The Resource-based Model Views Resources As Blank______.
Onlines
Mar 24, 2025 · 7 min read
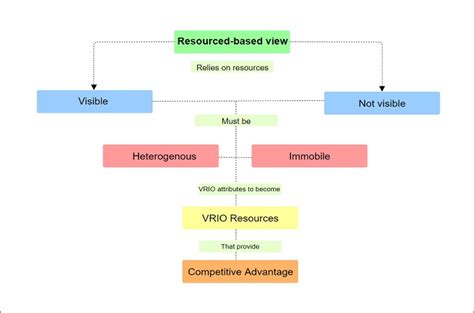
Table of Contents
The Resource-Based Model: Viewing Resources as Blank Slates
The resource-based view (RBV) of the firm is a cornerstone of strategic management. It posits that a firm's sustained competitive advantage stems not from its access to the same resources as its competitors, but rather from its ability to uniquely bundle and utilize those resources. This perspective fundamentally views resources as blank slates, devoid of inherent value until shaped and deployed by the firm's strategic choices and capabilities. This article will delve deep into this core concept, exploring the implications of viewing resources as blank slates, examining the critical role of organizational capabilities, and analyzing how firms can leverage this perspective to achieve and sustain a competitive edge.
Resources: Raw Potential, Not Automatic Advantage
The RBV rejects the notion that simply possessing valuable resources automatically translates to competitive advantage. Instead, it emphasizes the importance of resource heterogeneity and resource immobility. Resource heterogeneity refers to the fact that firms possess different bundles of resources. Resource immobility suggests that these resources are not easily transferable or imitated by competitors.
Imagine a blank canvas. The canvas itself is a resource, but its value is completely dependent on the artist's skill, vision, and the techniques employed. A masterpiece can emerge, or a simple, uninspired painting. Similarly, raw materials, skilled labor, technology, and brand reputation are all resources—blank slates—that acquire value only through a firm's strategic actions. They are potential, not predetermined outcomes.
Beyond Tangible Assets: The Spectrum of Resources
The RBV encompasses a broad spectrum of resources, extending far beyond the traditional focus on tangible assets like land and buildings. These blank slates include:
-
Tangible Resources: These are the physical assets a firm possesses, such as manufacturing facilities, equipment, and financial capital. Their value is contingent on how effectively they are integrated into the firm's operations. A state-of-the-art manufacturing plant is only valuable if it is efficiently utilized and contributes to the production of high-quality goods or services.
-
Intangible Resources: These are less visible but often more crucial resources, including intellectual property (patents, trademarks, copyrights), brand reputation, organizational culture, and knowledge. A strong brand, for instance, is a blank slate that can be leveraged to command premium pricing or attract loyal customers, but requires consistent investment and management to maintain its value.
-
Human Resources: The skills, knowledge, experience, and dedication of employees are invaluable resources. A highly skilled workforce, however, needs effective leadership and management to translate its potential into tangible results. The employees are the blank slate, waiting to be developed and used for the best effect.
-
Organizational Capabilities: This is where the transformative power of the RBV truly shines. Organizational capabilities refer to the firm's ability to coordinate and deploy its resources effectively. These capabilities are dynamic and evolve over time through learning and experience. They are the paintbrush and the artist's skill applied to the blank slate.
Organizational Capabilities: The Sculpting Force
Organizational capabilities are not simply the sum of individual skills within a firm. Instead, they represent the collective knowledge, processes, and routines that allow the organization to transform its resources into valuable outputs. These capabilities are often tacit, meaning they are difficult to codify or transfer. This is a key reason why competitors struggle to imitate successful strategies.
Consider a company with access to advanced technology and skilled engineers. This represents a collection of blank slates in themselves. However, without the organizational capability to efficiently integrate these resources, innovate quickly, and adapt to market changes, the firm will fail to gain a competitive advantage. The capability to utilize the resources is crucial.
Several crucial organizational capabilities are central to leveraging resources effectively:
-
Innovation: The ability to generate new ideas, develop new products and services, and improve existing processes is critical for sustained competitive advantage. This capability shapes the blank slate of resources into innovative solutions that meet evolving market demands.
-
Operational Excellence: Efficiently managing resources, streamlining processes, and minimizing costs are vital for achieving superior performance. This is akin to mastering the techniques of painting, bringing precision and efficiency to the art of shaping the blank canvas.
