Is Possible To Ping 8.8.8.8 Using Cisco Cml2
Onlines
Mar 13, 2025 · 6 min read
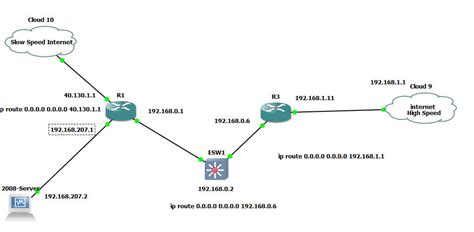
Table of Contents
Is it Possible to Ping 8.8.8.8 Using Cisco CML2? A Comprehensive Guide
The question of whether you can ping Google's public DNS server, 8.8.8.8, using Cisco Modeling Labs 2 (CML2) is a common one for network engineers and students alike. The answer is a resounding yes, but the process involves understanding the underlying network configuration within the CML2 environment. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the steps, troubleshooting common issues, and exploring the implications for network simulation and learning.
Understanding the Components: CML2 and Network Simulation
Before diving into the ping command, let's establish a foundational understanding of the key components involved:
Cisco Modeling Labs 2 (CML2): A Virtual Networking Sandbox
CML2 is a powerful network simulation tool that allows you to create and configure virtual networks using Cisco IOS images. This provides a safe and controlled environment to practice network administration, troubleshooting, and experimentation without the risk of impacting live networks. It's crucial to remember that CML2 is a virtual environment; the behavior of your simulated network reflects the configurations you apply, not the real-world limitations of physical hardware.
8.8.8.8: Google's Public DNS Server
This is a publicly accessible DNS server operated by Google. It's used to translate domain names (like www.google.com) into their corresponding IP addresses. Being able to successfully ping 8.8.8.8 indicates that your simulated network has appropriate connectivity to the internet (or, more accurately, to Google's network infrastructure).
The Ping Command: A Basic Network Diagnostic Tool
The ping command sends ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) echo requests to a specified IP address. A successful ping receives ICMP echo replies, confirming network connectivity. In the context of CML2, successfully pinging 8.8.8.8 demonstrates that your virtual router has a route to the internet and that ICMP traffic is permitted.
Setting up the CML2 Environment for a Successful Ping
To successfully ping 8.8.8.8 in CML2, you need to configure several key aspects of your simulated network:
1. Creating the Virtual Network
Begin by creating a new topology in CML2. You'll need at least one router (e.g., a Cisco IOSvL2 image). This router will act as your gateway to the internet.
2. Configuring the Router Interface
The router interface connected to the "internet" within CML2 needs a specific configuration:
- IP Address: Assign a valid IP address to the interface. This could be a public IP address (although not strictly required for this example, as we'll use NAT), or a private IP address within a suitable range (e.g., 192.168.1.1/24).
- Subnet Mask: Use the appropriate subnet mask for your chosen IP address (e.g., 255.255.255.0 for a /24 subnet).
- Default Gateway: This is crucial. This setting determines where packets destined for networks other than the directly connected network are sent. For this example, we'll configure NAT (Network Address Translation) allowing traffic to access the internet without requiring a publicly routable IP address.
3. Configuring Network Address Translation (NAT)
NAT is essential for successfully pinging external addresses, unless your simulated CML2 environment is configured to utilize a publicly routable IP. The process differs depending on the Cisco IOS version. However, a common approach involves using NAT inside source static translation to translate the internal private address of your device to a public IP address. The exact commands vary but will involve configuration within the router's interface.
4. Configuring the Client Device
You'll need a client device (e.g., a virtual PC or IOSv) connected to the router. This device will initiate the ping command. Ensure this device has an IP address within the same subnet as the router's interface.
5. Executing the Ping Command
Connect to the client device via the CML2 console or SSH and use the ping command:
ping 8.8.8.8
You should see replies from 8.8.8.8 if your configuration is correct. If not, proceed to the troubleshooting section.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
If the ping fails, several factors could be responsible:
1. Incorrect Interface Configuration
Double-check the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway of both the router and client interfaces. A single typo can prevent connectivity. Ensure the router interface uses appropriate IP addresses that are within the same subnet as the client PC interface.
2. NAT Misconfiguration
Incorrectly configured NAT is a frequent source of problems. Review your NAT statements carefully, ensuring they correctly map your private IP addresses to the public address space (or appropriately configured virtual environment).
3. ICMP Filtering
Firewalls or access control lists (ACLs) on the router might be blocking ICMP echo requests (ping). Verify that ICMP is permitted between the client and the internet. You may need to explicitly permit ICMP traffic through appropriate ACLs on your CML2 router.
4. Connectivity Issues within CML2
In some instances, problems might lie within the CML2 environment itself. Ensure the CML2 virtual machine has sufficient resources and that the network configuration within CML2 is appropriately simulating a realistic networking scenario.
5. Internet Access in the Host Machine
The CML2 environment requires network access on the host machine to reach the internet. Verify that the host machine hosting the CML2 application has adequate internet connectivity, as CML2 will leverage the host machine's internet connection.
Advanced Configurations and Considerations
Beyond the basic ping, several advanced considerations enhance the simulation:
Using Traceroute
Instead of just ping, use traceroute (or tracert on Windows) to trace the path packets take to 8.8.8.8. This provides insights into potential bottlenecks or network issues along the route.
Incorporating Multiple Routers
Create more complex topologies with multiple routers. This allows you to practice routing protocols and advanced network concepts, testing your ability to establish connectivity across a larger simulated network.
Implementing Security Measures
Integrate firewalls and ACLs to explore network security. Observe how these mechanisms impact your ability to ping 8.8.8.8, solidifying your understanding of security best practices.
Using Different DNS Servers
Instead of 8.8.8.8, try pinging other public DNS servers, like 1.1.1.1 (Cloudflare), to test wider connectivity.
Conclusion: Mastering Network Simulation with CML2
Successfully pinging 8.8.8.8 in CML2 is a foundational step in mastering network simulation. While the process involves several configuration steps, understanding these steps provides invaluable knowledge of networking fundamentals and practical troubleshooting skills. By incorporating the advanced configurations and troubleshooting techniques outlined in this guide, you can effectively utilize CML2 for comprehensive network simulations and enhance your understanding of network operations in a controlled and safe virtual environment. Remember to always thoroughly review your configurations and pay close attention to detail. Even seemingly minor errors can significantly affect your ability to connect your virtual devices to external networks.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Statements Regarding Anaphylaxis Is Correct
Mar 13, 2025
-
Water Water Everywhere But Please Dont Give Iv Answer Key
Mar 13, 2025
-
Functions And Slope Quick Check Answer Key
Mar 13, 2025
-
What Process Occurs In Structure H
Mar 13, 2025
-
Stacey Lloyd 2014 Ethos Pathos Logos Answer Key
Mar 13, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Possible To Ping 8.8.8.8 Using Cisco Cml2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
