What Is Also Called A Substitution Process
Onlines
Mar 18, 2025 · 6 min read
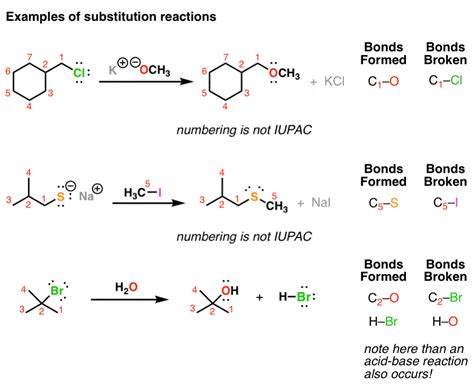
Table of Contents
What is Also Called a Substitution Process? A Deep Dive into Various Applications
The term "substitution process" might sound technical, but it's a concept that touches upon numerous aspects of our daily lives and various fields of study. It essentially refers to any process where one element, item, or value is replaced by another. This seemingly simple definition, however, encompasses a vast array of applications, from fundamental chemical reactions to complex algorithms in computer science. This article will explore the diverse facets of substitution processes, highlighting key examples and explaining their significance across different disciplines.
Substitution in Chemistry: Reactions and Transformations
In chemistry, substitution reactions form a cornerstone of organic and inorganic chemistry. These reactions involve the replacement of one atom or group of atoms within a molecule by another atom or group. This fundamental process is crucial for synthesizing countless compounds and understanding chemical transformations.
Types of Chemical Substitution Reactions
Several categories classify chemical substitution reactions, each characterized by unique mechanisms and reactivity patterns.
-
Nucleophilic Substitution: This type involves a nucleophile (an electron-rich species) attacking an electrophile (an electron-deficient species), leading to the displacement of a leaving group. This is a common mechanism in organic chemistry, particularly with alkyl halides. SN1 and SN2 reactions are prominent examples, differing primarily in their reaction mechanisms and stereochemistry.
-
Electrophilic Substitution: Here, an electrophile attacks an electron-rich molecule, often an aromatic compound, substituting one of the existing atoms or groups. Friedel-Crafts alkylation and nitration are classic examples of electrophilic aromatic substitution. These reactions are vital for introducing functional groups into aromatic rings, thereby creating a vast library of organic molecules.
-
Radical Substitution: This mechanism involves free radicals (species with unpaired electrons) as intermediates. Halogenation of alkanes is a prime example, where a halogen atom substitutes a hydrogen atom in the alkane molecule. These reactions are often initiated by UV light and proceed through a chain reaction mechanism.
Significance in Chemical Synthesis and Industry
Chemical substitution reactions are crucial in numerous industrial processes. The production of pharmaceuticals, polymers, and various other chemicals relies heavily on these reactions. Understanding and controlling these reactions are essential for efficiently synthesizing desired products and minimizing unwanted side reactions. Furthermore, the development of new catalysts and reaction conditions constantly refines the efficiency and selectivity of substitution processes in chemical manufacturing.
Substitution in Biology: Genetic Mechanisms and Enzyme Function
Substitution plays a crucial role in several biological processes, particularly in the context of genetics and enzyme activity.
Point Mutations and Genetic Variation
At the molecular level, substitution affects DNA sequences. Point mutations, which involve the replacement of a single nucleotide base in a DNA sequence, can have significant consequences. These changes can result in altered protein structures and functions, leading to genetic variation and potentially affecting an organism's phenotype. Some point mutations may be silent (having no effect on the amino acid sequence), while others can lead to missense (a change in amino acid) or nonsense (premature stop codon) mutations.
Enzyme-Substrate Interactions and Catalytic Mechanisms
Enzyme-catalyzed reactions frequently involve substitution. Enzymes, being biological catalysts, often facilitate the substitution of one functional group for another in their substrate molecules. These processes are precisely orchestrated through enzyme-substrate binding and conformational changes, ultimately determining the efficiency and specificity of enzymatic catalysis. The study of enzyme kinetics and reaction mechanisms heavily relies on understanding the substitution events that occur at the active site of the enzyme.
