For Which Of The Following Is Potential Energy Increasing
Onlines
Mar 12, 2025 · 6 min read
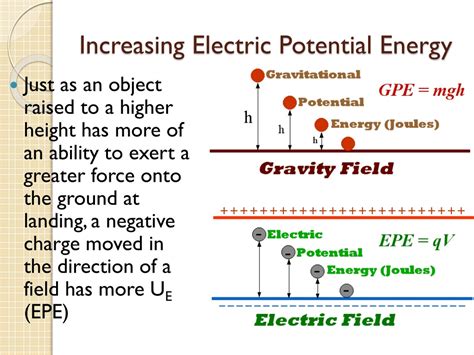
Table of Contents
For Which of the Following is Potential Energy Increasing? Understanding Potential Energy Changes
Potential energy, a fundamental concept in physics, represents stored energy that an object possesses due to its position or configuration. Unlike kinetic energy, which is associated with motion, potential energy is inherent in the object's state. Understanding when potential energy increases is crucial in various fields, from mechanics to chemistry. This comprehensive guide delves into the factors affecting potential energy and explores scenarios where this energy form is on the rise.
Types of Potential Energy
Before examining specific situations, let's clarify the different types of potential energy:
1. Gravitational Potential Energy:
This is the most common type, associated with an object's position relative to a gravitational field. The higher an object is above a reference point (usually the ground), the greater its gravitational potential energy. This energy is directly proportional to the object's mass (m), the acceleration due to gravity (g), and its height (h) above the reference point: PE<sub>gravitational</sub> = mgh.
2. Elastic Potential Energy:
This type arises when a deformable object, like a spring or rubber band, is stretched or compressed. The energy stored depends on the object's stiffness (spring constant, k) and the extent of deformation (x): PE<sub>elastic</sub> = (1/2)kx<sup>2</sup>.
3. Chemical Potential Energy:
This energy is stored within the chemical bonds of molecules. Breaking or forming bonds involves energy changes, leading to an increase or decrease in chemical potential energy. This is crucial in chemical reactions, combustion, and biological processes.
4. Electrical Potential Energy:
This form of potential energy relates to the position of a charged particle within an electric field. The closer a charged particle is to another charged particle of opposite polarity, the lower its potential energy. Conversely, the farther away, or closer to like charges, the greater its electrical potential energy.
Scenarios Where Potential Energy Increases
Let's now investigate specific scenarios where the different types of potential energy are increasing:
Gravitational Potential Energy Increases:
-
Lifting an object: The most straightforward example. As you lift an object against gravity, you're doing work on it, increasing its gravitational potential energy. The higher you lift it, the greater the increase. Think of a weightlifter raising a barbell – the barbell's potential energy increases with every inch of ascent.
-
A ball thrown upwards: As a ball travels upwards, it slows down due to gravity. However, its potential energy increases as it gains height. At the apex of its trajectory, its potential energy is maximal, and its kinetic energy is zero (before it starts falling).
-
Water flowing uphill: Water in a river gains gravitational potential energy as it flows uphill, driven by forces such as rainfall and the Earth's rotation. This potential energy is later converted into kinetic energy as the water flows downhill.
-
A rollercoaster climbing a hill: Rollercoasters demonstrate a beautiful exchange between potential and kinetic energy. As the coaster ascends a hill, it slows down, converting kinetic energy into potential energy. The higher the hill, the greater the increase in potential energy.
-
An airplane gaining altitude: Similar to the rollercoaster and the ball, an airplane's potential energy increases significantly as it climbs to higher altitudes. This increase is massive due to the airplane's considerable mass and the substantial increase in height.
Elastic Potential Energy Increases:
-
Stretching a rubber band: The more you stretch a rubber band, the greater the elastic potential energy stored within it. This energy is released when you let go, causing the rubber band to snap back.
-
Compressing a spring: Similarly, compressing a spring increases its elastic potential energy. The tighter the compression, the more energy is stored. Think of a spring-loaded toy – the spring's potential energy fuels its movement.
