Which Of The Following Is True Regarding Cavitation
Onlines
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
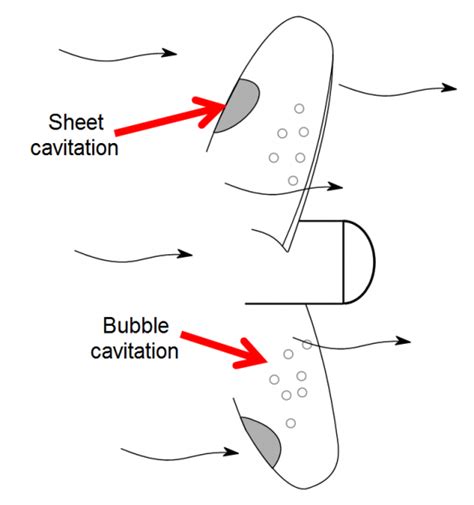
Table of Contents
Which of the following is true regarding cavitation? Understanding the Phenomena and its Implications
Cavitation, a phenomenon characterized by the formation and collapse of vapor-filled cavities in a liquid, is a complex process with significant implications across various engineering disciplines. Understanding its nuances is crucial for designing efficient and durable systems. This article delves into the intricacies of cavitation, exploring its causes, effects, and mitigation strategies. We'll address common misconceptions and clarify what statements about cavitation are true and false.
What is Cavitation?
Cavitation occurs when the local pressure within a liquid drops below its vapor pressure. This pressure reduction can be caused by several factors, including high velocities, changes in flow geometry, or the presence of obstacles. When the pressure drops sufficiently, the liquid vaporizes, forming small bubbles or cavities. These cavities subsequently collapse, often violently, generating localized high pressures, temperatures, and erosive forces.
Causes of Cavitation
Several factors contribute to the initiation and propagation of cavitation:
-
High Velocities: In high-velocity flows, such as those found in pumps, turbines, and propellers, the pressure can decrease significantly, leading to cavitation. The Bernoulli principle explains this; increased velocity leads to a decrease in static pressure.
-
Geometric Restrictions: Abrupt changes in flow geometry, like sharp bends or constrictions in pipes, can accelerate the fluid and reduce pressure, triggering cavitation.
-
Obstacles in the Flow Path: The presence of obstacles, such as partially closed valves or damaged impeller blades, can disrupt the flow, creating regions of low pressure prone to cavitation.
-
High Temperatures: While less common, high temperatures can lower the vapor pressure of the liquid, making it easier for cavitation to occur, even at moderate velocities.
Effects of Cavitation: Damage and Degradation
The consequences of cavitation can be detrimental, affecting both performance and lifespan of various systems. The primary effects include:
-
Erosion and Damage: The implosion of cavitation bubbles generates extremely high pressures and temperatures, leading to material erosion and surface damage. This is especially damaging to metallic components, resulting in pitting, corrosion, and eventual failure. The cumulative effect of repeated bubble collapse can significantly shorten the operational life of equipment.
-
Noise and Vibration: The collapse of cavitation bubbles produces intense noise and vibration. This can be problematic in applications where quiet operation is essential, such as underwater vehicles or medical ultrasound devices.
-
Reduced Efficiency: Cavitation can disrupt the flow of liquids, hindering the efficiency of pumps, turbines, and other fluid machinery. The formation of bubbles reduces the effective density of the fluid, decreasing the energy transfer and power output.
-
Performance Degradation: The localized erosion and efficiency reduction associated with cavitation can significantly degrade the overall performance of a system, leading to decreased productivity and increased maintenance costs.
Debunking Common Misconceptions about Cavitation
Several misconceptions surround cavitation. It's crucial to understand the true nature of this phenomenon:
Misconception 1: Cavitation only occurs in high-velocity flows.
Truth: While high velocity is a significant contributor, cavitation can also occur in low-velocity flows if the pressure drops sufficiently due to other factors, such as geometric restrictions or high temperatures.
Misconception 2: Cavitation is always visible.
Truth: In many cases, cavitation is initially invisible to the naked eye. The bubbles are often very small and transient. Visual detection may only be possible when cavitation is severe, manifesting as a cloudiness or noise.
