Choose The Correct Order Of Steps In The Production Process.
Onlines
Mar 13, 2025 · 6 min read
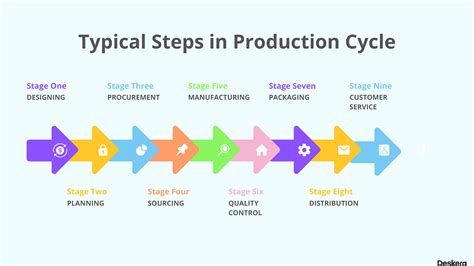
Table of Contents
Choose the Correct Order of Steps in the Production Process: A Comprehensive Guide
Optimizing your production process is crucial for efficiency, profitability, and maintaining a competitive edge. Understanding the correct order of steps is paramount. This guide will delve into the critical stages of a typical production process, exploring variations depending on the industry, and providing strategies for streamlining your workflow. We'll also look at the importance of planning and how to troubleshoot common production bottlenecks.
Understanding the Production Process: A Framework
Before diving into specific steps, let's establish a general framework applicable across various industries. While the specifics differ, the core principles remain consistent. The typical production process can be broken down into these key stages:
1. Planning and Design:
This initial phase is arguably the most critical. A well-defined plan lays the groundwork for smooth execution. This includes:
- Concept Development: Clearly defining the product, its features, and target market.
- Design and Engineering: Creating detailed specifications, blueprints, and prototypes. This stage involves considerations for materials, manufacturing processes, and quality control.
- Demand Forecasting: Accurately predicting future demand to optimize production levels and avoid overstocking or shortages. This frequently involves analyzing historical data, market trends, and economic factors.
- Resource Allocation: Identifying and securing the necessary resources – raw materials, machinery, labor, and capital – to support production. Effective resource management is key to cost optimization and timely completion.
- Scheduling and Sequencing: Developing a production schedule that outlines the order and timing of tasks. This often involves sophisticated scheduling software, particularly for complex projects.
2. Sourcing and Procurement:
This stage focuses on securing the necessary raw materials and components required for production. Efficient procurement is critical for cost-effectiveness and timely delivery. Key elements include:
- Supplier Selection: Identifying and evaluating potential suppliers based on factors such as quality, reliability, pricing, and delivery times. This often involves rigorous vetting processes and performance assessments.
- Negotiation and Contracts: Negotiating favorable terms with suppliers, including pricing, payment schedules, and quality standards. Strong contracts are crucial to protecting your interests.
- Inventory Management: Effectively managing inventory levels to avoid stockouts and minimize storage costs. This often involves utilizing inventory management systems and techniques like Just-In-Time (JIT) inventory.
- Quality Control (Incoming Inspection): Inspecting incoming materials and components to ensure they meet specified quality standards. This helps prevent defective products from entering the production line.
3. Manufacturing and Production:
This is where the actual production takes place. The specific steps involved will depend heavily on the industry and product. However, common elements include:
- Production Planning: Detailed scheduling of production tasks, allocation of machinery, and assignment of personnel. This stage uses the information gathered in the planning and design phase.
- Production Execution: The actual execution of the manufacturing process. This can range from highly automated processes to manual labor-intensive tasks.
- Quality Control (In-process Inspection): Regularly monitoring and inspecting the product at various stages of production to identify and correct defects early. This reduces waste and improves overall quality.
- Process Optimization: Continuously monitoring and improving the production process to enhance efficiency and reduce costs. This often involves data analysis, process mapping, and lean manufacturing principles.
4. Quality Assurance and Control:
Maintaining quality throughout the production process is crucial. This involves implementing rigorous quality control measures at each stage. Specific techniques include:
- Statistical Process Control (SPC): Using statistical methods to monitor and control the production process and identify potential problems early.
- Total Quality Management (TQM): A holistic approach to quality management, involving all aspects of the organization.
- Six Sigma: A data-driven approach to process improvement that aims to reduce defects to near-zero levels.
- Root Cause Analysis: Identifying the underlying causes of defects or problems to prevent recurrence.
