Oste O Chondr Itis Is An Example Of A
Onlines
Mar 25, 2025 · 7 min read
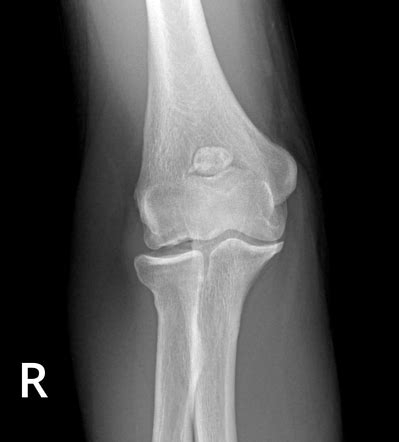
Table of Contents
Osteochondritis Dissecans: An Example of a Degenerative Joint Condition
Osteochondritis dissecans (OCD) serves as a prime example of a degenerative joint condition, specifically affecting the articular cartilage and underlying bone. This condition, while relatively uncommon, can significantly impact the lives of those affected, particularly athletes and young adults. Understanding its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment is crucial for effective management and improved patient outcomes. This comprehensive article will delve into the complexities of OCD, exploring its various facets and highlighting its significance as a model for understanding other degenerative joint disorders.
What is Osteochondritis Dissecans?
Osteochondritis dissecans is a condition characterized by the separation of a piece of articular cartilage and underlying bone from the rest of the bone. This separation, or lesion, typically occurs in weight-bearing joints such as the knee, ankle, elbow, and hip. The affected area becomes avascular (lacks blood supply), leading to further degeneration and potential detachment of the bone fragment. The exact cause of OCD remains unclear, but several factors are believed to contribute to its development.
Understanding the Pathophysiology of OCD
The precise mechanisms underlying OCD are still being investigated, but the prevailing theory centers on a disruption in the blood supply to the subchondral bone. This disruption can result from repetitive microtrauma, genetic predispositions, or a combination of factors. The subsequent avascular necrosis (bone death) leads to weakening of the bone-cartilage interface, increasing the susceptibility to separation and fragmentation. The process typically unfolds in stages:
-
Stage 1: Incipient Stage: This initial stage involves subtle changes within the subchondral bone, characterized by subtle softening and potential cystic changes. Clinical symptoms may be minimal or absent at this stage.
-
Stage 2: Stable Stage: A clear lesion is evident on imaging studies, but the bone fragment remains firmly attached to the underlying bone. Symptoms may vary depending on the location and size of the lesion.
-
Stage 3: Unstable Stage: The bone fragment is partially detached, and symptoms can become more pronounced. Pain, swelling, and locking of the joint may occur.
-
Stage 4: Detached Stage: The bone fragment is completely separated and may be loose within the joint. This stage often requires surgical intervention.
Risk Factors Associated with Osteochondritis Dissecans
Several factors increase the risk of developing OCD. These include:
-
Age and Sex: OCD most commonly affects adolescents during growth spurts, typically between the ages of 10 and 16 years. Males are more frequently affected than females.
-
Genetics: A family history of OCD can increase an individual's susceptibility.
-
Repetitive Stress: Repeated stress on the affected joint, particularly in sports activities like basketball, football, and gymnastics, plays a significant role. Rapid growth spurts can also exacerbate the stress on developing bones and joints.
-
Trauma: Acute trauma, such as a direct blow or a twisting injury, can also contribute to the development of OCD.
-
Underlying Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease (a condition affecting the hip joint), may increase the risk of developing OCD.
Clinical Presentation of Osteochondritis Dissecans
The clinical presentation of OCD varies depending on the location, size, and stage of the lesion. Common symptoms include:
-
Pain: Pain is often the most prominent symptom, typically localized to the affected joint. The pain may be intermittent or constant, and its severity can vary depending on activity levels.
-
Swelling: Swelling around the joint is common, especially during periods of inflammation or after activity.
-
Joint Locking or Giving Way: In more advanced stages, the loose bone fragment can interfere with normal joint mechanics, causing the joint to lock or give way unexpectedly.
-
Limited Range of Motion: Restricted movement in the affected joint may be present due to pain or the presence of a loose bone fragment.
-
Stiffness: Joint stiffness may be experienced, particularly after periods of inactivity.
Diagnostic Methods for Osteochondritis Dissecans
Accurate diagnosis of OCD is crucial for effective management. Several diagnostic methods are employed:
-
Physical Examination: A thorough physical examination by a physician or orthopedic specialist is the first step in the diagnostic process. This will involve assessing the patient's symptoms, range of motion, and any signs of instability.
