Which Of The Following Statements Regarding Anaphylaxis Is Correct
Onlines
Mar 13, 2025 · 5 min read
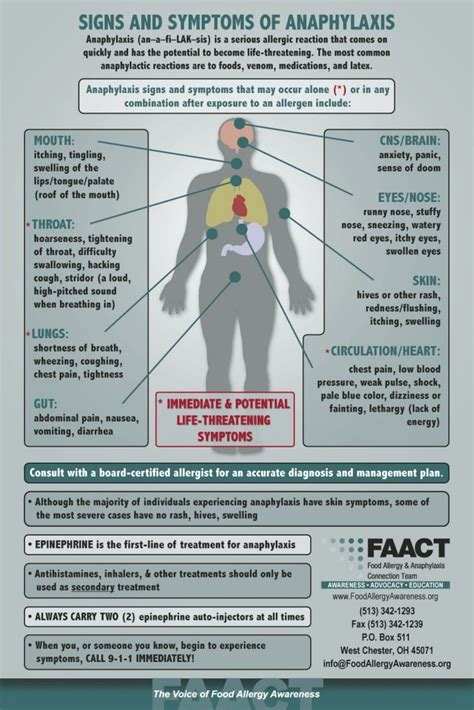
Table of Contents
Which of the Following Statements Regarding Anaphylaxis is Correct? A Deep Dive into Allergic Reactions
Anaphylaxis is a severe, potentially life-threatening allergic reaction that requires immediate medical attention. Understanding the nuances of anaphylaxis is crucial for both healthcare professionals and the general public. This article aims to clarify common misconceptions surrounding anaphylaxis by examining several statements and determining their accuracy. We'll explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of this serious condition.
Understanding Anaphylaxis: A Complex Allergic Reaction
Before delving into specific statements, let's establish a foundational understanding of anaphylaxis. It's a systemic, rapid-onset allergic reaction mediated by the release of immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies. This release triggers a cascade of events that lead to widespread vasodilation, bronchoconstriction, and increased vascular permeability. This, in turn, causes a drop in blood pressure, difficulty breathing, and swelling.
Key characteristics of anaphylaxis include:
- Rapid onset: Symptoms typically appear within minutes to hours of exposure to the allergen.
- Systemic involvement: Multiple organ systems are affected, including the respiratory, cardiovascular, and integumentary systems.
- Life-threatening potential: If left untreated, anaphylaxis can lead to cardiovascular collapse, respiratory arrest, and death.
- Variable presentation: Symptoms can vary widely between individuals and even within the same individual across different episodes.
Debunking Myths and Clarifying Facts: Analyzing Statements on Anaphylaxis
Now, let's analyze some common statements about anaphylaxis to determine their correctness:
Statement 1: "Anaphylaxis is always triggered by insect stings or food allergies."
Incorrect. While insect stings (particularly bee, wasp, hornet, and ant stings) and food allergies (such as peanuts, tree nuts, shellfish, milk, eggs, soy, and wheat) are common triggers, anaphylaxis can be triggered by a wide range of substances. These include:
- Medications: Penicillin and other antibiotics, NSAIDs, contrast dyes used in medical imaging.
- Latex: Exposure to latex products, such as gloves or balloons.
- Exercise: In some individuals, exercise can trigger anaphylaxis, especially in combination with certain foods or medications.
- Idiopathic anaphylaxis: In some cases, the trigger for anaphylaxis remains unidentified.
- Vaccines: Though rare, vaccines can rarely trigger anaphylaxis.
Statement 2: "Skin reactions, such as hives, are always indicative of anaphylaxis."
Incorrect. While hives (urticaria) are a common symptom of anaphylaxis, their presence alone does not confirm a diagnosis. Anaphylaxis can occur without any visible skin manifestations. Furthermore, many other conditions can cause hives without being life-threatening. The key is the combination of symptoms and the severity of the reaction.
Statement 3: "Difficulty breathing is the most common symptom of anaphylaxis."