-
Bending a bow: Drawing back the string of a bow increases the elastic potential energy stored in the bow's limbs. This energy is released when the arrow is released, propelling it forward.
-
Inflating a balloon: While seemingly simple, inflating a balloon involves increasing the elastic potential energy of the rubber material. The greater the inflation, the more stretched the material and the more potential energy it stores.
Chemical Potential Energy Increases:
-
Photosynthesis: Plants increase their chemical potential energy through photosynthesis. Sunlight provides the energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose (a sugar), storing energy in the glucose's chemical bonds.
-
Charging a battery: Charging a battery involves storing chemical potential energy. The charging process reverses chemical reactions, increasing the potential for subsequent energy release.
-
Synthesis reactions: Any chemical reaction that creates a more complex molecule from simpler ones will generally lead to an increase in chemical potential energy. This is because the newly formed bonds store additional energy.
Electrical Potential Energy Increases:
-
Separating opposite charges: Work must be done to separate two oppositely charged particles. This work increases their electrical potential energy. The further apart they are, the greater the increase.
-
Moving a positive charge away from a positive charge: Similar to the above, moving a positive charge further from another positive charge increases their electrical potential energy due to the repulsive force between them. The same applies to moving a negative charge away from another negative charge.
-
Charging a capacitor: A capacitor stores electrical energy by separating charges on two plates. As more charge accumulates, the electrical potential energy stored in the capacitor increases.
Factors Affecting Potential Energy Increase
Several factors influence the magnitude of potential energy increases:
-
Mass (for gravitational potential energy): A heavier object will have a greater increase in gravitational potential energy for the same height increase compared to a lighter object.
-
Height (for gravitational potential energy): The greater the increase in height, the greater the increase in gravitational potential energy.
-
Spring constant (for elastic potential energy): A stiffer spring (higher spring constant) will store more elastic potential energy for the same amount of compression or extension.
-
Extent of deformation (for elastic potential energy): Greater stretching or compression leads to a larger increase in elastic potential energy.
-
Number of bonds and bond strength (for chemical potential energy): The number and strength of chemical bonds directly impact the chemical potential energy stored in a molecule.
-
Magnitude of charge and distance (for electrical potential energy): The magnitude of the charges and the distance between them significantly affect the electrical potential energy.
Real-World Applications
Understanding potential energy increases is crucial in numerous applications:
-
Renewable energy: Hydroelectric power plants harness the gravitational potential energy of water stored at high elevations to generate electricity.
-
Mechanical systems: Many mechanical devices, from clocks to engines, rely on the conversion of potential energy (e.g., elastic or gravitational) into kinetic energy to perform work.
-
Chemistry and biology: Chemical reactions and biological processes depend on changes in chemical potential energy, driving metabolic reactions and energy storage.
-
Electronics: Capacitors and batteries store energy, relying on increases in electrical or chemical potential energy, respectively.
Conclusion
Potential energy is a vital concept with far-reaching implications across various scientific and engineering disciplines. By understanding the factors influencing potential energy and recognizing scenarios where it increases, we can better appreciate its role in shaping the physical world around us and leverage it for various applications. This knowledge is fundamental for comprehending energy transformations and designing efficient systems across diverse fields. Remember that the increase in potential energy is always linked to work done against a conservative force (like gravity or the restoring force of a spring). Understanding this relationship is key to mastering the concepts of potential energy and energy conservation.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
An Infant With A History Of Tracheal Stenosis Quizlet
Mar 13, 2025
-
According To The Principle Of Overload You Should
Mar 13, 2025
-
Clinical Neuropsychology Is Multidisciplinary And Overlaps With The Fields Of
Mar 13, 2025
-
Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration Color By Number
Mar 13, 2025
-
La Duena Nos Recomendo La Langosta
Mar 13, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about For Which Of The Following Is Potential Energy Increasing . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