-
Imaging Studies: Imaging studies are essential for confirming the diagnosis and evaluating the extent of the lesion. These commonly include:
-
X-rays: X-rays can reveal the presence of a bone fragment and assess the integrity of the articular cartilage. They may not always be definitive in the early stages of OCD.
-
MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) provides detailed images of the bone and cartilage, allowing for a more precise assessment of the lesion's size, location, and stability. MRI is considered the gold standard for diagnosing OCD.
-
CT scan: Computed tomography (CT) scans may be used in certain cases to provide additional information about the bone fragment and its relationship to the surrounding structures.
-
-
Arthroscopy: Arthroscopy, a minimally invasive surgical procedure, involves inserting a small camera into the joint. This allows for direct visualization of the lesion and assessment of its stability. Arthroscopy can also be used to perform certain treatment procedures.
Treatment Options for Osteochondritis Dissecans
Treatment for OCD depends on several factors, including the patient's age, the size and location of the lesion, and the stability of the bone fragment. Treatment options range from conservative measures to surgical intervention.
Conservative Management
Conservative management is often the initial approach, especially in patients with stable lesions and minimal symptoms. This typically includes:
-
Rest and Activity Modification: Avoiding activities that stress the affected joint is crucial to allow for healing.
-
Physical Therapy: Physical therapy plays a vital role in strengthening the muscles surrounding the joint, improving joint stability, and restoring normal range of motion.
-
Pain Management: Pain medication, such as over-the-counter analgesics or prescription pain relievers, may be necessary to manage pain and inflammation.
-
Bracing or Immobilization: In some cases, a brace or splint may be used to immobilize the joint and protect it from further injury.
Surgical Intervention
Surgical intervention may be necessary if conservative management fails, the lesion is unstable, or the bone fragment is detached. Surgical options include:
-
Arthroscopic Surgery: Arthroscopic surgery is a minimally invasive procedure that can be used to remove loose bone fragments, stimulate bone healing, or perform other procedures to improve joint stability.
-
Open Surgery: Open surgery may be required in cases of large or unstable lesions. This approach allows for more extensive procedures such as bone grafting or fixation of the bone fragment.
Prognosis and Long-Term Outcomes of Osteochondritis Dissecans
The prognosis for OCD varies depending on several factors, including the size and location of the lesion, the patient's age, and the effectiveness of treatment. With early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, many individuals can achieve excellent outcomes with minimal long-term limitations. However, in some cases, OCD can lead to chronic pain, joint instability, and the development of osteoarthritis. Regular follow-up care and adherence to the recommended treatment plan are crucial for optimizing outcomes.
Osteochondritis Dissecans: A Model for Degenerative Joint Disease
Osteochondritis dissecans serves as a valuable model for understanding broader degenerative joint conditions. Its pathophysiology, involving avascular necrosis and cartilage damage, mirrors processes observed in osteoarthritis and other joint disorders. Studying OCD provides insights into the underlying mechanisms of cartilage degeneration and bone remodeling. This knowledge informs research into potential therapies for a wider range of joint diseases. The focus on blood supply disruption in OCD highlights the importance of vascular health in maintaining joint integrity. This is a common theme in many degenerative joint conditions.
Conclusion: Understanding and Managing Osteochondritis Dissecans
Osteochondritis dissecans is a significant musculoskeletal condition that can affect individuals of various ages, particularly young athletes. Understanding its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment is crucial for effective management and improved patient outcomes. The condition's pathophysiology, characterized by avascular necrosis and cartilage damage, provides insights into broader degenerative joint diseases, making it a valuable model for research and development of new therapies. Through early diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and ongoing management, many individuals with OCD can achieve a good prognosis and maintain an active lifestyle. The importance of early detection and conservative measures cannot be overstated, as early intervention significantly improves the chance of successful outcomes. Continued research into the specific mechanisms underlying OCD will undoubtedly enhance our ability to prevent, diagnose, and treat this challenging musculoskeletal condition, contributing to improved understanding and management of a wider spectrum of degenerative joint diseases.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Intentionally Doing Things That Negatively Affect
Mar 25, 2025
-
Anaphylaxis Is Most Accurately Defined As An
Mar 25, 2025
-
Symbols In Dr Jekyll And Mr Hyde
Mar 25, 2025
-
Using Flattery To Influence Another Person Is A
Mar 25, 2025
-
Ap Lit Unit 5 Progress Check Mcq
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Oste O Chondr Itis Is An Example Of A . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