Incorrect. While difficulty breathing (dyspnea), wheezing, and shortness of breath are significant symptoms of anaphylaxis, they are not always the most prominent initial symptom. Other symptoms can precede respiratory distress, including:
- Sudden onset of itching or tingling: Especially around the mouth, throat, or tongue.
- Swelling: Of the face, lips, tongue, or throat (angioedema).
- Rapid pulse: Reflecting the body's attempt to compensate for low blood pressure.
- Lightheadedness or dizziness: Due to decreased blood pressure.
- Nausea and vomiting: Gastrointestinal symptoms can also be prominent.
- Hypotension: A drop in blood pressure is a hallmark of anaphylaxis.
Statement 4: "An epinephrine injection is the only effective treatment for anaphylaxis."
Incorrect. While epinephrine is the first-line and most crucial treatment for anaphylaxis, it's not the only intervention. Supportive care is essential and may include:
- Oxygen therapy: To improve oxygen saturation.
- Intravenous fluids: To restore blood pressure.
- Bronchodilators: Such as albuterol, to relieve bronchospasm.
- Antihistamines: To reduce inflammation.
- Corticosteroids: To reduce inflammation and prevent late-phase reactions.
Statement 5: "If symptoms improve after epinephrine injection, the individual is out of danger."
Incorrect. While epinephrine is life-saving, its effects are temporary. Symptoms can recur, and individuals need to be closely monitored for at least several hours after an episode. A second dose of epinephrine may be necessary, and further treatment, including hospitalization, might be required.
Statement 6: "Anaphylaxis is always fatal."
Incorrect. Anaphylaxis is potentially life-threatening, but it is not always fatal. With prompt recognition of symptoms, administration of epinephrine, and appropriate supportive care, the prognosis is generally good. However, delays in treatment can be fatal.
Statement 7: "Everyone with a history of allergic reactions will experience anaphylaxis."
Incorrect. Having a history of allergic reactions does not guarantee the development of anaphylaxis. Many individuals experience mild allergic reactions without ever progressing to anaphylaxis. However, a history of allergic reactions significantly increases the risk of anaphylaxis.
Statement 8: "Anaphylaxis can only happen once."
Incorrect. Anaphylaxis can recur in individuals with a history of the condition. Subsequent episodes can be triggered by the same allergen or a different one. The severity of subsequent episodes can vary.
Prevention and Management of Anaphylaxis: A Proactive Approach
Preventing anaphylaxis involves identifying and avoiding triggers. This might necessitate carrying an epinephrine auto-injector (like an EpiPen or Auvi-Q), adhering to a strict avoidance diet, or wearing medical alert jewelry. Regular consultations with an allergist-immunologist are vital for personalized management plans.
Key preventive measures include:
- Allergen identification: Through skin testing or blood tests.
- Allergen avoidance: Careful attention to diet, medications, and environmental exposures.
- Epinephrine auto-injector training: Proper training on the use of epinephrine auto-injectors is crucial.
- Emergency action plan: Developing a detailed plan for managing anaphylaxis episodes, including contacting emergency medical services.
- Medical alert bracelet or necklace: Clearly indicating allergies and need for epinephrine.
Conclusion: Navigating the Complexities of Anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis is a serious medical condition demanding prompt recognition, appropriate treatment, and careful prevention. This article highlights the critical importance of dispelling myths and emphasizing the accurate understanding of anaphylaxis. Individuals with a history of allergies should work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized prevention and management plan. Early intervention with epinephrine remains the cornerstone of treatment, potentially saving lives. Remember, seeking immediate medical attention is crucial if anaphylaxis is suspected.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Food Handler Misses Work Because A Roommate
Mar 13, 2025
-
Calculus Early Transcendentals 8th Edition Answers
Mar 13, 2025
-
Correctly Label The Following Anatomical Features Of The Cerebellum
Mar 13, 2025
-
The Crucible Act 1 Puritan Problems Answer Key
Mar 13, 2025
-
Nihss Group D Answers 2023 Pdf
Mar 13, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Statements Regarding Anaphylaxis Is Correct . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
