Identify The Range Of The Function Shown In The Graph.
Onlines
Mar 25, 2025 · 5 min read
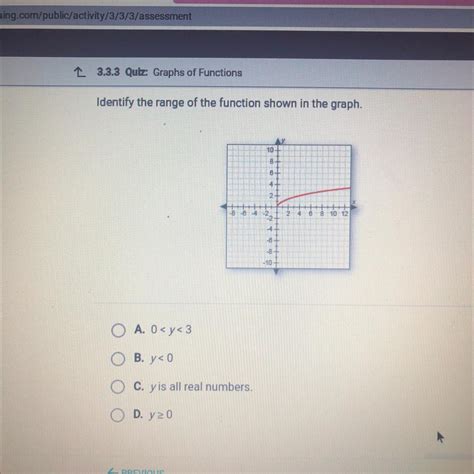
Table of Contents
Identifying the Range of a Function from its Graph
Determining the range of a function is a crucial step in understanding its behavior and properties. The range represents all possible output values (y-values) of the function. While algebraic methods can determine the range, visually inspecting the graph offers a quick and intuitive approach. This article will guide you through various techniques to identify the range of a function depicted graphically, covering different types of functions and complexities. We'll explore strategies for accurately determining the range, even with functions exhibiting asymptotes, discontinuities, or piecewise definitions.
Understanding Range and Function Notation
Before delving into the graphical analysis, let's solidify our understanding of fundamental concepts. A function is a relationship where each input (x-value) corresponds to exactly one output (y-value). The domain of a function comprises all possible input values, while the range encompasses all possible output values. We often represent functions using notation like f(x), g(x), or h(x), where 'x' represents the input and 'f(x)', 'g(x)', or 'h(x)' represents the corresponding output.
For example, if we have the function f(x) = x² + 1, and we input x = 2, the output is f(2) = 2² + 1 = 5. This signifies that 5 is within the range of the function f(x).
Identifying the Range Graphically: A Step-by-Step Guide
The graphical method for identifying the range relies on observing the vertical extent of the function's graph. Here's a step-by-step approach:
-
Examine the Graph: Carefully inspect the entire graph of the function. Pay close attention to the lowest and highest points on the graph, as well as any breaks or discontinuities.
-
Identify Minimum and Maximum Values: Determine the minimum and maximum y-values attained by the function. This might involve finding the lowest point (minimum) and the highest point (maximum) on the graph. For functions that extend infinitely upwards or downwards, you'll indicate this using infinity (∞) or negative infinity (-∞).
-
Consider Asymptotes: Asymptotes are lines that a function approaches but never touches. Horizontal asymptotes indicate limits on the range. If a function has a horizontal asymptote at y = c, then the range will not include c, or it might extend to c but never surpass it.
-
Account for Discontinuities: Discontinuities are breaks or gaps in the graph. These often create intervals within the range that are excluded. Pay close attention to "jumps" in the y-values where the graph is not connected.
-
Express the Range in Interval Notation: Finally, express the range using interval notation. Interval notation provides a concise and standardized method of representing a set of numbers.
- Closed Interval: [a, b] denotes all numbers between a and b, inclusive of a and b.
- Open Interval: (a, b) denotes all numbers between a and b, exclusive of a and b.
- Half-Open Intervals: [a, b) or (a, b] include one endpoint but exclude the other.
- Infinite Intervals: (-∞, a), (a, ∞), (-∞, a], [a, ∞) indicate ranges that extend to infinity.
Examples of Identifying Range Graphically
Let's illustrate the process with specific examples.
Example 1: A Simple Quadratic Function
Imagine a parabola representing the function f(x) = x² - 2. The vertex (lowest point) of this parabola is at (0, -2). The parabola extends infinitely upwards. Therefore, the range is [-2, ∞). This indicates that the y-values range from -2 (inclusive) to positive infinity.
Example 2: A Function with a Horizontal Asymptote
Consider a function with a horizontal asymptote at y = 1. If the graph approaches this asymptote but never reaches it, and the function extends downwards to negative infinity, the range would be (-∞, 1). Note the parenthesis indicating that 1 is not included in the range.
Example 3: A Piecewise Function
Piecewise functions are defined by different expressions across different intervals. For instance:
f(x) = { x², if x ≤ 0 { x + 1, if x > 0
This function would have a range that needs to consider both expressions. The first part, x², would produce y-values from 0 to positive infinity ([0, ∞) as x is less or equal to zero. The second part, x+1, would produce y-values from 1 to positive infinity (1, ∞) because x is greater than 0. Combining these, the total range would be [0, ∞).
Example 4: A Function with a Discontinuity
A function might have a "hole" or a jump discontinuity. Let's say a function has a range from (-∞, 2) and then jumps to (4, ∞). The overall range would be represented as (-∞, 2) ∪ (4, ∞), where '∪' denotes the union of the two intervals.
Advanced Considerations
While the basic approach outlined above covers a wide range of functions, some scenarios require further nuance:
-
Trigonometric Functions: The range of trigonometric functions like sine and cosine is often bounded. For example, sin(x) has a range of [-1, 1], regardless of the x-values.
-
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions: Exponential functions generally have a range of (0, ∞), excluding 0, while logarithmic functions typically have a range of (-∞, ∞). However, transformations can affect these ranges.
-
Functions with Multiple Branches: More complex functions might have multiple distinct parts or branches. Analyzing the range of each branch individually and then combining the results will give you the complete range of the function.
-
Using Calculus: For more complex functions, calculus can be instrumental in finding the minimum and maximum values, critical points, and hence, the range. Techniques involving derivatives can help identify extrema.
Practical Applications and Conclusion
The ability to identify the range of a function is crucial in various fields. In engineering, it helps determine the possible outputs of a system. In economics, it can be used to understand the limits of a model's predictions. In computer science, it helps define the boundaries of data sets.
Mastering the graphical method of determining the range enhances your understanding of function behavior and provides a valuable skill for solving problems in diverse applications. By systematically analyzing the graph, considering asymptotes, discontinuities, and using interval notation, you can accurately and efficiently identify the range of functions, regardless of their complexity. Remember to always practice and explore different types of functions to solidify your understanding. This approach allows for a quick, visual interpretation, saving time and offering a valuable insight into the function's behavior, particularly when algebraic methods might prove more cumbersome.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Emerging Technologies In Cybersecurity C844
Mar 26, 2025
-
The Book Of The City Of Ladies Summary
Mar 26, 2025
-
Quotes From It By Stephen King
Mar 26, 2025
-
A Primary Care Physician Performs A Chest X Ray
Mar 26, 2025
-
Bohr Model Worksheet Answer Key Pdf
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Identify The Range Of The Function Shown In The Graph. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
