Which Is A True Statement Regarding Gastric Cancer
Onlines
Apr 06, 2025 · 7 min read
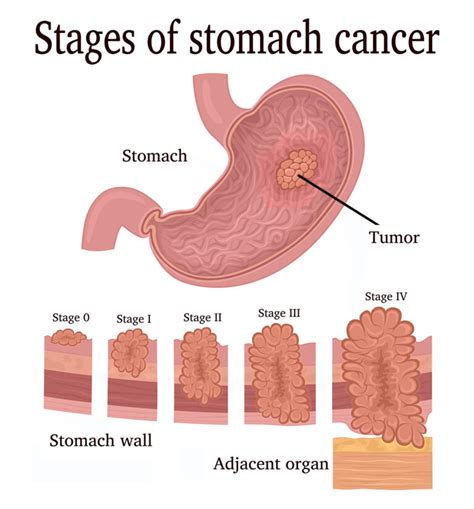
Table of Contents
Which is a True Statement Regarding Gastric Cancer? Unpacking the Facts
Gastric cancer, also known as stomach cancer, remains a significant global health concern. Understanding the disease, its risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment is crucial for early detection and improved outcomes. This comprehensive article aims to clarify common misconceptions and present accurate information regarding gastric cancer, focusing on identifying truly accurate statements about the disease.
Prevalence and Risk Factors: A Global Perspective
Which is a true statement regarding gastric cancer's prevalence? A true statement is that gastric cancer incidence varies significantly across the globe. While some regions, particularly East Asia (especially Japan, South Korea, and China), and Eastern Europe experience high rates, incidence is lower in North America and Western Europe. This geographical variation highlights the role of environmental and dietary factors in the development of the disease.
Key Risk Factors: Understanding Your Predisposition
Several factors increase the risk of developing gastric cancer. These include:
- Helicobacter pylori infection: This bacterium is a major risk factor, significantly increasing the chance of developing gastric cancer. Eradication of H. pylori through antibiotics can reduce this risk.
- Diet: A diet low in fruits and vegetables and high in salted, preserved, or smoked foods is strongly associated with an increased risk. Similarly, diets lacking in fresh produce and rich in processed meats are linked to a higher chance of developing this cancer.
- Age: The risk of gastric cancer increases significantly with age, with most cases occurring in individuals over 50. This highlights the importance of regular screening in older adults.
- Family history: A family history of gastric cancer, especially in first-degree relatives, significantly elevates an individual's risk. Genetic predisposition plays a vital role here.
- Smoking: Smoking is a proven risk factor for many cancers, including gastric cancer. Smoking damages the cells lining the stomach, increasing the risk of cancerous growths.
- Anemia: Certain types of anemia, particularly pernicious anemia (a vitamin B12 deficiency), are linked to an increased risk of gastric cancer.
- Gastric polyps: The presence of benign or precancerous polyps in the stomach increases the risk of developing gastric cancer. Regular endoscopy checks can help detect and remove these polyps.
- Previous gastric surgery: Individuals who have undergone previous stomach surgery, such as for ulcers or other conditions, have a slightly higher risk.
Types and Stages: Understanding the Disease's Progression
Gastric cancer is classified into different types based on the cells involved and their location within the stomach. The most common type is adenocarcinoma, which originates in the glandular cells lining the stomach. Less common types include lymphoma and gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs).
Staging is crucial in determining the extent of the cancer's spread. The staging system uses a combination of factors, including tumor size, lymph node involvement, and the presence of distant metastases (spread to other organs). The stage significantly influences treatment options and prognosis.
Symptoms: Recognizing the Warning Signs
Early-stage gastric cancer often presents with vague or non-specific symptoms, making early detection challenging. However, as the disease progresses, more noticeable symptoms may appear. These can include:
- Persistent abdominal pain or discomfort: This can range from mild discomfort to severe, persistent pain. The location and nature of the pain may vary.
- Indigestion or heartburn: Frequent or persistent indigestion or heartburn, unresponsive to over-the-counter medications, warrants medical attention.
- Nausea and vomiting: Persistent nausea and vomiting, especially if accompanied by other symptoms, should be investigated.
- Weight loss: Unexplained weight loss, especially if significant, is a serious warning sign.
- Loss of appetite: A decreased appetite or feeling full quickly after eating can be a symptom.
- Fatigue and weakness: These are general symptoms, but can indicate underlying health problems, including cancer.
- Blood in the stool or vomit: The presence of blood in the stool (melena) or vomit (hematemesis) is a serious symptom requiring immediate medical attention.
