The Percentile Rank Allows The Researcher To Determine:
Onlines
Mar 23, 2025 · 7 min read
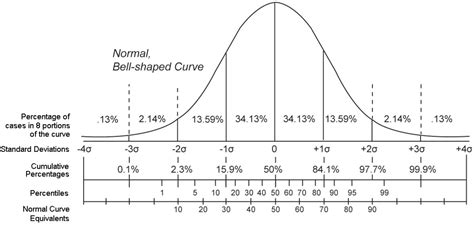
Table of Contents
The Percentile Rank: Understanding and Interpreting Positional Data
The percentile rank is a crucial statistical measure that allows researchers to determine the relative standing of a particular score within a dataset. It's a powerful tool for understanding the distribution of data and comparing individual scores to a larger group. Unlike simple measures like the mean or median, the percentile rank provides a more nuanced picture of an individual's performance or characteristic relative to others in the same distribution. This article will delve deep into the concept of percentile rank, exploring its definition, calculation methods, interpretation, applications, and limitations.
What is a Percentile Rank?
In simple terms, the percentile rank of a score indicates the percentage of scores in a distribution that fall below that particular score. For example, a score with a percentile rank of 75 means that 75% of the scores in the dataset are lower than that score. Conversely, only 25% of the scores are higher. This makes it a valuable tool for interpreting individual performance within a larger context.
It's important to differentiate between percentile rank and percentile. A percentile is a specific value in a data set that separates the data into two parts. For example, the 75th percentile is the point below which 75% of the data lies. The percentile rank, on the other hand, represents the percentage of scores that fall at or below a specific value within the dataset.
How to Calculate Percentile Rank
Calculating percentile ranks depends on the size and nature of the dataset. There are several methods, and the choice often depends on the dataset's characteristics and the desired level of precision. Here are two common approaches:
Method 1: Using the Formula for a Small Dataset
For smaller datasets (less than approximately 25 scores), a simple formula can be used. This method is straightforward but less precise for larger datasets:
Percentile Rank = (Number of scores below X + 0.5) / Total number of scores * 100
Where:
- X is the score for which you want to calculate the percentile rank.
- Number of scores below X is the count of scores in the dataset that are less than X.
Example:
Let's say we have the following dataset of test scores: {60, 65, 70, 75, 80, 85, 90, 95, 100}. We want to find the percentile rank of the score 80.
- Number of scores below 80: 4
- Total number of scores: 9
- Percentile Rank = (4 + 0.5) / 9 * 100 ≈ 50
Therefore, a score of 80 has a percentile rank of approximately 50, meaning it is at the 50th percentile.
Method 2: Interpolation for Larger Datasets
For larger datasets, a more accurate method involves interpolation. This accounts for the continuous nature of the data, producing more precise percentile ranks. Interpolation requires sorting the data from lowest to highest. The formula used here is more complex but provides better accuracy:
Percentile Rank = [(i + ( (n * p) - cf ) / f )] / n * 100
Where:
- n is the total number of observations.
- p is the desired percentile (e.g., 0.75 for the 75th percentile).
- i is the index of the observation where the percentile falls. If the result is a decimal, round it up to the nearest whole number to determine the location of the percentile in the dataset.
- cf is the cumulative frequency of the observation just before the percentile. This is the sum of all the frequencies less than the frequency at i.
- f is the frequency of the interval where the percentile falls.
Example: Applying this method to a larger dataset requires more involved calculations and is best performed using statistical software. Let's consider a dataset of 100 scores. Calculating the 75th percentile will involve finding the score that separates the top 25% from the bottom 75%. The interpolation formula considers the data within that range, leading to a more accurate percentile rank.
Interpreting Percentile Rank
The interpretation of a percentile rank is straightforward. A percentile rank of:
- 50: Indicates that the score is at the median; half of the scores are above, and half are below.
- 75: Indicates that the score is higher than 75% of the scores in the dataset.
- 25: Indicates that the score is higher than 25% of the scores in the dataset, but lower than 75% of them.
- 90: Represents a score that exceeds 90% of the scores in the dataset, signifying a high relative performance.
It's essential to remember that percentile ranks are relative to the specific dataset used. A score with a percentile rank of 90 in one dataset might represent a different level of performance in another dataset with a different distribution of scores.
Applications of Percentile Rank
The versatility of percentile ranks makes them applicable across a broad range of disciplines and scenarios:
- Education: Evaluating student performance on standardized tests. A student's percentile rank helps educators and parents understand how the student compares to their peers.
- Healthcare: Analyzing patient data, such as blood pressure or cholesterol levels. Percentile ranks assist in identifying individuals who fall outside the normal range.
- Business and Finance: Evaluating employee performance, assessing investment returns, and understanding customer satisfaction scores.
- Sports: Analyzing athlete performance, comparing individual players to others in their league, or tracking progress over time.
- Social Sciences: Understanding income distribution, comparing socioeconomic status, or analyzing survey responses.
Advantages of Using Percentile Rank
Several advantages make percentile ranks a preferred method of data interpretation:
- Easy to Understand: The percentage-based nature is intuitively accessible, even to individuals without a strong statistical background.
- Contextual Understanding: Percentile ranks place scores within a meaningful context by comparing them to other scores in the dataset.
- Robust to Outliers: Unlike the mean, which can be heavily influenced by outliers, percentile ranks are less sensitive to extreme values.
- Applicable to Various Data Types: Percentile ranks can be calculated for different data types, including numerical, ordinal, and even categorical data (though interpretation might require more careful consideration for non-numerical data).
Limitations of Percentile Rank
Despite its advantages, it is essential to be aware of percentile rank's limitations:
- Dependence on Dataset: The percentile rank is only meaningful within the context of the specific dataset used for calculation. A high percentile rank in one dataset does not guarantee a high percentile rank in another.
- Non-Linear Scale: Equal differences in percentile ranks do not necessarily represent equal differences in the underlying scores. The distance between the 90th and 95th percentile might be much larger than the distance between the 50th and 55th percentile, depending on the data distribution.
- Misinterpretation: A percentile rank should not be interpreted as a percentage of correctness or accuracy. For example, a percentile rank of 80 on a test doesn't mean the individual got 80% of the questions correct. It only signifies that their score was better than 80% of those who took the same test.
- Difficult Comparisons Across Different Distributions: Comparing percentile ranks from different distributions can be misleading if the underlying distributions have different shapes or scales.
Conclusion
The percentile rank is a valuable tool for understanding the relative position of a score within a dataset. Its ease of interpretation and application across diverse fields make it a cornerstone of statistical analysis. However, researchers and users must be aware of its limitations to avoid misinterpretations. By understanding both the strengths and weaknesses of percentile ranks, we can utilize this powerful statistical measure effectively for data analysis and decision-making. Remember to choose the appropriate calculation method depending on the dataset size and the desired precision. Always consider the context of the data and the specific research question when interpreting percentile ranks. Proper understanding and careful interpretation lead to meaningful insights drawn from the data. Using appropriate statistical software can streamline the calculation process for larger datasets and enhance the accuracy of the results. Ultimately, a thorough understanding of percentile ranks contributes to a more robust and insightful data analysis process.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Training The Model Is A Step In
Mar 25, 2025
-
How Many Chapters In The Shining
Mar 25, 2025
-
Rank Each Of The Following Firms Based On Market Power
Mar 25, 2025
-
Isolation Methods Quantification By Colony Counting
Mar 25, 2025
-
Nos Van A Servir El Cafe
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Percentile Rank Allows The Researcher To Determine: . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
