Transfer Prices Check All That Apply
Onlines
Mar 23, 2025 · 7 min read
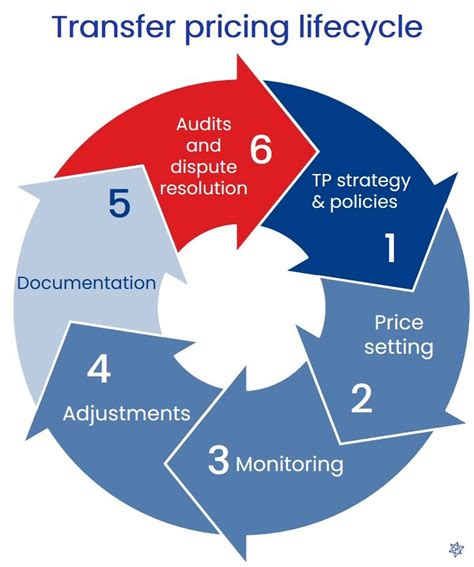
Table of Contents
Transfer Pricing: A Comprehensive Guide to Compliance and Best Practices
Transfer pricing, the pricing of goods, services, and intangible assets exchanged between related entities, is a critical aspect of international taxation. Understanding and complying with transfer pricing regulations is crucial for multinational enterprises (MNEs) to avoid penalties, disputes, and reputational damage. This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of transfer pricing, covering key concepts, compliance requirements, and best practices.
What is Transfer Pricing?
Transfer pricing refers to the setting of prices for transactions between associated enterprises (AEs). These AEs could be parent companies and their subsidiaries, sister companies, or other entities under common control. The arm's length principle (ALP) is the cornerstone of transfer pricing regulations globally. This principle dictates that transactions between AEs should be conducted at prices that would be agreed upon by independent, unrelated parties in comparable circumstances. Deviation from the ALP can lead to tax adjustments, as tax authorities aim to ensure that profits are taxed where they are economically generated.
Why is Transfer Pricing Important?
The importance of proper transfer pricing stems from several factors:
-
Tax Compliance: Accurate transfer pricing ensures compliance with tax laws in various jurisdictions. Failure to adhere to the ALP can result in double taxation (taxing the same profit in multiple countries) or no taxation (profit shifting to low-tax jurisdictions).
-
Profit Allocation: Transfer pricing directly impacts the allocation of profits across different entities within an MNE. Proper pricing ensures a fair distribution of profits reflecting the value added by each entity.
-
Dispute Avoidance: Well-documented transfer pricing policies and practices minimize the risk of disputes with tax authorities. These disputes can be costly, time-consuming, and damaging to an MNE's reputation.
-
Financial Reporting: Accurate transfer pricing is essential for reliable financial reporting, allowing for a clear and transparent picture of the MNE's financial performance.
Key Concepts in Transfer Pricing
Several core concepts underpin transfer pricing regulations:
-
Associated Enterprises (AEs): Entities that are under common control or influence. The definition of AEs varies across jurisdictions but generally includes parent-subsidiary relationships, joint ventures, and companies with shared management or ownership.
-
Arm's Length Principle (ALP): The fundamental principle that transactions between AEs should be priced as if they were conducted between unrelated parties.
-
Comparable Uncontrolled Price (CUP): A transfer pricing method that uses the price charged in comparable transactions between unrelated parties. This method is generally considered the most reliable when available.
-
Cost Plus Method: A method used when a comparable uncontrolled price is not available. It involves adding a markup to the cost of goods or services to determine the transfer price.
-
Resale Price Method: Used when a distributor resells goods purchased from a related party. It involves deducting a gross profit margin from the resale price to determine the transfer price.
-
Profit Split Method: Used for complex transactions where it's difficult to identify comparable transactions. It involves allocating profits between AEs based on their relative contributions.
-
Transactional Net Margin Method (TNMM): A method that compares the net profit margin of an AE to the net profit margins of comparable independent enterprises.
-
Comparable Companies: Identifying comparable companies is crucial in applying various transfer pricing methods. Comparability is determined by considering factors such as functions, assets, risks, and market conditions.
Transfer Pricing Documentation
Comprehensive documentation is vital for demonstrating compliance with transfer pricing regulations. This documentation typically includes:
-
Transfer Pricing Policy: A formal statement outlining the company's approach to transfer pricing, including the methods used and the rationale behind them.
-
Master File: A high-level document providing an overview of the MNE's global organization, business activities, and transfer pricing policies.
-
Local Files: Detailed documentation specific to individual transactions between AEs, including analysis of comparables, selection of methods, and justification of transfer prices.
