Which Of These Is An Ergonomic Guideline To Technology Use
Onlines
Mar 28, 2025 · 7 min read
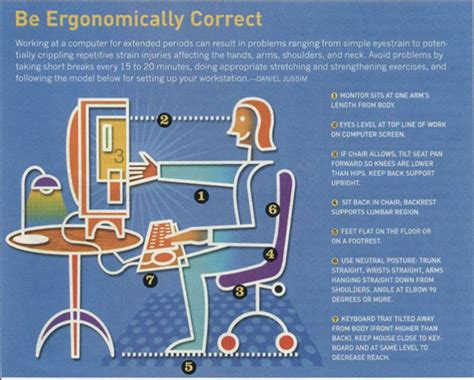
Table of Contents
Which of These is an Ergonomic Guideline to Technology Use? A Deep Dive into Workplace Wellness
In today's digitally driven world, technology is ubiquitous. From the moment we wake to the time we sleep, screens dominate our lives, both professionally and personally. This constant interaction necessitates a deep understanding of ergonomics, the science of designing the workplace to fit the worker. Ignoring ergonomic principles when using technology can lead to a range of health problems, impacting productivity and overall well-being. This comprehensive guide will explore various ergonomic guidelines for technology use, helping you optimize your workspace and safeguard your health.
Understanding Ergonomics and its Importance in Technology Use
Ergonomics isn't just about comfort; it's about preventing musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) and promoting long-term health. MSDs encompass a broad range of injuries affecting muscles, tendons, ligaments, nerves, and joints. These can manifest as carpal tunnel syndrome, tendonitis, back pain, neck pain, and eye strain – all significantly exacerbated by improper technology use.
The core principle of ergonomics is to adapt the workplace to the individual, not the other way around. This includes adjusting your chair, monitor placement, keyboard and mouse position, and even your posture to minimize strain and maximize efficiency.
The Cost of Ignoring Ergonomic Principles
The consequences of neglecting ergonomic guidelines extend beyond personal discomfort. Companies face substantial costs associated with:
- Increased absenteeism: Employees suffering from MSDs often require time off work for treatment and recovery.
- Reduced productivity: Pain and discomfort significantly impact an employee's ability to focus and perform tasks efficiently.
- Higher healthcare costs: Treating MSDs can be expensive, leading to increased healthcare expenses for both the employee and the employer.
- Increased worker's compensation claims: Companies face legal and financial liabilities when employees file claims due to work-related injuries.
- Decreased employee morale and retention: A painful and uncomfortable workspace can lead to decreased job satisfaction and higher employee turnover.
Key Ergonomic Guidelines for Technology Use
Let's delve into the specific ergonomic guidelines crucial for safe and efficient technology use. Remember, these guidelines are interconnected; optimizing one aspect often positively impacts others.
1. Posture: The Foundation of Ergonomic Wellness
Maintaining proper posture is paramount. Slouching, hunching, or twisting your body puts undue strain on your muscles and joints. Aim for a neutral posture, characterized by:
- Upright spine: Your back should be straight, with natural curves maintained. Avoid rounding your shoulders or slumping.
- Supported lower back: Use a chair with lumbar support or add a lumbar roll to maintain the natural curve of your lower back.
- Relaxed shoulders: Keep your shoulders relaxed and down, avoiding tension.
- Head aligned with torso: Your head should be positioned directly above your shoulders, not tilted forward or backward.
2. Chair Selection and Adjustment: The Ergonomic Throne
Your chair plays a crucial role in supporting proper posture. Choose a chair with:
- Adjustable height: Your feet should be flat on the floor, and your thighs should be parallel to the ground.
- Adjustable backrest: The backrest should support your lower back's natural curve.
- Armrests (optional): Armrests can provide support, but ensure they don't interfere with your keyboard and mouse position. If used, they should allow your elbows to be at a 90-degree angle.
- Stable base: The chair should be stable and not wobble.
3. Monitor Placement: Viewing Comfort is Key
Improper monitor placement strains your eyes and neck. Follow these guidelines:
- Eye level: The top of your monitor should be at or slightly below eye level. This prevents you from tilting your head upwards or downwards for extended periods.
- Arm's length: The monitor should be approximately an arm's length away to reduce eye strain.
- Proper viewing angle: The monitor should be positioned directly in front of you to avoid twisting your neck.
