Which Of The Following Are Used To Provide Electric Heating
Onlines
Apr 05, 2025 · 6 min read
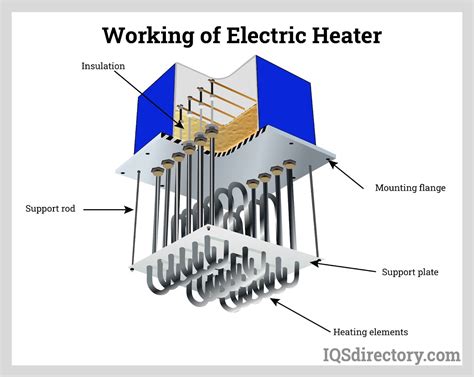
Table of Contents
Which of the Following are Used to Provide Electric Heating?
Electric heating offers a clean, efficient, and controllable way to warm your home or business. But understanding the various methods available can be tricky. This comprehensive guide will delve into the different types of electric heating systems, comparing their pros and cons, efficiency ratings, and suitability for various applications. We'll explore the options to help you choose the best electric heating solution for your specific needs.
Types of Electric Heating Systems
Several technologies provide electric heating, each with its unique characteristics. Let's examine some of the most common:
1. Electric Baseboard Heaters
These are arguably the most familiar type of electric heating. Baseboard heaters are long, low-profile units installed along the base of walls. They use resistance heating elements to warm the air directly.
Pros:
- Simple Installation: Relatively easy to install, often requiring minimal modifications to existing infrastructure.
- Affordable: Generally, a cost-effective initial investment compared to other electric heating systems.
- Zoned Heating: Individual units can be controlled, allowing for zoned heating, which optimizes energy efficiency by only heating occupied areas.
Cons:
- Inefficient: Resistance heating is inherently less efficient than heat pumps or other advanced systems. They directly convert electricity to heat, with no secondary energy source.
- Uneven Heating: Can sometimes lead to uneven heating within a room, especially in larger spaces.
- Aesthetically Unpleasing: The bulky units can detract from the aesthetic appeal of a room, depending on personal preferences and interior design.
2. Electric Radiant Heat
Radiant heating systems use electricity to warm a surface, such as flooring, ceilings, or walls. This heated surface then radiates heat into the room. This method can be incorporated into various materials including:
- Electric Radiant Floor Heating: This is a popular choice for new construction or renovations, offering comfortable, even heat. Electric heating elements are embedded within the subfloor, radiating warmth upwards.
- Electric Radiant Ceiling Heating: Less common than floor heating, ceiling systems can be effective in certain situations, such as high-ceilinged rooms or spaces where floor heating isn't feasible.
- Electric Radiant Wall Heating: This approach is usually integrated into wall panels or plasterboard, providing a subtle and even heating solution.
Pros:
- Even Heat Distribution: Provides a very comfortable and evenly distributed heat.
- Improved Energy Efficiency (Compared to Baseboard): While still using electricity directly, radiant heating can be more efficient due to its ability to heat objects and people directly, rather than just the air.
- Quiet Operation: Extremely quiet operation compared to forced-air systems.
Cons:
- High Initial Cost: Significantly more expensive to install than baseboard heaters, especially for retrofitting existing structures.
- Slow Response Time: Radiant heating systems can take longer to heat up and cool down compared to other methods.
- Potential for Damage: Improper installation can lead to damage to the flooring or other materials.
3. Electric Heat Pumps
Unlike resistance heating, heat pumps move heat rather than generating it. They extract heat from the outside air (even in cold temperatures) and transfer it indoors. They can also function in reverse, removing heat from your home during warmer months, acting as an air conditioner.
Pros:
- High Energy Efficiency: Significantly more efficient than resistance heating systems, leading to lower energy bills.
- Cooling and Heating: Offer both heating and cooling capabilities in one unit.
- Environmentally Friendly: Heat pumps utilize a refrigerant, which has minimal environmental impact.
Cons:
- High Initial Cost: Heat pumps are considerably more expensive to purchase and install than other electric heating options.
