Transcription And Translation Coloring Answer Key
Onlines
Mar 17, 2025 · 6 min read
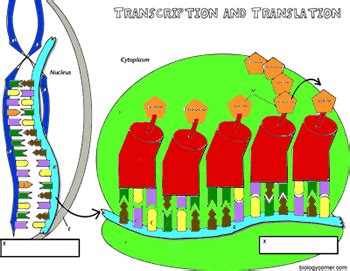
Table of Contents
Transcription and Translation Coloring Answer Key: A Comprehensive Guide
Unlocking the secrets of molecular biology can be a fascinating journey, and understanding the processes of transcription and translation is key to this exploration. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of transcription and translation, providing a detailed coloring answer key to aid your understanding and reinforce learning. We'll explore the key players, the steps involved, and the crucial differences between these two vital processes. By the end, you'll have a solid grasp of these fundamental concepts and a handy reference to check your work.
What is Transcription?
Transcription is the first step in gene expression, the process by which information from a gene is used to create a functional product, such as a protein. Think of it as copying a recipe from a cookbook. The "cookbook" is our DNA, which contains the genetic code. The "recipe" is a specific gene, a sequence of DNA that codes for a particular protein. During transcription, the DNA sequence of a gene is copied into a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule.
Key Players in Transcription:
- DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid): The template containing the genetic information. It's a double-stranded molecule with a specific sequence of nucleotides (adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine).
- RNA Polymerase: The enzyme responsible for synthesizing the mRNA molecule. It unwinds the DNA double helix and adds complementary RNA nucleotides to the template strand.
- mRNA (Messenger RNA): The single-stranded molecule that carries the genetic information from the DNA to the ribosome for translation. It uses uracil (U) instead of thymine (T) to pair with adenine (A).
- Promoter Region: A specific DNA sequence that signals the start of a gene. RNA polymerase binds to this region to initiate transcription.
- Terminator Region: A DNA sequence that signals the end of a gene. This signals RNA polymerase to stop transcription.
Steps in Transcription:
- Initiation: RNA polymerase binds to the promoter region of the gene.
- Elongation: RNA polymerase unwinds the DNA double helix and synthesizes the mRNA molecule by adding complementary RNA nucleotides.
- Termination: RNA polymerase reaches the terminator region and detaches from the DNA, releasing the newly synthesized mRNA molecule.
What is Translation?
Translation is the second step in gene expression, where the genetic information encoded in mRNA is used to synthesize a protein. Imagine it as following the recipe to bake a cake. The "recipe" (mRNA) is translated into a specific sequence of amino acids that form a protein. This process takes place in the ribosome, a cellular organelle responsible for protein synthesis.
Key Players in Translation:
- mRNA (Messenger RNA): The molecule carrying the genetic code from the nucleus to the ribosome.
- Ribosomes: The cellular machinery where protein synthesis occurs. They consist of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and proteins.
- tRNA (Transfer RNA): Adapter molecules that carry specific amino acids to the ribosome. Each tRNA has an anticodon, a sequence of three nucleotides that complements a specific codon on the mRNA.
- Amino Acids: The building blocks of proteins. Each codon on the mRNA specifies a particular amino acid.
- Codons: Three-nucleotide sequences on the mRNA that specify a particular amino acid.
- Anticodons: Three-nucleotide sequences on the tRNA that are complementary to the codons on the mRNA.
Steps in Translation:
- Initiation: The ribosome binds to the mRNA molecule and identifies the start codon (AUG).
- Elongation: tRNA molecules, each carrying a specific amino acid, bind to the mRNA codons. The ribosome forms peptide bonds between adjacent amino acids, forming a polypeptide chain.
- Termination: The ribosome reaches a stop codon (UAA, UAG, or UGA), and the polypeptide chain is released. The polypeptide chain then folds into a functional protein.
