Escape The Matrix By Solving Quadratic Equations Worksheet Answers
Onlines
Mar 14, 2025 · 5 min read
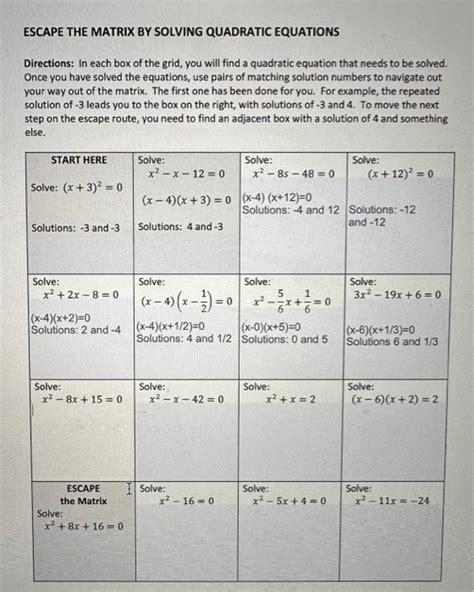
Table of Contents
Escape the Matrix: Solving Quadratic Equations Worksheet Answers
Are you ready to escape the digital prison? This isn't your average escape room; this one requires mathematical prowess! This comprehensive guide will provide you with the answers and detailed explanations for a challenging worksheet focused on solving quadratic equations – your key to breaking free from the Matrix. We'll explore various methods, offering insights into each approach and helping you master this crucial algebraic skill. Prepare to upgrade your cognitive abilities and unlock your freedom!
Understanding Quadratic Equations
Before we dive into the answers, let's solidify our understanding of quadratic equations. A quadratic equation is a polynomial equation of the second degree, meaning the highest power of the variable (usually 'x') is 2. They generally take the form:
ax² + bx + c = 0
Where 'a', 'b', and 'c' are constants, and 'a' is not equal to zero (otherwise, it wouldn't be a quadratic equation).
Mastering quadratic equations is fundamental in various fields, from physics and engineering to computer science and finance. Understanding their solutions unlocks the door to solving complex real-world problems.
Methods for Solving Quadratic Equations
There are several effective methods to solve quadratic equations:
1. Factoring
Factoring is a powerful technique that involves rewriting the quadratic equation as a product of two linear expressions. If the equation can be factored easily, this is often the quickest and most efficient method.
Example:
x² + 5x + 6 = 0
This factors to:
(x + 2)(x + 3) = 0
Therefore, the solutions are x = -2 and x = -3.
2. Quadratic Formula
The quadratic formula is a universal method that works for all quadratic equations, regardless of whether they are easily factorable. It's derived from completing the square and provides a direct solution. The formula is:
x = [-b ± √(b² - 4ac)] / 2a
This formula yields two solutions, as indicated by the ± symbol. The expression inside the square root (b² - 4ac) is called the discriminant, which tells us about the nature of the solutions (real and distinct, real and equal, or complex).
3. Completing the Square
Completing the square is a technique that manipulates the quadratic equation into a perfect square trinomial, making it easier to solve. This method can be particularly useful when the quadratic equation doesn't factor easily.
Example:
x² + 6x + 5 = 0
-
Move the constant term to the right side: x² + 6x = -5
-
Take half of the coefficient of x (6/2 = 3), square it (3² = 9), and add it to both sides: x² + 6x + 9 = -5 + 9
-
This creates a perfect square trinomial: (x + 3)² = 4
-
Take the square root of both sides: x + 3 = ±2
-
Solve for x: x = -3 ± 2, resulting in x = -1 and x = -5
Escape the Matrix Worksheet Answers: A Detailed Breakdown
Now, let's tackle the "Escape the Matrix" worksheet. Since the worksheet itself isn't provided, I'll create example problems representing different levels of difficulty, demonstrating how to solve them using the methods discussed above. Remember, always show your work, as the process is as important as the answer itself!