- Performance in Extreme Cold: Efficiency can decrease in very cold climates, requiring supplemental heating.
- Outdoor Unit Required: Requires an outdoor unit, which can be a consideration based on space and aesthetics.
4. Electric Forced-Air Furnaces
These furnaces use electric resistance heating elements to heat air, which is then circulated throughout the home by a fan and ductwork system. While often associated with gas furnaces, electric versions exist.
Pros:
- Even Heating (with proper ductwork): Can provide even heating throughout a home, assuming a well-designed and properly maintained ductwork system.
- Good for Larger Spaces: Suitable for heating larger homes or buildings.
- Integrated with AC: Often integrates with central air conditioning systems.
Cons:
- Inefficient: Electric resistance heating is inherently less efficient than heat pumps.
- High Energy Costs: Can lead to high energy costs if not properly insulated and sealed.
- Maintenance: Requires regular maintenance, including filter changes and ductwork cleaning.
5. Infrared Electric Heaters
These heaters work by emitting infrared radiation, which directly heats objects and people within their range. They are often used for supplemental heating or in specific areas like bathrooms or garages.
Pros:
- Fast Heating: Heat up very quickly and provide instant warmth.
- Targeted Heating: Can be directed at specific areas, reducing energy waste.
- Portable: Many models are portable, allowing for easy repositioning.
Cons:
- Uneven Heating: Can lead to uneven heating if not strategically positioned.
- Can be Expensive: Some high-end infrared heaters can be expensive.
- Safety Considerations: Direct exposure to high-intensity infrared radiation can be harmful, so cautious placement is vital.
Choosing the Right Electric Heating System
The best electric heating system for your needs depends on several factors:
- Budget: Initial costs vary widely, from affordable baseboard heaters to the more expensive heat pumps and radiant systems.
- Climate: Heat pump efficiency decreases in extreme cold, while resistance heating performs consistently regardless of outdoor temperature.
- Home Size and Layout: Larger homes may benefit from forced-air systems, while smaller spaces can be effectively heated with baseboard heaters or radiant systems.
- Existing Infrastructure: Installation costs and feasibility depend on the existing infrastructure. Radiant heating requires significant renovation for retrofitting.
- Aesthetic Preferences: Consider the aesthetic impact of different systems on your home's interior design.
Efficiency and Energy Costs
Electric heating efficiency is often expressed as a coefficient of performance (COP) for heat pumps or as an energy factor (EF) for other systems. Higher values indicate better efficiency. However, the actual energy cost depends on your local electricity prices and your energy consumption patterns.
Maintenance and Lifespan
Regular maintenance is crucial for extending the lifespan and efficiency of your electric heating system. This includes:
- Baseboard Heaters: Regular cleaning to prevent dust buildup.
- Radiant Heating: Minimal maintenance, primarily ensuring the system operates correctly.
- Heat Pumps: Annual inspection and maintenance by a qualified technician.
- Forced-Air Furnaces: Regular filter changes and ductwork cleaning.
- Infrared Heaters: Cleaning to remove dust and debris.
Conclusion
Choosing the right electric heating system requires careful consideration of your individual needs and preferences. While resistance heating offers affordable upfront costs, heat pumps provide superior long-term energy efficiency. Radiant systems deliver comfortable, even warmth, but at a higher initial investment. Understanding the pros and cons of each system will help you make an informed decision that optimizes both comfort and energy efficiency for your home or business. Remember to consult with qualified professionals for installation and ongoing maintenance to ensure optimal performance and safety.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Using Logic To Compare Samples With Different Sources Of Variation
Apr 06, 2025
-
Blueprint Reading For Welders 9th Edition Pdf Free
Apr 06, 2025
-
How Much Land Does A Man Need Summary
Apr 06, 2025
-
Aide Care For A Conscious Patient Should Be Preceded By
Apr 06, 2025
-
Summary Of Chapter 2 To Kill A Mockingbird
Apr 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Are Used To Provide Electric Heating . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
