Use The Graph To Determine The Following
Onlines
Mar 24, 2025 · 6 min read
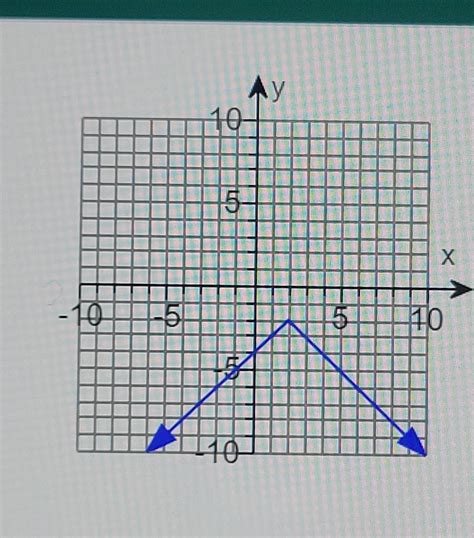
Table of Contents
Decoding Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Interpreting Graphs and Charts
Graphs and charts are fundamental tools for visualizing data, transforming complex information into easily digestible formats. Understanding how to interpret these visual representations is crucial in various fields, from business analytics and scientific research to everyday decision-making. This comprehensive guide will equip you with the skills to effectively analyze graphs and charts, extracting meaningful insights and drawing informed conclusions. We'll explore various graph types, common pitfalls, and advanced techniques for data interpretation.
H2: Understanding Different Graph Types
Before diving into interpretation techniques, it's vital to understand the different types of graphs and their specific applications. Choosing the right graph is crucial for effective data communication. Misusing a graph type can lead to misinterpretations and inaccurate conclusions.
H3: Bar Charts & Column Charts
Bar charts and column charts are used to compare different categories or groups. Bar charts display data horizontally, while column charts use vertical bars. They are ideal for showing differences in quantities, frequencies, or proportions across distinct categories.
- Key Features: Easy to understand, visually appealing, excellent for comparing discrete data.
- Interpreting Data: Focus on the height or length of the bars. Identify the highest and lowest values, and analyze the relative differences between categories. Look for patterns and trends.
- Example: Comparing sales figures across different product lines in a company.
H3: Line Graphs
Line graphs are perfect for illustrating trends over time or continuous data. They show the relationship between two variables, typically time and a measured quantity.
- Key Features: Effectively displays changes over time, highlights trends (increasing, decreasing, stable), suitable for continuous data.
- Interpreting Data: Follow the line's direction to identify trends. Note any significant peaks, valleys, or points of inflection. Look for patterns and correlations.
- Example: Tracking stock prices over a period of months or years, showing the growth of a population over time.
H3: Pie Charts
Pie charts represent proportions or percentages of a whole. Each slice of the pie represents a category, and its size corresponds to its relative contribution to the total.
- Key Features: Excellent for showing parts of a whole, easy to understand visually, ideal for displaying percentages.
- Interpreting Data: Pay attention to the size of each slice relative to the others. Identify the largest and smallest segments. Look for significant differences in proportions.
- Example: Showing the market share of different brands in an industry, illustrating the distribution of age groups within a population.
H3: Scatter Plots
Scatter plots display the relationship between two variables, showing individual data points on a graph. They help identify correlations or associations between the variables.
- Key Features: Reveals correlations between two variables, identifies clusters or outliers, useful for exploring relationships.
- Interpreting Data: Look for patterns in the distribution of points. A positive correlation implies that as one variable increases, the other also increases. A negative correlation suggests the opposite. No clear pattern indicates a weak or no correlation.
- Example: Analyzing the relationship between hours of study and exam scores, plotting the relationship between income and expenditure.
H3: Histograms
Histograms are used to display the frequency distribution of continuous data. They show how often data falls within specific ranges or intervals.
- Key Features: Shows the distribution of continuous data, identifies central tendency and spread, useful for understanding data patterns.
- Interpreting Data: Examine the shape of the histogram. Is it symmetrical, skewed to the left or right? Identify the most frequent range of values (mode). Look for outliers.
- Example: Showing the distribution of student test scores, illustrating the frequency of rainfall amounts in a region.
H2: Essential Steps in Graph Interpretation
Interpreting graphs effectively involves a structured approach:
H3: 1. Understand the Context
Before analyzing the data, understand the context of the graph. What is the graph trying to communicate? What are the variables being represented? Who created the graph and why?
