Modeling The Regulatory Switches Of The Pitx1 Gene
Onlines
Mar 14, 2025 · 6 min read
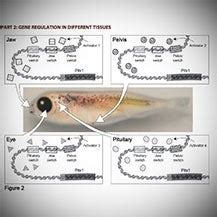
Table of Contents
Modeling the Regulatory Switches of the Pitx1 Gene
The Pitx1 gene, a pivotal transcription factor, plays a multifaceted role in vertebrate development, influencing a diverse array of processes from left-right asymmetry to limb and craniofacial morphogenesis. Understanding the intricate regulatory mechanisms controlling Pitx1 expression is crucial for deciphering its developmental functions and elucidating the genetic basis of associated human diseases. This article delves into the complexities of Pitx1 gene regulation, focusing on the identification and characterization of its regulatory switches, also known as enhancers and silencers. We will explore the methodologies employed in modeling these regulatory elements, highlighting the advancements in computational and experimental approaches. The ultimate goal is to provide a comprehensive overview of the current understanding and future directions in this exciting field of research.
The Pleiotropic Roles of Pitx1 and the Need for Precise Regulation
Pitx1, a bicoid-related homeobox gene, is expressed in a highly spatiotemporal-specific manner during development. Its expression patterns are meticulously controlled, reflecting its diverse functions. These roles include:
Left-Right Asymmetry:
Pitx1 is essential for establishing left-right asymmetry in the body plan. Its expression is specifically restricted to the left side of the body in several tissues, influencing the development of organs like the heart and gut, which exhibit distinct left-right morphologies. Disruption of Pitx1 expression leads to situs inversus or heterotaxy, conditions characterized by reversed or randomized organ positioning.
Limb Development:
Pitx1 plays a critical role in limb development, particularly in hindlimb patterning and growth. Its expression in the developing limb bud contributes to the differentiation of specific skeletal elements and influences overall limb morphology. Mutations affecting Pitx1 expression are associated with limb malformations.
Craniofacial Development:
Pitx1 also contributes to craniofacial development. Its expression is observed in developing craniofacial structures, influencing the formation of specific bones and cartilages. Alterations in Pitx1 expression can result in craniofacial abnormalities.
The precise spatiotemporal regulation of Pitx1 is crucial for its diverse functions. Mistakes in its expression can lead to severe developmental anomalies, highlighting the importance of understanding the regulatory mechanisms controlling its expression.
Identifying Pitx1 Regulatory Switches: Computational and Experimental Approaches
Unraveling the regulatory landscape of Pitx1 necessitates a multi-pronged approach that integrates both computational and experimental methodologies.
Computational Approaches:
Advances in genomic sequencing and bioinformatics have enabled the development of powerful computational tools for predicting cis-regulatory elements. These tools analyze genomic sequences to identify potential enhancers and silencers based on the presence of conserved sequence motifs, epigenetic marks (histone modifications), and chromatin accessibility.
-
Sequence Conservation Analysis: Comparison of Pitx1 genomic regions across various vertebrate species can reveal conserved non-coding sequences (CNSs), which are often indicative of regulatory elements. Highly conserved regions are more likely to be functional due to selective pressure maintaining their sequence.
-
Transcription Factor Binding Site Prediction: Bioinformatic tools predict the presence of binding sites for transcription factors known to regulate Pitx1 expression. These tools analyze the sequence for consensus motifs that are recognized by specific transcription factors.
-
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Sequencing (ChIP-seq): ChIP-seq identifies genomic regions bound by specific transcription factors or modified histones. By performing ChIP-seq for transcription factors known to regulate Pitx1, researchers can pinpoint potential regulatory elements.
-
DNase I Hypersensitivity Site (DHS) Analysis: DHSs are regions of open chromatin that are accessible to nucleases like DNase I. These regions are often associated with regulatory elements and can be identified using DNase I hypersensitivity assays.
-
ATAC-seq (Assay for Transposase-Accessible Chromatin using sequencing): Similar to DNase I hypersensitivity assays, ATAC-seq identifies open chromatin regions using a hyperactive Tn5 transposase. This technique offers higher sensitivity and requires less starting material.