-
Customer Responsiveness: Understanding and adapting to customer needs is paramount. This capability allows firms to tailor their offerings to specific customer segments and build strong relationships, maximizing the value extracted from resource slates.
-
Strategic Leadership: Effective leadership is essential for aligning resources, setting strategic direction, and motivating employees. This leadership acts as the guiding hand, defining the vision and making crucial choices.
VRIN Framework: Assessing Resource Value
To evaluate whether a firm's resources are capable of generating sustained competitive advantage, the VRIN framework is frequently employed:
-
Valuable: Do the resources and capabilities enable the firm to exploit opportunities or neutralize threats?
-
Rare: Are the resources and capabilities controlled by only a few firms?
-
Inimitable: Are the resources and capabilities costly to imitate? Are they protected by patents, trademarks, or unique organizational processes?
-
Non-substitutable: Are there no strategically equivalent valuable resources that are neither rare nor costly to imitate?
Only resources that meet all four VRIN criteria are likely to lead to a sustained competitive advantage. The blank slate analogy emphasizes that even valuable resources are not inherently advantageous; they must be skillfully shaped and utilized to create a sustainable competitive advantage.
Dynamic Capabilities and Sustaining Competitive Advantage
The RBV acknowledges that the competitive landscape is constantly evolving. Firms must therefore possess dynamic capabilities—the ability to sense, seize, and reconfigure resources—to adapt to changing market conditions and maintain their competitive edge.
Dynamic capabilities are the meta-capabilities, the skills required to constantly reshape the resources at the firm's disposal. It's the artist's continuous learning and adaptation of their style. They involve:
-
Sensing: Identifying opportunities and threats in the external environment.
-
Seizing: Acquiring or developing resources and capabilities to exploit opportunities.
-
Reconfiguring: Modifying existing resources and capabilities or creating new ones to maintain competitiveness.
Implications for Strategic Management
The resource-based model's view of resources as blank slates has significant implications for strategic management:
-
Internal Focus: Firms should focus on developing and leveraging their unique resource bundles, rather than simply imitating competitors.
-
Resource Development: Investment in resource development and enhancement is crucial for achieving and sustaining competitive advantage.
-
Organizational Learning: Continuous learning and adaptation are essential for maintaining dynamic capabilities and responding to change.
-
Strategic Integration: Effective integration of resources and capabilities is key to transforming potential into competitive advantage.
Case Studies: Resources as Blank Slates in Action
Numerous real-world examples highlight the resource-based model in action, showcasing the transformative power of shaping resources.
Example 1: Apple and Brand Loyalty: Apple’s initial resources were relatively modest—computers, software, and talented employees. However, by focusing on user experience, design, and creating a strong brand identity, they transformed these blank slates into a global powerhouse with immense brand loyalty.
Example 2: Netflix and Streaming Technology: Netflix leveraged existing streaming technology and consumer demand for on-demand content. By combining this technology with a sophisticated recommendation engine and an effective content acquisition strategy, they created a disruptive business model that transformed the entertainment industry. The raw material (streaming technology) was a blank slate that was transformed into a global empire.
Example 3: Google and Search Algorithms: Google's initial resources were simple: a powerful search algorithm and a team of talented engineers. However, their ability to constantly refine and improve their algorithms, combined with effective marketing and expansion into other related businesses, created a dominant market position. The initial algorithm—a blank slate—became the foundation of a technological behemoth.
These examples demonstrate that resources are merely raw materials; their value is ultimately determined by the firm's strategic choices, capabilities, and ability to constantly adapt and innovate.
Conclusion: Unlocking the Potential
The resource-based view's perspective that resources are blank slates underscores the crucial role of strategic management in creating and sustaining competitive advantage. Firms must not only possess valuable resources but also cultivate the organizational capabilities to effectively utilize, develop, and reconfigure those resources to achieve and maintain a superior position in the marketplace. This necessitates a strong internal focus, continuous learning, and a willingness to embrace innovation and change. Only then can firms truly unlock the potential inherent within their seemingly blank resource slates. It’s not the resources themselves but the masterful handling and strategic sculpting that determines success.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Dell Roadmap Of A Digital Supply Chain Transformation
Mar 26, 2025
-
Catcher In The Rye Chapter 15 Summary
Mar 26, 2025
-
Factors That Lead To Personal Offenses Include
Mar 26, 2025
-
You Are Collecting Email Addresses From 74
Mar 26, 2025
-
There Is A Design Methodology Called Rapid
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Resource-based Model Views Resources As Blank______. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