H3: 2. Examine the Axes and Labels
Carefully examine the axes and labels. Understand the units of measurement, the range of values, and the categories represented. Inconsistent or unclear labeling can lead to misinterpretations.
H3: 3. Identify Key Features
Identify the key features of the graph, such as trends, patterns, outliers, peaks, and valleys. Look for significant differences or similarities between data points or categories.
H3: 4. Analyze the Data
Analyze the data by comparing different points, identifying trends, and calculating relevant statistics. Consider the overall shape and distribution of the data.
H3: 5. Draw Conclusions
Based on your analysis, draw conclusions that are supported by the data. Avoid making generalizations or assumptions that are not supported by the evidence.
H3: 6. Consider Limitations
Acknowledge the limitations of the data and the graph. The data may be incomplete, biased, or subject to error. The chosen graph type may not be the most appropriate for the data.
H2: Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Several common errors can lead to inaccurate interpretations of graphs:
- Misleading Scales: Manipulating the scales of axes can distort the perception of the data. Always check the scales to ensure they are appropriate and not misleading.
- Truncated Axes: Starting the y-axis at a value other than zero can exaggerate differences between data points.
- Lack of Context: Presenting a graph without sufficient context can lead to misunderstandings. Always provide sufficient background information.
- Ignoring Outliers: Outliers can significantly influence the interpretation of data. Investigate outliers to understand their potential impact.
- Cherry-Picking Data: Selecting only data points that support a particular conclusion while ignoring contradictory data is a form of bias.
- Confusing Correlation with Causation: Just because two variables are correlated does not mean one causes the other.
H2: Advanced Interpretation Techniques
For more in-depth analysis, consider these techniques:
- Trend Analysis: Identify the overall direction of the data over time. Is it increasing, decreasing, or fluctuating?
- Correlation Analysis: Determine the relationship between two variables using statistical methods.
- Regression Analysis: Model the relationship between variables to make predictions.
- Data Transformation: Apply mathematical transformations to the data to improve its interpretability.
- Statistical Significance Testing: Determine whether observed differences or patterns are statistically significant or due to chance.
H2: Applying Your Skills: Real-World Examples
Let's illustrate the application of graph interpretation through a few scenarios:
Scenario 1: Analyzing Sales Data
Imagine a bar chart showing monthly sales figures for a new product. To interpret this effectively, examine the heights of the bars representing each month. Identify the highest and lowest sales months, noting any significant differences. Look for trends – is sales increasing, decreasing, or staying relatively constant? Are there any seasonal patterns? Based on this, you can draw conclusions about product performance and plan marketing strategies accordingly.
Scenario 2: Tracking Website Traffic
A line graph illustrating website traffic over a year reveals significant peaks during specific times. Analyzing the graph allows you to pinpoint periods of high and low activity. Understanding these trends helps optimize website content and marketing efforts. You might discover that particular blog posts or social media campaigns significantly impacted traffic.
Scenario 3: Evaluating Customer Satisfaction
A pie chart displaying customer satisfaction ratings (e.g., excellent, good, fair, poor) helps understand the overall level of customer happiness. Identify the largest segment to gauge the prevailing sentiment. The distribution of responses informs strategies for improvement. A high percentage of negative feedback signals a need for addressing specific issues.
H2: Conclusion
Mastering the art of graph interpretation is a valuable skill in navigating the data-rich world we inhabit. By understanding the various types of graphs, following a structured interpretation process, and avoiding common pitfalls, you can extract meaningful insights, draw accurate conclusions, and make informed decisions based on data visualization. Remember to always consider the context, critically evaluate the data, and acknowledge limitations for a comprehensive and reliable analysis. This comprehensive understanding will empower you to effectively communicate data-driven insights, facilitating informed decisions across various fields.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Summary Of Chapter 13 Of The Giver
Mar 25, 2025
-
A Provider Calls Asking Why A Claim Was Denied
Mar 25, 2025
-
A Disadvantage Of A Bus Network Is That
Mar 25, 2025
-
El Huipil Es Una Vestimenta De Origen Maya Cierto Falso
Mar 25, 2025
-
Silvia Y Gisela Llegaron Juntas A La Fiesta
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Use The Graph To Determine The Following . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
