Fibromuscular Hyperplasia Of Renal Artery Is Reported With Icd-10-cm Code
Onlines
Apr 05, 2025 · 5 min read
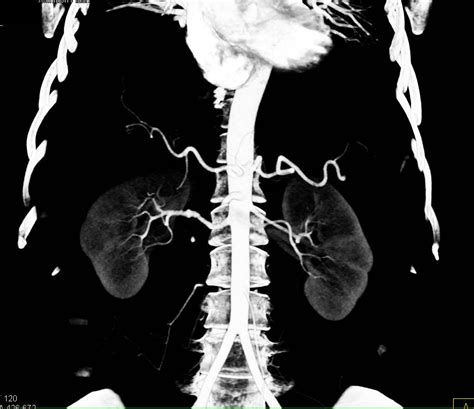
Table of Contents
Fibromuscular Hyperplasia of the Renal Artery: ICD-10-CM Code and Comprehensive Overview
Fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD) affecting the renal artery is a relatively common, non-atherosclerotic vascular disorder predominantly affecting women. Characterized by abnormal cell growth within the arterial wall, it leads to stenosis (narrowing) of the renal artery, potentially causing hypertension, renal insufficiency, and other cardiovascular complications. Understanding this condition, its diagnostic criteria, associated ICD-10-CM codes, and management strategies is crucial for healthcare professionals. This comprehensive article delves into all aspects of renal artery fibromuscular hyperplasia (also known as fibromuscular dysplasia of the renal artery), providing a detailed overview for both medical professionals and patients seeking information.
Understanding Fibromuscular Dysplasia (FMD) of the Renal Artery
Fibromuscular dysplasia is a non-atherosclerotic disease affecting medium-sized and small arteries throughout the body. While it can affect various arteries, its manifestation in the renal arteries is particularly significant due to its potential to cause secondary hypertension. The exact etiology remains unclear, but several factors are implicated, including:
- Genetic predisposition: While no single gene has been definitively identified, a familial occurrence suggests a genetic component.
- Hormonal influence: The higher prevalence in women of childbearing age suggests a role for estrogen.
- Connective tissue disorders: FMD may be associated with other connective tissue disorders.
The pathophysiology involves abnormal development of the arterial wall, leading to the formation of:
- String-of-beads appearance: This characteristic radiological finding is caused by alternating areas of stenosis and dilation.
- Medial hyperplasia: This refers to the thickening of the arterial media, the middle layer of the artery wall.
- Intimal fibroplasia: This involves the thickening of the intima, the innermost layer of the arterial wall.
These structural changes result in narrowing of the renal artery lumen, reducing blood flow to the kidney. This reduction in renal perfusion activates the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), leading to the elevation of blood pressure.
Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis
The clinical presentation of renal artery FMD is highly variable. Many individuals are asymptomatic, with the condition discovered incidentally during imaging studies performed for other reasons. However, symptomatic patients may present with:
- Hypertension: This is the most common symptom and often resistant to standard antihypertensive medications.
- Renal insufficiency: In advanced cases, reduced renal perfusion can lead to impaired kidney function.
- Acute renal failure: This can occur due to sudden occlusion of the affected renal artery.
- Abdominal bruit: An audible murmur may be detected over the affected artery during physical examination.
- Headaches, dizziness, and palpitations: These can be associated with hypertension.
Diagnosis of renal artery FMD relies on several imaging techniques:
- Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA): This non-invasive technique provides high-resolution images of the renal arteries, clearly demonstrating the characteristic string-of-beads appearance.
- Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA): Another non-invasive method that offers excellent visualization of the renal arteries.
- Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA): This invasive technique provides the most detailed images but carries a slightly higher risk compared to MRA and CTA. It is often reserved for cases requiring intervention.
- Renal vein renin assay: Measuring renin levels in the renal vein can help determine the source of hypertension and confirm the diagnosis.
Differential diagnosis includes other conditions causing renal artery stenosis, such as atherosclerosis.
ICD-10-CM Code for Fibromuscular Hyperplasia of the Renal Artery
The International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) is a system used for coding diagnoses and procedures in healthcare settings. The specific code for fibromuscular hyperplasia of the renal artery is:
I77.1: This code represents other specified disorders of the renal vessels. While it is not explicitly "fibromuscular hyperplasia," it is the most appropriate code for this condition in the absence of a more specific code. It's crucial that detailed documentation accompanies the code in the medical record to clarify the diagnosis.
Important Note: Accurate coding is essential for reimbursement and healthcare data analysis. Consult the latest ICD-10-CM manual for the most current coding guidelines and any potential revisions. Improper coding can lead to billing errors and hinder accurate epidemiological data collection.
Management and Treatment Strategies
Management of renal artery FMD depends on several factors, including the severity of stenosis, the presence of symptoms (especially hypertension), and the patient's overall health.
Medical Management:
- Antihypertensive medications: These are the cornerstone of management, aiming to control blood pressure and protect the kidneys. Multiple medications may be necessary, including ACE inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), calcium channel blockers, and diuretics.
- Regular monitoring: Close monitoring of blood pressure, kidney function (eGFR), and electrolytes is crucial.
Interventional Procedures:
- Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA): This minimally invasive procedure involves inserting a catheter into the affected artery and inflating a balloon to widen the narrowed segment. Stent placement is often used to maintain patency.
- Stent placement: Stents are small, expandable metal tubes that are placed within the artery to keep it open. This is usually performed in conjunction with PTA.
Surgical Intervention:
Surgical intervention is usually reserved for patients who are not candidates for or have failed interventional procedures. Options include:
- Renal artery bypass: This involves creating a new pathway for blood to flow around the affected segment of the artery.
Prognosis and Long-Term Outlook
The prognosis for patients with renal artery FMD is generally favorable, especially with early diagnosis and appropriate management. Effective blood pressure control is crucial for preserving kidney function and preventing cardiovascular complications. Regular follow-up appointments and monitoring are essential for assessing the effectiveness of treatment and detecting any potential complications.
Conclusion
Fibromuscular hyperplasia of the renal artery, while a relatively uncommon condition, represents a significant cause of secondary hypertension. Understanding its pathogenesis, clinical presentation, diagnostic modalities, ICD-10-CM coding, and treatment strategies is essential for healthcare professionals. Early diagnosis and appropriate management, including lifestyle modifications, medical therapy, and potentially interventional procedures, are crucial to improve patient outcomes and reduce the risk of complications. The information provided in this article serves as a comprehensive overview; individual cases require tailored management plans based on patient-specific factors. Always consult with a healthcare professional for any health concerns or before making any decisions related to your health or treatment. The information contained herein is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Lesson Summary Toni Cade Bambara
Apr 05, 2025
-
Chapter 1 Summary Of Catcher In The Rye
Apr 05, 2025
-
Find The Probability That X Falls In The Shaded Area
Apr 05, 2025
-
The Patriot Movie Questions And Answers
Apr 05, 2025
-
Secondary Math 1 Module 5 3 Answer Key
Apr 05, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Fibromuscular Hyperplasia Of Renal Artery Is Reported With Icd-10-cm Code . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