Misconception 3: Cavitation only affects metallic components.
Truth: While metallic components are particularly susceptible to the erosive effects of cavitation, it can also damage other materials, including polymers, composites, and even biological tissues. The extent of damage depends on the material properties and the intensity of cavitation.
Misconception 4: Cavitation is easily predictable.
Truth: Predicting the onset and extent of cavitation is challenging due to the complex interplay of various factors influencing its development. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations are used to model and predict cavitation, but accurate predictions require detailed knowledge of the flow conditions and material properties.
Which Statements Regarding Cavitation are True?
Based on the information provided above, let's evaluate several potential statements about cavitation:
Statement 1: Cavitation is a process involving the formation and collapse of vapor-filled cavities in a liquid. TRUE This is the fundamental definition of cavitation.
Statement 2: High velocities are always necessary for cavitation to occur. FALSE While high velocities are a common cause, other factors like geometric restrictions and high temperatures can also trigger cavitation.
Statement 3: Cavitation always leads to visible bubble formation. FALSE Early-stage cavitation is often invisible to the naked eye.
Statement 4: Cavitation can cause significant erosion and material damage. TRUE The implosion of cavitation bubbles generates high pressures leading to pitting and material degradation.
Statement 5: Cavitation only affects pumps and turbines. FALSE While prevalent in these systems, cavitation can occur in various other applications involving liquid flows, including medical devices, marine propellers, and hydraulic systems.
Statement 6: Cavitation can reduce the efficiency of fluid machinery. TRUE The formation of vapor cavities reduces the effective fluid density, hindering energy transfer and decreasing efficiency.
Mitigation Strategies: Preventing and Reducing Cavitation
Minimizing or preventing cavitation is crucial for ensuring the long-term performance and reliability of equipment. Several strategies can be implemented:
-
Design Modifications: Careful design of fluid machinery, including optimization of flow passages and avoidance of abrupt changes in geometry, can reduce the likelihood of cavitation.
-
Material Selection: Using cavitation-resistant materials, such as stainless steels or specialized alloys, can mitigate the erosive effects. Coatings and surface treatments can also enhance resistance.
-
Operational Changes: Adjusting operational parameters, such as flow rates and pressures, can minimize the risk of cavitation.
-
Cavitation Inhibitors: Introducing additives to the liquid can alter its properties and reduce the tendency for cavitation.
-
Improved Manufacturing Techniques: Precise manufacturing techniques that minimize surface roughness and imperfections can reduce the nucleation sites for cavitation bubbles.
Advanced Techniques for Cavitation Analysis
Modern techniques contribute significantly to the understanding and mitigation of cavitation:
-
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD): CFD simulations allow for the detailed modeling and prediction of cavitation behavior under various conditions.
-
Experimental Techniques: Techniques like high-speed photography and acoustic emission monitoring are used to visualize and analyze cavitation in real-time.
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML algorithms can be employed to analyze large datasets generated from experiments and simulations, improving the predictive capabilities of cavitation models.
Conclusion: The Ongoing Importance of Understanding Cavitation
Cavitation, a complex and multifaceted phenomenon, presents significant challenges across diverse engineering applications. Its understanding requires a multidisciplinary approach, integrating fluid mechanics, material science, and advanced computational methods. By understanding the causes, effects, and mitigation strategies, engineers can design and operate systems that minimize the detrimental effects of cavitation, ultimately improving performance, durability, and efficiency. Continued research and development in this field are vital for addressing the ongoing challenges posed by cavitation in increasingly demanding engineering environments. The development of new materials, advanced simulation techniques, and innovative mitigation strategies will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping the future of cavitation research and control.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Excel 2021 In Practice Ch 2 Advanced Project 2 7
Mar 19, 2025
-
At Which Area Of The Oblong Does Molding Begin
Mar 19, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Not True About Childhood Obesity
Mar 19, 2025
-
Which Statement By The Nurse Is An Example Of Deception
Mar 19, 2025
-
Aliyah Is Preparing To Expand Her It
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is True Regarding Cavitation . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
