Consist Of Hollow Tubes Which Provide Support For The Cell
Onlines
Mar 21, 2025 · 7 min read
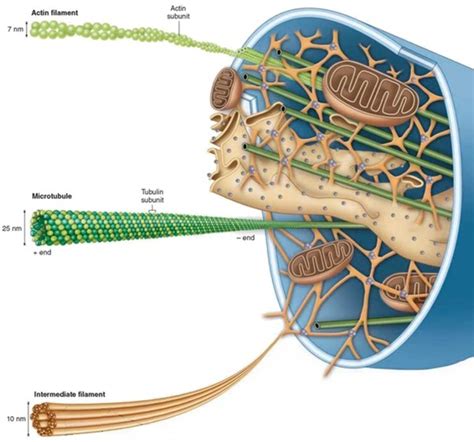
Table of Contents
Microtubules: The Hollow Pillars Supporting Cellular Life
Microtubules, the dynamic and versatile components of the cytoskeleton, are fascinating structures that play a crucial role in maintaining cell shape, facilitating intracellular transport, and enabling essential cellular processes like cell division. These hollow tubes, constructed from α- and β-tubulin dimers, are far from static; they constantly assemble and disassemble, adapting to the cell's ever-changing needs. This article delves deep into the structure, function, and significance of microtubules, exploring their multifaceted contributions to cellular life.
The Architecture of Microtubules: A Closer Look
Microtubules are cylindrical polymers with a remarkable architecture. Their basic building blocks are α- and β-tubulin dimers, which are heterodimers—meaning they are composed of two different proteins. These dimers spontaneously associate head-to-tail, forming protofilaments. Typically, thirteen protofilaments arrange themselves laterally to create the hollow cylindrical structure of the microtubule. This hollow core, with a diameter of approximately 25 nanometers, is a defining characteristic of these cellular components.
The dynamic instability of microtubules is a critical feature. This refers to their ability to rapidly switch between phases of growth and shrinkage. This dynamic behavior is essential for their diverse functions, allowing them to explore the cellular environment and respond effectively to changing conditions. The plus end of a microtubule, typically located near the cell periphery, exhibits more rapid growth and shrinkage than the minus end, usually anchored near the microtubule-organizing center (MTOC).
The Role of Microtubule-Associated Proteins (MAPs)
Microtubule function is tightly regulated by a diverse array of microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs). These proteins bind to microtubules, influencing their stability, dynamics, and interactions with other cellular components. Different MAPs perform distinct functions, some promoting microtubule assembly and stability, while others stimulate disassembly or mediate interactions with motor proteins.
Examples of MAPs and their functions include:
- Tau proteins: Important for stabilizing microtubules in axons. Dysfunction in tau proteins is linked to neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's disease.
- MAP2: Primarily found in dendrites, this protein plays a crucial role in dendritic morphology and synaptic plasticity.
- Catastrophins: Proteins that promote microtubule catastrophe, the transition from growth to shrinkage.
- Kinesins and Dyneins: Motor proteins that transport cargo along microtubules.
Microtubules: The Cellular Highways for Intracellular Transport
One of the most significant roles of microtubules is their contribution to intracellular transport. They act as "cellular highways," providing tracks along which motor proteins transport various cargos, including organelles, vesicles, and macromolecules.
Two prominent families of motor proteins use microtubules as their tracks: kinesins and dyneins. Kinesins generally move towards the plus end of microtubules (anterograde transport), while dyneins move towards the minus end (retrograde transport). This directional movement is crucial for transporting essential materials throughout the cell, ensuring the proper distribution of resources and signaling molecules.
Specific examples of transport mediated by microtubules and motor proteins include:
- Vesicular transport: Movement of vesicles containing neurotransmitters, hormones, or other molecules to their target destinations.
- Organelle trafficking: Relocation of organelles like mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum to specific regions within the cell.
- Chromosomal movement: During cell division, microtubules guide the movement of chromosomes to ensure accurate segregation.
Microtubules and Cell Shape: Maintaining Structural Integrity
Microtubules are essential components of the cytoskeleton, the internal scaffolding of the cell. They contribute significantly to maintaining cell shape and structure, providing resistance to compressive forces and preventing cell collapse. Their dynamic behavior allows them to adapt to changes in the cell's environment and adjust the cell's shape accordingly. This is particularly important in cells that undergo frequent changes in shape, such as migrating cells or cells involved in immune responses.