Transcription and Translation Coloring Answer Key: A Visual Guide
(Note: This section would ideally include a series of diagrams or illustrations showing the processes of transcription and translation. Each diagram would be accompanied by numbered sections for coloring, with a corresponding answer key at the end. Due to the limitations of this text-based format, I will provide a descriptive answer key instead. You can easily find numerous suitable diagrams online.)
Transcription Coloring Answer Key (Hypothetical Diagram):
- DNA Template Strand: Color this strand blue.
- DNA Non-Template Strand: Color this strand red.
- RNA Polymerase: Color this enzyme green.
- Promoter Region: Highlight this region with a yellow box.
- Terminator Region: Highlight this region with an orange box.
- mRNA Molecule: Color this molecule purple.
- Direction of Transcription: Indicate the direction with an arrow.
Translation Coloring Answer Key (Hypothetical Diagram):
- mRNA Molecule: Color this molecule purple (consistent with the Transcription diagram).
- Ribosome: Color this organelle brown.
- tRNA Molecules: Color these molecules yellow.
- Amino Acids: Use different shades of green for each different amino acid.
- Codons: Circle the codons on the mRNA in orange.
- Anticodons: Circle the anticodons on the tRNA in blue.
- Growing Polypeptide Chain: Color this chain pink.
- Start Codon (AUG): Highlight this codon in red.
- Stop Codon (UAA, UAG, or UGA): Highlight this codon in black.
Differences between Transcription and Translation: A Comparative Analysis
While both transcription and translation are crucial for gene expression, they have distinct characteristics:
| Feature | Transcription | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Nucleus (in eukaryotes) | Cytoplasm (in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes) |
| Template | DNA | mRNA |
| Product | mRNA | Protein |
| Enzyme | RNA polymerase | Ribosomes |
| Monomers | Nucleotides (RNA) | Amino acids |
| Language | Nucleotide sequence (DNA to RNA) | Codon sequence (mRNA to amino acid sequence) |
Common Mistakes and Misconceptions: Debunking the Myths
Understanding the nuances of transcription and translation requires careful attention to detail. Here are some common misconceptions to avoid:
- Confusing DNA and RNA: Remember that DNA is double-stranded and contains thymine (T), while RNA is single-stranded and contains uracil (U).
- Misinterpreting the Genetic Code: The genetic code is a triplet code, meaning that each codon consists of three nucleotides.
- Overlooking the Role of tRNA: tRNA molecules are crucial for bringing the correct amino acids to the ribosome during translation.
- Neglecting the Importance of Ribosomes: Ribosomes are the workhorses of protein synthesis, and their structure and function are vital for understanding translation.
Advanced Concepts and Applications: Expanding Your Knowledge
The principles of transcription and translation form the foundation for many advanced concepts in molecular biology, including:
- Gene Regulation: Understanding how transcription and translation are controlled is essential for comprehending how cells regulate gene expression.
- Genetic Engineering: Techniques like PCR and CRISPR-Cas9 rely on manipulating transcription and translation processes.
- Pharmaceutical Drug Development: Many drugs target specific steps in transcription and translation to treat diseases.
- Cancer Biology: Errors in transcription and translation can lead to cancer development.
Conclusion: Mastering the Molecular Mechanisms
This comprehensive guide has provided a detailed explanation of transcription and translation, along with a descriptive answer key to aid in understanding. By mastering these fundamental processes, you'll gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate mechanisms that govern life at the molecular level. Remember to practice, review, and seek out additional resources to reinforce your understanding. The journey of learning about molecular biology is ongoing and rewarding, so keep exploring!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Ati Growth And Development Template Preschool
Mar 17, 2025
-
You Have Just Been Hired As The Assistant Manager
Mar 17, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Linux File Systems Support Journaling
Mar 17, 2025
-
Medical Surgical Lpn Rn Assessment 1 Shiftkey Answers
Mar 17, 2025
-
Project Stem 7 4 Code Practice Question 1
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Transcription And Translation Coloring Answer Key . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
