Graphing Skill 1 What Type Of Graph Is It
Onlines
Apr 04, 2025 · 6 min read
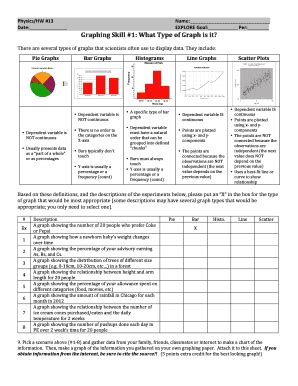
Table of Contents
Graphing Skills 1: What Type of Graph Is It? A Comprehensive Guide
Choosing the right graph is crucial for effective data visualization. A poorly chosen graph can obscure trends, mislead the audience, and render your data analysis useless. This comprehensive guide explores various graph types, their strengths, weaknesses, and ideal applications, empowering you to select the perfect graph for your data. We'll delve into the core principles of data representation and help you build strong graphing skills.
Understanding the Purpose of Graphing
Before diving into specific graph types, it's crucial to understand the fundamental purpose of graphing: to communicate data effectively. A well-designed graph should clearly and concisely convey information, highlighting key trends, patterns, and relationships within the data. The choice of graph directly impacts the effectiveness of this communication.
The process of choosing the right graph begins with asking yourself key questions about your data and your audience:
- What type of data do you have? Is it categorical, numerical, or a combination of both?
- What is the key message you want to convey? Are you highlighting trends, comparing values, showing distribution, or demonstrating correlation?
- Who is your audience? Are they experts in the field, or do they need a simpler, more intuitive representation?
Answering these questions will guide you towards the most appropriate graph type.
Categorical Data Graphs: Showing Differences and Frequencies
Categorical data represents qualitative characteristics, such as colors, categories, or names. Several graph types are suitable for visualizing categorical data:
1. Bar Charts: Comparing Categories
Bar charts are excellent for comparing the frequencies or values of different categories. Each category is represented by a separate bar, with the height (or length) of the bar proportional to its value.
Strengths: Simple to understand, effective for comparisons, clearly shows differences between categories.
Weaknesses: Can become cluttered with many categories, not suitable for showing changes over time.
Ideal for: Comparing sales figures for different products, showing the distribution of survey responses, illustrating the prevalence of different diseases.
2. Pie Charts: Showing Proportions
Pie charts represent the proportion of each category within a whole. Each category is represented by a slice of the pie, with the size of the slice proportional to its value.
Strengths: Visually appealing, effectively shows proportions, easy to understand at a glance.
Weaknesses: Difficult to compare small slices, not ideal for many categories, can be misleading if not labeled accurately.
Ideal for: Showing market share, representing the composition of a budget, illustrating the percentage breakdown of a population.
3. Pareto Charts: Combining Bar and Line Charts
Pareto charts combine a bar chart (showing frequency) with a line graph (showing cumulative frequency). This is particularly useful for identifying the most significant categories contributing to a problem or phenomenon (the "vital few").
Strengths: Effectively identifies the most important categories, combines the strengths of bar charts and line graphs, useful for quality control and problem-solving.
Weaknesses: Can be more complex to understand than simple bar or pie charts.
Ideal for: Identifying the major causes of defects in a manufacturing process, analyzing customer complaints, prioritizing tasks based on impact.
Numerical Data Graphs: Displaying Trends and Relationships
Numerical data represents quantitative measurements, such as height, weight, temperature, or time. Several graph types are best suited for numerical data:
1. Line Graphs: Showing Trends Over Time
Line graphs are ideal for displaying trends and changes in numerical data over time or another continuous variable. The data points are connected by lines, revealing the pattern of change.
Strengths: Excellent for showing trends, clearly illustrates changes over time, can display multiple variables on the same graph.
Weaknesses: Can be cluttered with too many data points, may not be suitable for comparing categories.
Ideal for: Showing stock prices over time, tracking temperature changes, visualizing the growth of a population.