Experimental Approaches:
Computational predictions require experimental validation to confirm the functionality of identified regulatory elements. Several techniques are commonly used:
-
Reporter Gene Assays: This classic approach involves cloning a candidate regulatory element upstream of a reporter gene (e.g., luciferase) and transfecting the construct into cells. Expression of the reporter gene indicates the activity of the regulatory element. Tissue-specific expression can be assessed by using tissue-specific cell lines.
-
Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA): EMSA is used to detect direct binding of transcription factors to candidate regulatory elements. This method assesses the binding affinity of proteins to DNA fragments.
-
Chromatin Conformation Capture (3C) and its variations (4C, 5C, Hi-C): These techniques reveal the three-dimensional organization of chromatin and identify long-range interactions between regulatory elements and the Pitx1 promoter. This information is crucial for understanding how distant enhancers can regulate gene expression.
Modeling the Regulatory Network of Pitx1
Integrating the data obtained from both computational and experimental approaches allows the construction of a comprehensive model of the Pitx1 regulatory network. This model encompasses:
-
Identification of key regulatory elements: This includes mapping the location and characterization of enhancers and silencers responsible for the spatiotemporal expression of Pitx1.
-
Characterization of transcription factors involved: This involves identifying the transcription factors that bind to these regulatory elements and modulate Pitx1 expression. This might involve analyzing the sequence specificity of these transcription factors and studying the interactions between them.
-
Understanding the interplay between different regulatory elements: This aspect focuses on how multiple enhancers and silencers cooperate to determine the precise expression pattern of Pitx1. Understanding the combinatorial action of these elements is critical.
-
Modeling the dynamics of Pitx1 regulation: This entails developing mathematical models that capture the temporal changes in Pitx1 expression and how these changes are governed by the regulatory network. This approach helps to predict the effects of perturbations in the network.
Clinical Implications and Future Directions
A thorough understanding of the Pitx1 regulatory network has significant clinical implications. Mutations affecting Pitx1 regulatory elements can lead to developmental disorders similar to those caused by mutations in the coding sequence. By identifying these regulatory mutations, researchers can improve diagnostics and potentially develop therapeutic strategies.
Future directions in modeling Pitx1 regulation include:
-
Integrating single-cell technologies: Analyzing Pitx1 expression and regulatory element activity at single-cell resolution will provide a more detailed understanding of the heterogeneity in Pitx1 regulation.
-
Developing more sophisticated computational models: Incorporating information about chromatin structure, epigenetic modifications, and transcription factor interactions into computational models will provide more accurate predictions of Pitx1 expression patterns.
-
Investigating the role of non-coding RNAs: Non-coding RNAs, such as long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), can regulate gene expression and may play a role in controlling Pitx1 expression. Further research is needed to determine the contribution of non-coding RNAs to Pitx1 regulation.
-
Utilizing CRISPR-Cas9 technology: CRISPR-Cas9 technology can be employed to precisely target and modify regulatory elements in vivo, allowing researchers to investigate the function of specific regulatory elements in a living organism and potentially pave the way for novel therapeutic approaches.
Conclusion:
Modeling the regulatory switches of the Pitx1 gene is a complex but crucial undertaking. Integrating computational and experimental approaches has yielded significant insights into the mechanisms that control the spatiotemporal expression of this pivotal transcription factor. Further research, incorporating advanced technologies and integrative modeling approaches, will be essential for fully elucidating the Pitx1 regulatory network and translating this knowledge into clinical applications for understanding and treating associated developmental disorders. The continued exploration of Pitx1 regulation promises to reveal fundamental principles of gene regulation and developmental biology, furthering our understanding of the intricate processes that shape vertebrate development.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Final Exam For Is 100 C
Mar 14, 2025
-
Amoeba Sisters Video Recap Pedigrees Answer Key
Mar 14, 2025
-
1 The Five Common Types Of Expressway Interchanges Are
Mar 14, 2025
-
What Is The Authors Viewpoint In This Excerpt
Mar 14, 2025
-
Po Box 115009 Carrollton Tx 75011
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Modeling The Regulatory Switches Of The Pitx1 Gene . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
