Monomers And Polymers Worksheet Option 1 Answer Key
Onlines
Mar 27, 2025 · 6 min read
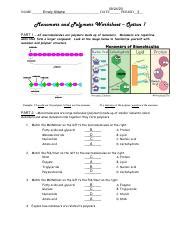
Table of Contents
Monomers and Polymers Worksheet: Option 1 Answer Key & Comprehensive Guide
This comprehensive guide provides answers and in-depth explanations for a hypothetical "Monomers and Polymers Worksheet, Option 1." Since I don't have access to a specific worksheet titled "Option 1," this guide will cover the key concepts of monomers and polymers, providing example questions and answers that align with typical worksheet content at various educational levels. This will ensure you have a solid understanding, regardless of the specific worksheet you're working on. Remember to always refer to your specific worksheet for the most accurate answers.
Understanding Monomers and Polymers: The Building Blocks of Matter
Before diving into the answers, let's solidify our understanding of monomers and polymers. This foundational knowledge is crucial for correctly answering any worksheet questions on this topic.
Monomers: These are small, simple molecules that act as the basic building blocks for larger molecules. Think of them as individual LEGO bricks. They possess reactive sites, allowing them to bond with other monomers. Examples include:
- Glucose: A simple sugar, a monomer of starch and cellulose.
- Amino acids: The building blocks of proteins.
- Nucleotides: The monomers that make up DNA and RNA.
- Ethylene: A simple hydrocarbon monomer that forms polyethylene.
Polymers: These are large molecules composed of many repeating monomer units linked together. Imagine connecting numerous LEGO bricks to create a complex structure. The properties of a polymer are often significantly different from its constituent monomers. For example, individual glucose molecules are sweet and soluble, while the polymer cellulose (made of glucose) is insoluble and forms the structural component of plant cell walls.
Polymerization: This is the process of joining monomers together to form a polymer. This process often involves the removal of a small molecule, like water (dehydration synthesis), or the addition of monomers directly (addition polymerization).
Worksheet Question Examples & Answer Key (Option 1 – Hypothetical)
This section presents example questions that typically appear in a monomers and polymers worksheet, along with detailed answers and explanations. These examples cover a broad range of difficulty, mimicking what you might encounter.
Section 1: Identifying Monomers and Polymers
Question 1: Identify the monomer(s) for each of the following polymers:
- (a) Starch:
- (b) Protein:
- (c) DNA:
- (d) Polyethylene:
Answer 1:
- (a) Starch: Glucose
- (b) Protein: Amino acids
- (c) DNA: Nucleotides (specifically, deoxyribonucleotides)
- (d) Polyethylene: Ethylene
Question 2: Which of the following is a polymer?
(a) Glucose (b) Amino acid (c) Cellulose (d) Ethylene
Answer 2: (c) Cellulose. Cellulose is a polymer made of many glucose monomers linked together. Glucose, amino acids, and ethylene are all monomers.
Section 2: Types of Polymerization
Question 3: Explain the difference between addition polymerization and condensation polymerization (dehydration synthesis). Give an example of each.
Answer 3:
-
Addition Polymerization: Monomers directly add to each other to form a polymer without the loss of any atoms. The double or triple bonds in the monomers break, allowing them to form new single bonds with adjacent monomers. Example: The formation of polyethylene from ethylene monomers. Each ethylene molecule (CH2=CH2) opens its double bond to create single bonds with other ethylene molecules, forming a long chain.
-
Condensation Polymerization (Dehydration Synthesis): Monomers join together with the removal of a small molecule, usually water. This often involves functional groups on the monomers reacting, such as hydroxyl (-OH) and carboxyl (-COOH) groups. Example: The formation of a peptide bond between amino acids in protein synthesis. A water molecule is removed as the carboxyl group of one amino acid reacts with the amino group of another.
Section 3: Properties and Applications of Polymers
Question 4: Describe two properties of polymers that make them suitable for use in packaging materials.
Answer 4:
-
Flexibility: Many polymers are flexible, allowing them to be molded into various shapes and sizes for packaging. This is crucial for creating containers and films that can conform to the product being packaged.
-
Impermeability: Certain polymers are impermeable to gases and liquids, protecting the packaged contents from moisture, oxygen, and other environmental factors. This is essential for maintaining product quality and extending shelf life.
Question 5: Name three different types of polymers and their common uses.
Answer 5:
- Polyethylene (PE): Used in plastic bags, films, bottles, and containers due to its flexibility and low cost.
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC): Used in pipes, flooring, and window frames due to its durability and resistance to chemicals.
- Polypropylene (PP): Used in food containers, textiles, and automotive parts because it is strong, lightweight, and resistant to heat.
Section 4: Advanced Concepts (for higher-level worksheets)
Question 6: Explain the concept of polymer degradation and its environmental implications.
Answer 6: Polymer degradation is the breakdown of polymers into smaller molecules. This can occur naturally through processes like oxidation and hydrolysis, or it can be accelerated through exposure to heat, light, or microbial action. The environmental implications are significant because many synthetic polymers are non-biodegradable or degrade very slowly. This leads to the accumulation of plastic waste in landfills and the environment, causing pollution and harming ecosystems. Research into biodegradable polymers and effective recycling methods is crucial to address these issues.
Question 7: What is a copolymer? Give an example.
Answer 7: A copolymer is a polymer derived from more than one species of monomer. The monomers are incorporated into the polymer chain in various ways, depending on the polymerization conditions and the specific monomers involved. Example: Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), a common type of synthetic rubber, is a copolymer of styrene and butadiene monomers.
Question 8: Describe the relationship between the structure of a polymer and its properties.
Answer 8: The structure of a polymer, including the type of monomers, the arrangement of monomers in the chain (linear, branched, cross-linked), and the presence of functional groups, directly impacts its properties. For instance:
- Linear polymers: Tend to be more flexible.
- Branched polymers: Can be less dense and more flexible.
- Cross-linked polymers: Are generally stronger and more rigid.
- Crystalline polymers: Tend to be harder, stronger, and more resistant to solvents.
- Amorphous polymers: Tend to be more flexible and transparent. The presence of specific functional groups can also influence properties like reactivity, water absorption, and melting point.
Conclusion: Mastering Monomers and Polymers
This comprehensive guide provides a solid foundation for understanding monomers and polymers. By reviewing the key concepts and working through the example questions and answers, you'll be well-prepared to tackle any monomers and polymers worksheet. Remember to always consult your specific worksheet for accurate answers and adapt your learning to the specific material presented. Understanding the relationship between monomers, polymers, and their properties is essential in various scientific fields, from materials science and chemistry to biology and environmental science. Continued learning and exploration of this topic will undoubtedly enrich your scientific understanding.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Edulastic Formative And Summative Assessments Made Easy Answer Key
Mar 30, 2025
-
Mary Is A Department Of The Navy Employee
Mar 30, 2025
-
James Bond In A Honda Answer Key
Mar 30, 2025
-
Ready Player One How Many Chapters
Mar 30, 2025
-
Identifying Transformations Worksheet Homework 5 Answer Key
Mar 30, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Monomers And Polymers Worksheet Option 1 Answer Key . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
