Punnett Square Practice All About Dogs Answer Key
Onlines
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
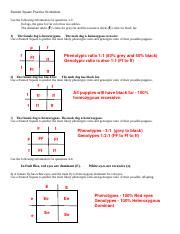
Table of Contents
Punnett Square Practice: All About Dogs – Answer Key & Beyond
Understanding genetics is crucial for responsible dog breeding and ownership. The Punnett square is a fundamental tool used in genetics to predict the probability of offspring inheriting specific traits. This comprehensive guide provides numerous Punnett square practice problems focused on canine genetics, along with detailed answer keys and explanations. We'll explore various dog traits, from coat color to size, and delve into the complexities of inheritance patterns. This resource is perfect for students, breeders, or anyone fascinated by canine genetics.
Understanding Basic Genetics Terminology
Before diving into Punnett squares, let's refresh some key genetic terms:
- Gene: A unit of heredity that determines a specific trait.
- Allele: Different forms of a gene (e.g., the allele for black coat color vs. the allele for brown coat color).
- Genotype: The genetic makeup of an organism (e.g., BB, Bb, bb).
- Phenotype: The observable physical characteristics of an organism (e.g., black coat, brown coat).
- Homozygous: Having two identical alleles for a particular gene (e.g., BB, bb).
- Heterozygous: Having two different alleles for a particular gene (e.g., Bb).
- Dominant Allele: An allele that masks the expression of another allele (represented by a capital letter, e.g., B).
- Recessive Allele: An allele whose expression is masked by a dominant allele (represented by a lowercase letter, e.g., b).
Punnett Square Practice Problems: Coat Color in Labrador Retrievers
Labrador Retrievers exhibit a classic example of Mendelian inheritance for coat color. The gene for coat color has two alleles:
- B: Black coat (dominant)
- b: Brown coat (recessive)
Problem 1: A homozygous black Labrador (BB) is bred with a homozygous brown Labrador (bb). What are the possible genotypes and phenotypes of their offspring?
Answer Key:
| B | B | |
|---|---|---|
| b | Bb | Bb |
| b | Bb | Bb |
- Genotype: 100% Bb (heterozygous black)
- Phenotype: 100% Black coat
Problem 2: Two heterozygous black Labradors (Bb) are bred together. What are the possible genotypes and phenotypes of their offspring?
Answer Key:
| B | b | |
|---|---|---|
| B | BB | Bb |
| b | Bb | bb |
- Genotypes: 25% BB (homozygous black), 50% Bb (heterozygous black), 25% bb (homozygous brown)
- Phenotypes: 75% Black coat, 25% Brown coat
Problem 3: A black Labrador with an unknown genotype is bred with a brown Labrador (bb). All the puppies are black. What is the genotype of the black parent?
Answer Key: The black parent must be homozygous (BB). If it were heterozygous (Bb), some brown puppies would have been produced.
Punnett Square Practice Problems: Size in Dogs
Dog size is a polygenic trait, meaning it's controlled by multiple genes. However, we can simplify this for practice purposes using a single gene with two alleles:
- L: Large size (dominant)
- l: Small size (recessive)
Problem 4: A homozygous large dog (LL) is bred with a homozygous small dog (ll). What are the possible genotypes and phenotypes of their offspring?
Answer Key:
| L | L | |
|---|---|---|
| l | Ll | Ll |
| l | Ll | Ll |
- Genotype: 100% Ll (heterozygous large)
- Phenotype: 100% Large
Problem 5: Two heterozygous large dogs (Ll) are bred together. What are the possible genotypes and phenotypes of their offspring?
Answer Key:
| L | l | |
|---|---|---|
| L | LL | Ll |
| l | Ll | ll |
- Genotypes: 25% LL (homozygous large), 50% Ll (heterozygous large), 25% ll (homozygous small)
- Phenotypes: 75% Large, 25% Small
Punnett Square Practice Problems: Coat Texture in Dogs
Coat texture can also be explored using Punnett squares. Let's consider a simplified example with:
- C: Curly coat (dominant)
- c: Straight coat (recessive)
Problem 6: A homozygous curly-coated dog (CC) is bred with a straight-coated dog (cc). What are the possible genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring?
Answer Key: All offspring will be heterozygous (Cc) with a curly coat.
Problem 7: Two heterozygous curly-coated dogs (Cc) are bred together. Predict the genotypic and phenotypic ratios of the offspring.
Answer Key: The genotypic ratio will be 25% CC, 50% Cc, 25% cc. The phenotypic ratio will be 75% curly coat, 25% straight coat.
Beyond Simple Mendelian Inheritance: Exploring Complex Traits
Many dog traits are influenced by more than one gene. These polygenic traits show a wider range of phenotypes. For example:
- Coat color: Many genes contribute to the vast array of coat colors seen in dogs, often involving multiple alleles and complex interactions. The agouti gene, for instance, influences the distribution of pigment along the hair shaft.
- Size: As mentioned previously, size is a polygenic trait. Multiple genes interact to determine the final size of a dog.
- Temperament: Temperament is a complex behavioral trait influenced by both genetics and environment. Multiple genes likely contribute, making it difficult to predict using simple Punnett squares.
The Importance of Ethical Breeding Practices
Understanding genetics and using tools like Punnett squares is essential for responsible dog breeding. Breeders can use this knowledge to:
- Reduce the incidence of genetic disorders: By carefully selecting breeding pairs, breeders can minimize the likelihood of passing on inherited diseases.
- Maintain breed standards: Punnett squares can help breeders predict the likelihood of offspring inheriting desirable traits.
- Improve the overall health and well-being of dogs: By focusing on genetic health, breeders contribute to a healthier dog population.
Limitations of Punnett Squares
While Punnett squares are valuable tools, they have limitations:
- Simplified representation: They often simplify complex genetic interactions. Many traits are not controlled by a single gene with two alleles.
- Probability, not certainty: They predict probabilities, not certain outcomes. The actual results of a breeding may deviate from the predicted ratios.
- Environmental influences: They don't account for the influence of environmental factors on gene expression.
Conclusion: Punnett Squares as a Foundation for Understanding Canine Genetics
Punnett squares are an essential starting point for understanding the basics of inheritance in dogs. While they offer a simplified model, they provide a powerful tool for predicting the probabilities of offspring inheriting specific traits. By combining this knowledge with an understanding of complex genetic interactions and ethical breeding practices, breeders and dog owners can contribute to the health and well-being of the canine population. This comprehensive guide offers a strong foundation for further exploration of canine genetics and responsible breeding. Remember, responsible dog ownership includes understanding the genetic predispositions of your breed and making informed decisions about breeding (if applicable). Further research into specific breed genetics and potential health concerns is always encouraged.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Things Fall Apart Ch 7 Summary
Mar 24, 2025
-
Summary Of Ceremony By Leslie Marmon Silko
Mar 24, 2025
-
Unit 5 Reasoning And Organization Reading Quiz
Mar 24, 2025
-
Ati Nursing Skill Template Mobility And Immobility
Mar 24, 2025
-
Io Experiences Tidal Heating Primarily Because
Mar 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Punnett Square Practice All About Dogs Answer Key . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
