For Each Scenario Calculate The Income Elasticity Of Demand
Onlines
Apr 02, 2025 · 6 min read
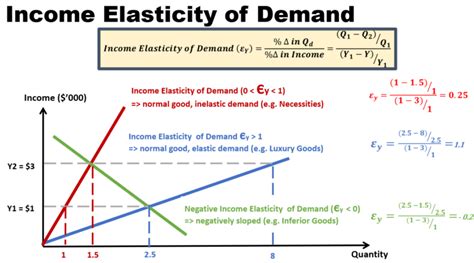
Table of Contents
Calculating Income Elasticity of Demand: A Comprehensive Guide with Scenarios
Income elasticity of demand (YED) is a crucial economic concept measuring the responsiveness of quantity demanded to changes in consumer income. Understanding YED is vital for businesses in forecasting sales, managing inventory, and making strategic decisions. This article provides a detailed explanation of YED, its calculation, interpretation, and application through various scenarios. We'll delve into different types of goods based on their YED values and examine how to interpret the results in real-world contexts.
What is Income Elasticity of Demand?
Income elasticity of demand quantifies the percentage change in quantity demanded of a good or service resulting from a one percent change in consumer income. It's calculated using the following formula:
YED = (% Change in Quantity Demanded) / (% Change in Income)
A positive YED indicates a normal good, where demand increases as income rises. A negative YED signifies an inferior good, where demand falls as income increases. The magnitude of the YED value further classifies goods:
- YED > 1: This signifies a luxury good, where the demand is highly responsive to income changes. A small increase in income leads to a proportionally larger increase in demand.
- 0 < YED < 1: This indicates a necessary good, where demand increases with income but at a slower rate. The demand is less responsive to income changes compared to luxury goods.
- YED < 0: This represents an inferior good, where demand decreases as income rises. Consumers tend to switch to superior substitutes as their income increases.
- YED = 0: This suggests that the demand for the good is completely unresponsive to changes in income.
Scenarios and Calculations
Let's explore various scenarios to illustrate YED calculations and interpretations:
Scenario 1: Luxury Cars
Suppose the quantity demanded for luxury cars increases by 15% when consumer income rises by 5%.
- % Change in Quantity Demanded = 15%
- % Change in Income = 5%
YED = 15% / 5% = 3
This indicates that luxury cars are a luxury good with a high income elasticity of demand. A relatively small increase in income leads to a significantly larger increase in the demand for luxury cars. This is because consumers are more likely to purchase luxury goods when their disposable income increases. Luxury car manufacturers can capitalize on this by strategically targeting high-income demographics and offering premium features.
Scenario 2: Organic Food
Let's consider the case of organic food. Assume that when consumer income rises by 10%, the quantity demanded for organic food increases by 8%.
- % Change in Quantity Demanded = 8%
- % Change in Income = 10%
YED = 8% / 10% = 0.8
This signifies that organic food is a normal good, specifically a necessary good. While the demand increases with income, the increase is less than proportional. This suggests that even with increased income, consumers may not drastically increase their organic food consumption. This understanding helps organic food companies in formulating pricing strategies and targeting market segments effectively. They might focus on showcasing the value proposition of organic food to maintain demand, even during periods of economic fluctuation.
Scenario 3: Instant Noodles
Now, let's look at instant noodles, often considered an inferior good. Suppose a 20% increase in income results in a 5% decrease in the quantity demanded for instant noodles.
- % Change in Quantity Demanded = -5%
- % Change in Income = 20%
YED = -5% / 20% = -0.25
This clearly indicates that instant noodles are an inferior good. As consumer income increases, the demand for instant noodles falls. This is because consumers tend to opt for more expensive and possibly healthier food alternatives as their income rises. This information is vital for instant noodle manufacturers, who might need to adjust their marketing strategy to target lower-income demographics or reposition their product as a convenient option, regardless of income level. They might introduce premium variations to cater to a broader range of consumers.
Scenario 4: Salt
Let's consider a basic necessity like salt. Suppose a 10% increase in income results in only a 0.5% increase in the quantity of salt demanded.
- % Change in Quantity Demanded = 0.5%
- % Change in Income = 10%
YED = 0.5% / 10% = 0.05
This shows that salt is a normal good, but its demand is relatively inelastic with respect to income. Changes in income have minimal impact on salt consumption. This understanding is important for salt producers in terms of pricing and production planning, as they can expect relatively stable demand even with fluctuations in consumer income.
Scenario 5: Public Transportation
Consider the demand for public transportation. Imagine that a 15% increase in income leads to a 3% decrease in the quantity demanded for public transport.
- % Change in Quantity Demanded = -3%
- % Change in Income = 15%
YED = -3% / 15% = -0.2
This illustrates that, in this specific context, public transport is acting as an inferior good. This might occur because as income rises, individuals are more likely to switch to private transportation. Public transport authorities could use this insight to offer incentives and improve services to remain competitive despite increased consumer income.
Interpreting the Results and Implications for Businesses
The YED values calculated in these scenarios provide valuable insights for businesses in different industries. Understanding whether a product is a normal, inferior, luxury, or necessary good helps companies make informed decisions about:
- Pricing Strategies: Luxury goods can command higher prices, while necessary goods may require competitive pricing to maintain demand. Inferior goods might necessitate targeted marketing to specific income groups.
- Marketing and Advertising: The target audience for each type of good differs based on its YED. Marketing efforts should be tailored to reach the appropriate income segments.
- Production Planning: Knowledge of YED helps businesses forecast demand and optimize production levels according to economic forecasts and income changes.
- Investment Decisions: Understanding the sensitivity of demand to income fluctuations is crucial for making investment decisions related to product development, expansion, and resource allocation.
Factors Affecting Income Elasticity of Demand
Several factors influence the income elasticity of demand for a given good or service:
- Availability of Substitutes: Goods with many close substitutes tend to have higher YED values, as consumers can easily switch to alternatives when their income changes.
- Proportion of Income Spent: Goods that consume a larger proportion of a consumer's income tend to have higher income elasticity of demand.
- Necessities vs. Luxuries: The inherent nature of a good – whether it's a necessity or a luxury – significantly impacts its YED.
- Time Horizon: The income elasticity of demand might change over time as consumer preferences and habits evolve.
Conclusion
Calculating and interpreting the income elasticity of demand is a fundamental aspect of economic analysis and business decision-making. By understanding how consumer demand responds to income changes, businesses can refine their strategies, optimize their operations, and achieve sustainable growth. The scenarios outlined above demonstrate the practical application of YED calculations and their implications for various industries and product categories. Remember that YED is a dynamic measure, influenced by various factors, and requires continuous monitoring and adaptation in response to changing economic conditions and consumer behavior.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Quiz 4 1 Classifying And Solving For Sides
Apr 03, 2025
-
The Lord Of The Flies Chapter 12 Summary
Apr 03, 2025
-
Which Is Not True Of Laser Caries Detector Readings
Apr 03, 2025
-
3 Choices Ralph Contemplates For Escape And Survival
Apr 03, 2025
-
What Is The Difference Between A Load And A Control
Apr 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about For Each Scenario Calculate The Income Elasticity Of Demand . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