-
Country-by-Country Reporting (CbCR): A requirement in many jurisdictions for MNEs to report certain financial information on a country-by-country basis. This helps tax authorities gain a global view of an MNE’s activities and profits.
Challenges in Transfer Pricing
Transfer pricing presents several challenges for MNEs:
-
Comparability Issues: Finding truly comparable transactions between unrelated parties can be difficult, as differences in functions, assets, risks, and market conditions can affect prices.
-
Complexity of Regulations: Transfer pricing regulations are complex and vary across jurisdictions, requiring specialized knowledge and expertise.
-
Data Availability: Gathering the necessary data to support transfer pricing analyses can be challenging, especially for companies with complex structures and diverse operations.
-
Subjectivity in Method Selection: The selection of an appropriate transfer pricing method can involve subjective judgment, potentially leading to differing interpretations by tax authorities.
-
Advance Pricing Agreements (APAs): APAs are agreements between an MNE and one or more tax authorities that provide certainty regarding transfer pricing for a specified period. Obtaining an APA can be a lengthy and complex process, but it can offer valuable protection against future disputes.
Best Practices for Transfer Pricing Compliance
To ensure compliance and mitigate risks, MNEs should adopt the following best practices:
-
Proactive Planning: Developing a comprehensive transfer pricing policy and strategy before engaging in cross-border transactions.
-
Robust Documentation: Maintaining meticulous and detailed transfer pricing documentation that is consistent with the chosen methodology and readily available for review.
-
Consistent Application: Applying transfer pricing policies consistently across all transactions to avoid discrepancies and potential inconsistencies.
-
Independent Review: Regularly reviewing transfer pricing policies and documentation by independent experts to ensure accuracy and compliance.
-
Collaboration with Tax Authorities: Proactively engaging with tax authorities to address any concerns and clarify interpretations of transfer pricing regulations.
-
Staying Updated: Keeping abreast of changes in transfer pricing regulations and guidance across relevant jurisdictions.
-
Utilize Technology: Employing technology to streamline data collection, analysis, and documentation processes.
-
Seek Professional Advice: Consulting with experienced transfer pricing professionals to navigate the complexities of the regulations and ensure compliance.
Transfer Pricing Methods: A Deeper Dive
While we briefly touched on several methods earlier, let's delve deeper into their applications and limitations.
1. Comparable Uncontrolled Price (CUP) Method: This method is generally considered the most reliable when applicable. It directly compares the price of a controlled transaction to the price of a comparable uncontrolled transaction. However, finding truly comparable transactions is often the biggest hurdle. Factors like differences in contract terms, quality, quantities, and timing can significantly impact comparability.
2. Cost Plus Method: This method is suitable for situations where a manufacturer sells goods to a related distributor. It adds a markup to the cost of producing the goods to arrive at an arm's length price. The key challenge is determining the appropriate markup, which often relies on benchmarking against the profit margins of comparable independent manufacturers.
3. Resale Price Method: This method is typically used when a distributor resells goods to unrelated customers after purchasing them from a related supplier. It starts with the resale price and deducts a gross profit margin to arrive at the transfer price. The crucial aspect here is accurately determining the appropriate gross profit margin based on comparable independent distributors.
4. Transactional Net Margin Method (TNMM): This method is commonly used when finding comparable uncontrolled prices is challenging. It compares the net profit margin of a controlled transaction to the net profit margins of comparable independent enterprises. The selection of comparable companies is crucial, and factors like functions, assets, risks, and market conditions need meticulous consideration.
5. Profit Split Method: This method is particularly useful for complex transactions involving shared risks and rewards between related parties. It divides the profits generated by the joint activity between the participants based on their relative contributions. This method can be complex and requires sophisticated economic analysis.
Conclusion: Navigating the Complexities of Transfer Pricing
Transfer pricing is a multifaceted area with significant implications for MNEs. Strict adherence to the arm's length principle and meticulous documentation are vital for avoiding penalties, disputes, and reputational damage. By implementing robust transfer pricing policies, engaging in proactive planning, and seeking professional advice, companies can effectively navigate these complexities and ensure long-term compliance. The continuous evolution of regulations highlights the need for ongoing vigilance and adaptation to the latest best practices and guidance. Remember, understanding and applying the principles outlined here is crucial for navigating the complexities of international taxation and maintaining a strong, sustainable global presence.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Magic Number In Figure 1
Mar 25, 2025
-
Deviations From The True Matching Curve Towards Indifference
Mar 25, 2025
-
Which Statement About This Figure Is True
Mar 25, 2025
-
Summary Of Nicomachean Ethics Book 2
Mar 25, 2025
-
Which Statement Correctly Describes A Feature Of The Rock Cycle
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Transfer Prices Check All That Apply . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