- Anemia: Iron-deficiency anemia can result from chronic blood loss in the stomach.
- Dysphagia: Difficulty swallowing can occur as the tumor grows and obstructs the esophagus.
- Feeling bloated: Persistent feelings of bloating after eating, especially if accompanied by other symptoms, warrants investigation.
It's crucial to remember that these symptoms can be associated with other, less serious conditions. However, if you experience any persistent or concerning symptoms, it's essential to seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and evaluation. Early detection is key to improving treatment outcomes.
Diagnosis: Techniques for Accurate Detection
Diagnosing gastric cancer involves a combination of diagnostic tests, including:
- Upper endoscopy: This procedure involves inserting a thin, flexible tube with a camera into the esophagus and stomach to visualize the lining and obtain tissue samples (biopsy). This is a critical test for both diagnosis and staging.
- Biopsy: A small tissue sample is taken during an endoscopy and examined under a microscope to confirm the presence of cancer cells and determine the type of cancer.
- Imaging tests: Imaging tests, such as CT scans, MRI scans, and PET scans, may be used to assess the extent of the cancer's spread and identify any distant metastases.
- Barium swallow: Although less commonly used now with the advent of endoscopy, this x-ray procedure can show abnormalities in the shape and structure of the esophagus and stomach.
- Blood tests: Blood tests may be used to check for anemia, markers of inflammation, or other indicators of gastric cancer.
Treatment Options: A Multifaceted Approach
Treatment for gastric cancer depends on several factors, including the type, stage, and location of the cancer, as well as the patient's overall health. Common treatment modalities include:
- Surgery: Surgery is the primary treatment for many cases of gastric cancer, aiming to remove the cancerous tumor and surrounding tissues. The extent of surgery depends on the stage of the cancer.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells. It may be used before surgery (neoadjuvant chemotherapy) to shrink the tumor, after surgery (adjuvant chemotherapy) to reduce the risk of recurrence, or as the primary treatment in advanced stages.
- Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells. It may be used alone or in combination with chemotherapy.
- Targeted therapy: Targeted therapy uses drugs that specifically target cancer cells, minimizing damage to healthy cells. This approach is particularly useful in certain types of gastric cancer.
- Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy harnesses the body's own immune system to fight cancer cells. This relatively newer approach holds promise in treating certain gastric cancers.
Prognosis and Survival Rates: Understanding the Outlook
The prognosis for gastric cancer depends heavily on several factors, most importantly the stage at which it's diagnosed. Early-stage gastric cancer, diagnosed and treated promptly, offers significantly better survival rates. Advanced-stage gastric cancer presents a greater challenge, but advancements in treatment continue to improve outcomes.
Which is a true statement regarding gastric cancer survival rates? A true statement is that early detection and treatment significantly improve survival rates. While survival rates vary depending on the stage of the cancer and the individual's response to treatment, early diagnosis gives patients a substantially better chance of long-term survival.
Prevention and Early Detection: Taking Control of Your Health
While not all cases of gastric cancer are preventable, adopting certain lifestyle changes can reduce the risk. These include:
- Maintaining a healthy diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and low in processed meats, salted foods, and smoked foods, is essential.
- Eradicating H. pylori infection: If diagnosed with H. pylori, treatment with antibiotics can reduce the risk of developing gastric cancer.
- Quitting smoking: Smoking cessation is crucial for reducing the risk of various cancers, including gastric cancer.
- Regular health screenings: Regular checkups, especially for individuals with risk factors, can enable early detection and timely intervention. Discussions with your physician about appropriate screening strategies based on your risk profile is crucial.
- Managing weight: Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise reduces overall cancer risk.
In conclusion, accurate information about gastric cancer is vital for raising awareness, promoting early detection, and improving patient outcomes. While the disease's presentation can be complex and varied, understanding the key risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and the importance of early detection is crucial. This comprehensive overview aims to empower individuals with knowledge to make informed decisions about their health and seek timely medical attention should concerns arise. Regular discussions with your healthcare provider are essential for personalized advice and appropriate preventative measures.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Exercise 40 Review Sheet Art Labeling Activity 3
Apr 07, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Best Describes A Hypothesis
Apr 07, 2025
-
Why Cant You Detect A Cockroachs Heartbeat
Apr 07, 2025
-
Apush Period 1 And 2 Review Challenge Answer Key
Apr 07, 2025
-
Fin 320 Final Project Financial Analysis Report
Apr 07, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Is A True Statement Regarding Gastric Cancer . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