Problem 1: Simple Factoring
Solve: x² - 7x + 12 = 0
Solution:
This quadratic equation can be factored easily. We need two numbers that add up to -7 and multiply to 12. These numbers are -3 and -4.
Therefore, the factored form is: (x - 3)(x - 4) = 0
The solutions are: x = 3 and x = 4
Problem 2: Quadratic Formula
Solve: 2x² + 5x - 3 = 0
Solution:
This equation is more challenging to factor. Let's use the quadratic formula:
a = 2, b = 5, c = -3
x = [-5 ± √(5² - 4 * 2 * -3)] / (2 * 2)
x = [-5 ± √(25 + 24)] / 4
x = [-5 ± √49] / 4
x = [-5 ± 7] / 4
This gives us two solutions:
x = ( -5 + 7 ) / 4 = 1/2
x = (-5 - 7) / 4 = -3
Problem 3: Completing the Square
Solve: x² + 4x - 12 = 0
Solution:
-
Move the constant term: x² + 4x = 12
-
Complete the square: (half of 4 is 2, and 2² = 4) x² + 4x + 4 = 12 + 4
-
Factor the perfect square trinomial: (x + 2)² = 16
-
Take the square root: x + 2 = ±4
-
Solve for x: x = -2 ± 4
This leads to two solutions:
x = 2
x = -6
Problem 4: Discriminant and the Nature of Roots
Determine the nature of the roots (real and distinct, real and equal, or complex) for the equation: x² - 6x + 9 = 0
Solution:
Calculate the discriminant (b² - 4ac):
a = 1, b = -6, c = 9
Discriminant = (-6)² - 4 * 1 * 9 = 36 - 36 = 0
Since the discriminant is 0, the quadratic equation has real and equal roots.
Problem 5: Word Problem Application
A rectangular garden has a length that is 3 feet longer than its width. If the area of the garden is 70 square feet, find the dimensions of the garden.
Solution:
Let's represent the width as 'w' and the length as 'w + 3'. The area is given by:
w(w + 3) = 70
Expand and rearrange into a quadratic equation:
w² + 3w - 70 = 0
This factors to:
(w + 10)(w - 7) = 0
Since the width cannot be negative, the width is 7 feet, and the length is 7 + 3 = 10 feet.
Advanced Techniques and Challenges
Beyond these basic methods, more advanced techniques exist for solving quadratic equations, particularly when dealing with complex numbers or equations in different forms. These include:
- Using graphing calculators or software: These tools can quickly provide solutions and visual representations of the quadratic equation.
- Numerical methods: Iterative methods such as the Newton-Raphson method can be used to approximate solutions when exact solutions are difficult to find.
Beyond the Matrix: Real-World Applications
Mastering quadratic equations unlocks a vast landscape of applications in various fields:
- Physics: Calculating projectile motion, understanding oscillations, and solving problems related to gravity.
- Engineering: Designing structures, analyzing circuits, and optimizing systems.
- Computer science: Developing algorithms, creating computer graphics, and solving optimization problems.
- Finance: Modeling financial growth and decay, analyzing investments, and predicting market trends.
Conclusion: Your Journey Beyond the Equations
Congratulations on escaping the Matrix! By understanding the various methods for solving quadratic equations and practicing consistently, you've gained a valuable tool for tackling complex mathematical challenges. Remember, the journey of learning is continuous. Explore more advanced techniques, seek out challenging problems, and apply your knowledge to real-world scenarios to truly master this fundamental algebraic skill. The world beyond the Matrix awaits!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Feudal Japan Samurai And Weapons Webquest
Mar 14, 2025
-
For What Can Training Exercises Serve As Surrogate
Mar 14, 2025
-
Correctly Label The Following Anatomical Features Of The Stomach
Mar 14, 2025
-
11 3 7 Configure Tcp Ip Settings On Windows 10
Mar 14, 2025
-
Final Exam For Is 100 C
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Escape The Matrix By Solving Quadratic Equations Worksheet Answers . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