Substitution in Computer Science: Algorithms and Data Structures
Substitution finds its way into the realm of computer science, specifically within algorithms and data structures.
Cryptography and Encryption Techniques
Substitution ciphers are fundamental cryptographic techniques where each letter (or symbol) in a plaintext message is replaced with a different letter or symbol. The Caesar cipher, one of the simplest forms of substitution cipher, shifts each letter a fixed number of positions down the alphabet. More complex substitution ciphers, such as the Vigenère cipher, employ more intricate substitution schemes. While these classic ciphers are relatively easy to crack, they represent the fundamental concept of substitution in cryptography. Modern encryption algorithms also employ sophisticated substitution techniques, though they're far more complex and robust.
String Manipulation and Pattern Matching
Substitution processes are commonly used in string manipulation operations, particularly when working with text data. Replacing specific characters or substrings within a string is a fundamental task in various programming applications. Pattern matching algorithms, such as regular expressions, utilize substitution processes extensively for finding and replacing specific patterns within text. These algorithms play a critical role in tasks like text editing, data cleaning, and web scraping.
Variable Substitution in Programming Languages
In programming languages, variable substitution is an integral part of the evaluation process. The interpreter or compiler replaces variable names with their corresponding values during execution. This process allows for dynamic behavior and facilitates complex computations. Variable substitution plays a fundamental role in making computer programs flexible and adaptable.
Substitution in Mathematics: Equations and Transformations
Mathematical operations often involve substitution as a key technique.
Solving Equations and Systems of Equations
Substitution is a common method for solving systems of algebraic equations. By expressing one variable in terms of the other(s), one can substitute this expression into other equations, simplifying the system and ultimately finding the solution. This approach is particularly useful in linear algebra and in solving more complex equations.
Coordinate Transformations and Geometric Transformations
In geometry and other mathematical fields, transformations often involve substitution. For example, changing coordinate systems may involve substituting expressions to represent points or objects in a new coordinate frame. Geometric transformations, such as rotations, translations, and scaling, often use substitution to determine new coordinates based on transformation rules.
Substitution in Everyday Life: Analogies and Metaphors
Beyond these formal applications, substitution is present in countless everyday scenarios. We often use substitution as a strategy for problem-solving, adaptation, and resource management.
Replacing Ingredients in Recipes: Culinary Substitution
In cooking, substituting ingredients is a common practice. If a recipe calls for an ingredient you don't have, you might substitute a similar ingredient to achieve a comparable result. This exemplifies the practical application of substitution in everyday life. The success depends on the similarity of the properties of the substituted ingredient to the original one.
Using Alternatives in Transportation or Communication: Adaptive Substitution
In cases where our primary mode of transport or communication is unavailable, we may resort to alternatives. Substituting a bus for a train or an email for a phone call are examples of adaptive substitution. This highlights the substitution process as a response to constraints or limitations.
Problem-Solving Strategies: Creative Substitution
In problem-solving, substituting approaches or ideas can lead to breakthroughs. If an initial method proves ineffective, adopting an alternative approach can resolve the problem effectively. Creative substitution demonstrates the adaptive nature of this process.
Conclusion: The Ubiquitous Nature of Substitution
The concept of a substitution process, while seemingly simple, permeates various fields. From fundamental chemical reactions to complex algorithms and everyday decision-making, the act of replacing one element with another is a universal principle. Understanding the different facets of substitution processes allows for deeper insight into the workings of the physical world, the intricacies of biological systems, the elegance of mathematical models, and the ingenuity of human problem-solving. As technology continues to advance, the application of substitution methods will likely expand even further, highlighting its enduring importance across diverse disciplines.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Https Www Raterhub Com Evaluation Rater
Mar 18, 2025
-
1 4 Additional Practice Literal Equations And Formulas
Mar 18, 2025
-
7 3 Additional Practice Proving Triangles Similar
Mar 18, 2025
-
Tc 3 20 31 1 Gunnery Skills Test Pdf
Mar 18, 2025
-
Hardware Lab Simulation 8 2 Cable Tester
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Also Called A Substitution Process . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
