions are formed when atoms lose electrons. (True/False)
- All atoms are ions. (True/False)
- Noble gases are highly reactive. (True/False)
- The number of protons determines the element. (True/False)
- Isotopes have different numbers of electrons. (True/False)
- The mass number represents the number of protons only. (True/False)
- Ions always have a stable electron configuration. (True/False)
Part 2: Multiple Choice
- Which subatomic particle carries a positive charge? a) Electron b) Neutron c) Proton d) All of the above
- Which of the following is an example of a cation? a) Cl⁻ b) O²⁻ c) Na⁺ d) S²⁻
- What is the atomic number of an atom with 6 protons? a) 6 b) 12 c) 18 d) Cannot be determined
- What is the mass number of an atom with 6 protons and 8 neutrons? a) 6 b) 8 c) 14 d) 48
- What is the charge of an ion with 10 protons and 8 electrons? a) -2 b) +2 c) 0 d) +18
Part 3: Short Answer
- Explain the difference between an atom and an ion.
- Describe how a cation is formed.
- Describe how an anion is formed.
- Why do atoms form ions?
- Explain the significance of the octet rule in ion formation.
Atoms vs. Ions Worksheet Answer Key
Part 1: True or False
- True
- False (protons or electrons)
- True
- False (gain electrons)
- False
- False (they are unreactive)
- True
- False (neutrons)
- False (protons and neutrons)
- True
Part 2: Multiple Choice
- c) Proton
- c) Na⁺
- a) 6
- c) 14
- b) +2
Part 3: Short Answer
-
An atom is a neutral particle with equal numbers of protons and electrons. An ion is a charged particle formed when an atom gains or loses electrons.
-
A cation is formed when a neutral atom loses one or more electrons. This leaves the atom with more protons than electrons, resulting in a net positive charge.
-
An anion is formed when a neutral atom gains one or more electrons. This gives the atom more electrons than protons, resulting in a net negative charge.
-
Atoms form ions to achieve a stable electron configuration, usually a full outermost electron shell (octet rule). This stable configuration results in lower energy and increased stability.
-
The octet rule states that atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons in order to have eight electrons in their outermost electron shell. This is a driving force behind ion formation, as atoms will readily gain or lose electrons to achieve this stable, lower-energy configuration. This is particularly relevant for elements in Groups 1, 2, 16, and 17 of the periodic table.
This comprehensive worksheet and answer key provide a thorough review of atoms and ions. By understanding these fundamental concepts, you'll be well-equipped to tackle more advanced chemistry topics. Remember to practice regularly and consult additional resources if you need further clarification. Understanding atomic structure and ionic bonding is foundational to success in chemistry.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Texas Has A Reputation Of Being A State
Apr 03, 2025
-
Thompson Simone Biles And The Most Human Meaning Of Courage
Apr 03, 2025
-
Why Is Take 5 So Expensive
Apr 03, 2025
-
Nursing Care Plan For Neonatal Jaundice
Apr 03, 2025
-
Famous Forensic Christmas Mystery Picture Answer Key
Apr 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Atoms Vs Ions Worksheet Answers Key . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