2. Scatter Plots: Showing Correlations
Scatter plots display the relationship between two numerical variables. Each point represents a single data point, with its position determined by its values on the two axes. They reveal correlations (positive, negative, or no correlation).
Strengths: Effectively shows correlations between variables, identifies outliers, useful for exploratory data analysis.
Weaknesses: Can be difficult to interpret with many data points, doesn't directly show causality.
Ideal for: Investigating the relationship between income and education level, exploring the correlation between advertising spend and sales, identifying outliers in a dataset.
3. Histograms: Showing Data Distribution
Histograms display the frequency distribution of numerical data. The data is grouped into intervals (bins), and the height of each bar represents the frequency of data points within that interval.
Strengths: Shows the shape of the data distribution, identifies central tendency and spread, useful for understanding the variability of the data.
Weaknesses: The choice of bin size can affect the appearance of the histogram, less effective for comparing specific values.
Ideal for: Showing the distribution of exam scores, analyzing the distribution of income levels, understanding the range and variability of a dataset.
4. Box Plots (Box and Whisker Plots): Summarizing Data Distribution
Box plots provide a concise summary of the data distribution, showing the median, quartiles, and outliers. They are useful for comparing the distribution of data across different groups.
Strengths: Effectively summarizes the data distribution, easily compares distributions across groups, highlights outliers.
Weaknesses: Can be less informative than histograms for detailed analysis of the data distribution.
Ideal for: Comparing the distribution of test scores across different classes, analyzing the variability of income across different demographics, identifying outliers in a dataset.
Combining Graph Types: Enhanced Data Storytelling
In many cases, combining different graph types can enhance the storytelling capabilities of your data visualization. For instance, you might use a bar chart to show overall trends and then use a line graph to highlight specific changes within those trends. This layered approach can create a more nuanced and comprehensive understanding of the data.
Choosing the Right Graph: A Decision Tree Approach
To streamline the process of choosing the appropriate graph, consider using a decision tree approach:
- Identify your data type: Categorical or numerical?
- Determine your objective: Comparison, trend analysis, correlation, distribution analysis?
- Consider your audience: Technical experts or general audience?
Based on these considerations, you can select the most effective graph type.
For instance:
- Categorical data & Comparison: Bar chart or Pie chart
- Numerical data & Trend over time: Line graph
- Numerical data & Correlation: Scatter plot
- Numerical data & Distribution: Histogram or Box plot
Advanced Graphing Techniques and Considerations
Beyond the fundamental graph types, several advanced techniques and considerations can further enhance your data visualizations:
- Multiple axes: Using multiple y-axes can allow you to compare variables with different scales on the same graph. However, use this cautiously as it can sometimes be confusing.
- Data transformations: Transforming your data (e.g., using logarithmic scales) can make certain patterns or trends more apparent.
- Annotations: Adding annotations to your graphs can help to highlight specific data points or trends.
- Color and Aesthetics: Using color effectively can make your graphs more visually appealing and easier to interpret. However, avoid using too many colors, and be mindful of color blindness.
- Interactive Graphs: For digital presentations, consider using interactive graphs that allow users to explore the data in more detail.
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Data Visualization
Selecting the right graph is a crucial aspect of effective data visualization. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of different graph types, and by carefully considering your data, your objective, and your audience, you can create compelling visualizations that effectively communicate your findings. Remember, the goal is to tell a clear and concise story with your data, and the right graph can be the key to unlocking its insights. Continuous practice and exploration of various graphing techniques will ultimately hone your graphing skills and enhance your ability to translate complex data into easily digestible and impactful visual representations.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Welding Principles And Applications 9th Edition Pdf Free Download
Apr 05, 2025
-
Julius Caesar Act 3 Scene 2 Summary
Apr 05, 2025
-
How To Manage Your Checking Account Chapter 8 Lesson 3
Apr 05, 2025
-
Fundamentals Of Applied Electromagnetics 8th Edition
Apr 05, 2025
-
A Means To Guarantee Continuity In Career Development
Apr 05, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Graphing Skill 1 What Type Of Graph Is It . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