The arrangement of microtubules within the cell can significantly influence its overall shape. For instance, in epithelial cells, microtubules are organized in a parallel fashion, contributing to the polarized and elongated shape of these cells. In contrast, microtubules in fibroblasts are arranged more randomly, reflecting the irregular shape of these cells.
Microtubules' Crucial Role in Cell Division
Microtubules play a pivotal role in cell division (mitosis and meiosis). They form the mitotic spindle, a complex structure responsible for segregating chromosomes accurately into daughter cells. The mitotic spindle comprises microtubules that attach to chromosomes at their kinetochores, pulling them apart during anaphase. Proper spindle formation and function are essential for generating genetically identical daughter cells and preventing genomic instability.
The dynamic behavior of microtubules is crucial for successful chromosome segregation. Microtubules constantly grow, shrink, and attach to chromosomes, ensuring proper alignment and separation. Errors in microtubule dynamics during cell division can lead to aneuploidy (abnormal chromosome number), a hallmark of many cancers.
Microtubule Targeting Agents in Cancer Therapy
The importance of microtubules in cell division has made them a prime target for cancer therapeutics. Microtubule-targeting agents are drugs that interfere with microtubule dynamics, disrupting cell division and ultimately leading to cancer cell death. These agents are widely used in cancer chemotherapy and represent a cornerstone of cancer treatment. Examples include:
- Taxanes (e.g., paclitaxel): These drugs stabilize microtubules, preventing their depolymerization and inhibiting cell division.
- Vinca alkaloids (e.g., vinblastine): These drugs inhibit microtubule polymerization, disrupting spindle formation and chromosome segregation.
Microtubules and Cilia and Flagella: Enabling Movement
Microtubules are the structural foundation of cilia and flagella, hair-like appendages found on the surface of many eukaryotic cells. These structures are responsible for cell motility and fluid movement. Cilia and flagella share a common internal structure, the axoneme, which consists of nine outer microtubule doublets surrounding a central pair of microtubules (9+2 arrangement).
The movement of cilia and flagella is driven by the action of dynein motor proteins, which slide the microtubule doublets against each other. This sliding generates bending forces that propel the cilia and flagella, enabling cells to swim or move fluids across their surface. Defects in microtubule structure or function can lead to dysfunction of cilia and flagella, causing a variety of diseases, collectively known as ciliopathies.
Microtubules and Intracellular Organization: Compartmentalization and Signaling
Beyond their roles in transport and motility, microtubules contribute significantly to intracellular organization. They act as scaffolding, influencing the positioning and organization of various organelles and cellular components. This spatial organization is crucial for maintaining cellular function and coordinating cellular processes.
Microtubules also play a role in intracellular signaling. Their dynamic behavior and interactions with signaling molecules can influence various signaling pathways, regulating cellular responses to external stimuli. This aspect of microtubule function is still being actively investigated, but it highlights the multifaceted roles of these cellular structures.
Microtubule Dysfunction and Disease: A Broad Impact
Disruptions in microtubule function have far-reaching consequences, leading to a wide range of human diseases. As previously mentioned, microtubule dysfunction plays a role in neurodegenerative diseases, cancer, and ciliopathies. Furthermore, defects in microtubule dynamics are implicated in other conditions, highlighting their importance in maintaining cellular homeostasis.
Understanding the intricate roles of microtubules in various cellular processes is essential for developing therapeutic strategies for a variety of diseases. Continued research in this area is critical for advancing our knowledge of cellular biology and improving human health.
Conclusion: Microtubules – The Dynamic Pillars of Cellular Life
In conclusion, microtubules are remarkably versatile and dynamic structures that are indispensable for a vast array of cellular functions. Their role in maintaining cell shape, facilitating intracellular transport, enabling cell division, and powering ciliary and flagellar movement underscore their critical contribution to cellular life. Their dynamic instability, regulated by a plethora of associated proteins, ensures they can rapidly respond to cellular needs, adapting their structure and function to maintain cellular homeostasis. Further exploration of the intricacies of microtubule biology promises to reveal even more about their multifaceted roles and their involvement in human health and disease. The ongoing research in this field continues to yield vital insights, offering exciting possibilities for therapeutic interventions in various disease conditions.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Themes For I Know Why The Caged Bird Sings
Mar 22, 2025
-
Astro 7n Art Project 3 Reading Quiz
Mar 22, 2025
-
You Re Doing Housekeeping Tasks For A Patient
Mar 22, 2025
-
Benito Embroiders And Sells T Shirts
Mar 22, 2025
-
A Mass Customization Strategy Seeks To Blank
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Consist Of Hollow Tubes Which Provide Support For The Cell . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
