L-dopa Is Used To Treat _____.
Onlines
Mar 13, 2025 · 6 min read
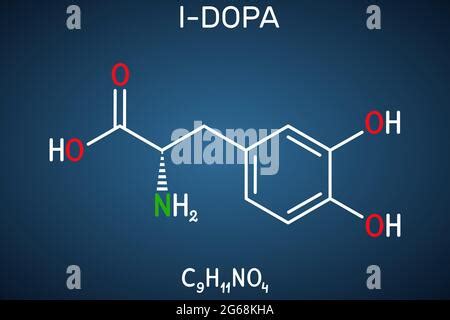
Table of Contents
L-Dopa is Used to Treat Parkinson's Disease and Other Movement Disorders
L-dopa, short for L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine, is a medication primarily used to treat the symptoms of Parkinson's disease. It's a crucial element in managing this debilitating neurological condition, significantly improving the quality of life for millions worldwide. However, its applications extend beyond Parkinson's, playing a role in treating other movement disorders as well. Understanding its mechanism of action, therapeutic benefits, side effects, and ongoing research is crucial for both patients and healthcare professionals.
Understanding Parkinson's Disease and the Role of Dopamine
Parkinson's disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the deterioration of dopamine-producing neurons in a specific area of the brain called the substantia nigra. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter responsible for smooth, coordinated muscle movements. Its depletion leads to the hallmark motor symptoms of Parkinson's:
- Tremor: Involuntary shaking, often starting in one limb.
- Rigidity: Stiffness and resistance to movement in the limbs and trunk.
- Bradykinesia: Slowness of movement.
- Postural instability: Difficulty with balance and coordination, increasing the risk of falls.
Beyond motor symptoms, Parkinson's can also manifest non-motor symptoms like sleep disturbances, depression, cognitive impairment, and constipation.
L-dopa works by replenishing the brain's depleted dopamine levels. However, it doesn't directly act as dopamine. Instead, it's a precursor to dopamine, meaning the body converts L-dopa into dopamine. This conversion primarily occurs in the brain, maximizing its therapeutic impact while minimizing systemic side effects.
How L-Dopa Works: A Detailed Look at its Mechanism
The effectiveness of L-dopa relies on its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier, a protective layer separating the bloodstream from the brain. Once inside the brain, it's converted to dopamine by the enzyme aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase (AADC). This newly synthesized dopamine then interacts with dopamine receptors in the brain, helping restore the balance of neurotransmission and alleviate Parkinson's symptoms.
However, this process isn't entirely efficient. A significant portion of L-dopa is converted to dopamine before crossing the blood-brain barrier, leading to peripheral side effects. To counteract this, L-dopa is often administered in combination with a decarboxylase inhibitor, such as carbidopa or benserazide. These inhibitors block the peripheral conversion of L-dopa to dopamine, ensuring more of the drug reaches the brain and reducing side effects.
Therapeutic Benefits and Effectiveness of L-Dopa
L-dopa offers substantial therapeutic benefits for individuals with Parkinson's disease, primarily improving motor function. Studies have consistently shown its effectiveness in:
- Reducing tremor, rigidity, and bradykinesia: L-dopa significantly improves motor control, allowing patients to perform daily tasks more easily.
- Improving balance and coordination: This reduction in postural instability minimizes the risk of falls and improves mobility.
- Enhancing quality of life: By alleviating motor symptoms and improving daily functioning, L-dopa significantly contributes to a better quality of life for Parkinson's patients.
However, it's crucial to note that L-dopa is not a cure for Parkinson's disease. It only treats the symptoms, and its effectiveness can diminish over time, requiring adjustments in dosage or the addition of other medications. The development of motor fluctuations and dyskinesias (involuntary movements) is a common occurrence with long-term L-dopa use.
Side Effects and Management
While L-dopa offers significant benefits, it's associated with several side effects, some mild and others more severe. Common side effects include:
- Nausea and vomiting: These are often experienced early in treatment and can be managed with antiemetic medications.
- Dizziness and lightheadedness: Patients should be cautious when changing positions to avoid falls.
- Orthostatic hypotension: A sudden drop in blood pressure upon standing, leading to dizziness and fainting.
- Sleep disturbances: Insomnia or vivid dreams are common.
- Hallucinations and psychosis: These are more common in older patients or those on higher doses.
- Impulse control disorders: These can include compulsive gambling, shopping, or sexual behavior.
- Dyskinesias: Involuntary movements, often appearing as twisting or writhing, typically develop with prolonged use.
- "On-off" fluctuations: Periods of good motor control ("on" time) alternating with periods of poor motor control ("off" time).
Managing these side effects is crucial for maximizing the therapeutic benefits of L-dopa while minimizing discomfort. Adjusting the dosage, changing the administration schedule, or adding other medications can often alleviate many side effects.
L-Dopa in Other Movement Disorders
While predominantly used for Parkinson's disease, L-dopa's application extends to other movement disorders, although its efficacy varies considerably depending on the specific condition. These include:
- Secondary Parkinsonism: This refers to Parkinson's-like symptoms caused by other neurological conditions or medications. L-dopa may provide some symptom relief in these cases.
- Progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP): A rare neurodegenerative disorder affecting eye movements and balance. L-dopa may offer modest benefits in some patients, but its effects are generally less pronounced than in Parkinson's disease.
- Multiple system atrophy (MSA): Another rare neurological disorder characterized by a combination of Parkinsonian and cerebellar symptoms. L-dopa's benefit is limited and often temporary.
- Dopamine-responsive dystonia: A rare inherited movement disorder characterized by muscle spasms and dystonia. L-dopa can be highly effective in these cases.
Ongoing Research and Future Directions
Research on L-dopa continues to evolve, focusing on several key areas:
- Improved drug delivery systems: Developing more effective ways to deliver L-dopa to the brain, potentially reducing side effects and improving efficacy. This includes exploring novel drug formulations and advanced drug delivery methods like implantable pumps.
- Combination therapies: Investigating the synergistic effects of combining L-dopa with other medications to enhance its therapeutic benefits and delay the onset of motor fluctuations and dyskinesias.
- Neuroprotective strategies: Exploring the potential of L-dopa or related compounds to protect dopamine neurons from further degeneration. This is a significant area of research with the potential to slow the progression of Parkinson's disease.
- Understanding the mechanisms of L-dopa-induced dyskinesias: Further research is crucial to understand the underlying mechanisms causing dyskinesias and develop strategies to prevent or mitigate this common side effect.
Conclusion: L-Dopa—A Cornerstone in Movement Disorder Management
L-dopa remains a cornerstone in the treatment of Parkinson's disease and certain other movement disorders. Its ability to effectively alleviate motor symptoms significantly improves the quality of life for many patients. However, it's crucial to understand its limitations, side effects, and potential interactions with other medications. Close monitoring by healthcare professionals is essential to optimize treatment, manage side effects, and ensure the best possible outcomes for individuals living with these conditions. Ongoing research continues to refine L-dopa's use and explore novel therapeutic strategies to enhance its effectiveness and improve the lives of those affected by movement disorders. The future holds promise for advancements that will further optimize the use of L-dopa and potentially delay or even prevent the progression of neurodegenerative diseases.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Beauty Professionals Are Permitted And Encouraged To
Mar 14, 2025
-
How Is The Gold Van Violating The Uniform Traffic Law
Mar 14, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Best Describes A Honeypot
Mar 14, 2025
-
El Futbol En Europa Es Muy Similar Al Futbol Americano
Mar 14, 2025
-
Sinners In The Hands Of An Angry God Quotes
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about L-dopa Is Used To Treat _____. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