5. Packaging and Distribution:
Once production is complete, the products need to be packaged and distributed to customers. Efficient packaging and distribution are essential for customer satisfaction and minimizing costs. This involves:
- Packaging Design: Designing appropriate packaging to protect the product during transport and enhance its visual appeal.
- Warehousing and Inventory Management (Finished Goods): Efficiently managing finished goods inventory to ensure timely delivery to customers.
- Order Fulfillment: Processing customer orders and ensuring timely delivery.
- Shipping and Transportation: Selecting appropriate transportation methods to ensure timely and cost-effective delivery.
6. Sales and Marketing:
While not strictly part of the production process itself, effective sales and marketing strategies are crucial for ensuring that the products reach the target market and generate sales. This includes:
- Market Research and Analysis: Understanding customer needs and preferences to ensure that the product is well-positioned in the market.
- Product Promotion and Advertising: Developing effective marketing campaigns to generate awareness and drive sales.
- Sales Management and Customer Service: Managing sales activities and providing excellent customer service to build customer loyalty.
Variations in Production Processes: Industry-Specific Examples
The above framework serves as a general guideline. The specific steps and their order can vary significantly depending on the industry and the nature of the product. Let's examine some examples:
Manufacturing (Automotive): A highly complex process involving numerous suppliers, sophisticated assembly lines, and rigorous quality control measures. The order of steps is crucial due to the intricate nature of automobile assembly.
Food Processing: Focuses heavily on hygiene and safety regulations, with stringent quality control at each step, from raw material sourcing to packaging and distribution. Speed and efficiency are paramount to maintain product freshness.
Software Development: A less tangible production process, but still follows a similar structure, encompassing planning (design, requirements gathering), development (coding, testing), quality assurance (bug fixing, user testing), and release (distribution, marketing). Iterations and feedback loops are crucial here.
Textile Production: Involves a linear sequence of steps, from fiber processing to weaving, dyeing, finishing, and garment manufacturing. The efficiency of each stage impacts the overall production time and cost.
Streamlining Your Production Process: Best Practices
Optimizing the production process is an ongoing effort. Several best practices can help:
- Lean Manufacturing: A philosophy focused on eliminating waste and maximizing efficiency throughout the production process.
- Six Sigma: A data-driven methodology for process improvement that aims to reduce defects and variability.
- Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory: A system that aims to minimize inventory levels by receiving materials only when needed.
- Automation: Implementing automated systems to improve efficiency and reduce labor costs.
- Technology Integration: Utilizing software and technology to streamline processes and improve data analysis.
Troubleshooting Production Bottlenecks
Inefficiencies can arise at any stage of the production process. Identifying and resolving bottlenecks requires careful analysis. Common bottlenecks include:
- Supplier Issues: Delayed deliveries or substandard materials from suppliers.
- Equipment Malfunctions: Breakdown of machinery leading to production downtime.
- Lack of Skilled Labor: Shortage of trained personnel to operate equipment or perform tasks.
- Poor Process Design: Inefficient workflow leading to delays and waste.
- Ineffective Inventory Management: Shortages or overstocking of materials leading to disruptions.
Addressing these bottlenecks requires proactive measures, including preventative maintenance, robust supplier relationships, and employee training programs. Data analysis and process mapping can help identify specific areas for improvement.
Conclusion: The Importance of Order and Optimization
The correct order of steps in the production process is not simply a matter of chronology; it's a crucial determinant of efficiency, quality, and profitability. By understanding the general framework and adapting it to your specific industry and product, you can create a streamlined and optimized production process that delivers high-quality products efficiently and cost-effectively. Continuous monitoring, analysis, and improvement are essential for maintaining a competitive edge in today's dynamic market. Remember that the journey to optimization is continuous; embrace change, adapt to new technologies, and consistently strive for excellence.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Es Mas Importante Doblar La Ropa Que Hablar Por Telefono
Mar 14, 2025
-
Modeling The Regulatory Switches Of The Pitx1 Gene
Mar 14, 2025
-
Match Each Term Or Structure Listed With Its Correct Description
Mar 14, 2025
-
Section 20 1 Electric Charge And Static Electricity
Mar 14, 2025
-
The Letter S College Essay Pdf
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Choose The Correct Order Of Steps In The Production Process. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