- Reduce glare: Adjust the brightness and contrast of your monitor and position it to minimize glare from windows or lights.
4. Keyboard and Mouse Placement: Precision and Comfort
The positioning of your keyboard and mouse is crucial for preventing repetitive strain injuries.
- Neutral wrist position: Keep your wrists straight and relaxed, avoiding bending or flexing. Use a keyboard tray if necessary to achieve this.
- Elbows at 90 degrees: Your elbows should be bent at approximately a 90-degree angle while typing.
- Mouse close to keyboard: Place your mouse close to your keyboard to minimize unnecessary arm movement.
- Consider ergonomic keyboards and mice: Ergonomic keyboards and mice are designed to promote neutral wrist positions and reduce strain.
5. Breaks and Movement: The Antidote to Sedentary Lifestyle
Regular breaks are essential to prevent fatigue and strain. Aim for short breaks every 30-60 minutes, incorporating these activities:
- Stretch: Perform simple stretches to relieve muscle tension.
- Walk around: Stand up and walk around to improve circulation.
- Eye exercises: Focus on distant objects to relax your eye muscles.
- Change posture: Shift your position to avoid prolonged static postures.
6. Lighting: Illuminating the Workspace
Proper lighting reduces eye strain and improves overall comfort.
- Ambient lighting: Use soft, diffused ambient lighting to reduce glare and shadows.
- Task lighting: Use a desk lamp to illuminate your work area specifically.
- Avoid harsh overhead lighting: Bright, harsh overhead lighting can cause eye strain and headaches.
7. Workspace Organization: Streamlining Efficiency and Health
A well-organized workspace improves efficiency and reduces strain.
- Keep frequently used items within easy reach: This minimizes reaching and twisting.
- Declutter your workspace: A cluttered workspace can lead to frustration and poor posture.
- Maintain a clean and tidy workspace: A clean workspace promotes a sense of calm and order.
Specific Examples of Ergonomic Guidelines in Action
Let's look at some concrete examples to illustrate these principles:
Scenario 1: A graphic designer spends hours daily working on a laptop.
- Ergonomic Solution: The designer should use an external keyboard and mouse to maintain proper posture and avoid hunching. They should also elevate their laptop to eye level using a laptop stand, ensuring their neck is not strained.
Scenario 2: A programmer works long hours at a desktop computer.
- Ergonomic Solution: The programmer should ensure their chair provides adequate lumbar support and adjust their monitor to eye level. They should take regular breaks, perform stretches, and utilize ergonomic keyboard and mouse if necessary.
Scenario 3: A customer service representative spends their day on the phone.
- Ergonomic Solution: The representative should use a headset to avoid holding the phone between their shoulder and ear. They should take frequent breaks to stretch their neck and shoulders.
Beyond the Physical: Mental Well-being and Technology Use
While physical ergonomics are crucial, mental well-being is equally important. Prolonged technology use can lead to:
- Eye strain: Regular breaks, proper lighting, and adjusting monitor settings can mitigate this.
- Mental fatigue: Regular breaks, mindfulness exercises, and time away from screens are essential.
- Stress and anxiety: Creating a calm and organized workspace, practicing stress-reduction techniques, and setting boundaries around technology use can help.
Investing in Ergonomic Equipment: A Long-Term Investment
Investing in ergonomic equipment may seem expensive initially, but it's a worthwhile long-term investment. The cost savings associated with reduced absenteeism, increased productivity, and decreased healthcare expenses often far outweigh the initial investment.
Conclusion: Prioritizing Ergonomic Wellness
Prioritizing ergonomics in technology use is crucial for both individual and organizational well-being. By implementing the guidelines outlined above, you can create a healthier, more efficient, and more productive work environment. Remember, ergonomics is not a one-size-fits-all approach; it requires individual assessment and adjustment to ensure optimal comfort and safety. Investing in your ergonomic well-being is an investment in your future health and productivity. Don't underestimate the power of a well-designed workspace in contributing to a healthier and more fulfilling life, both personally and professionally. By actively addressing ergonomic concerns, we can transform our relationship with technology from one of potential harm to one of supportive collaboration.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Letrs Unit 4 Session 4 Check For Understanding
Mar 31, 2025
-
A Way To Make Lower Toned Instruments Would Be To Use
Mar 31, 2025
-
Solving Rational Equations Quiz Part 1
Mar 31, 2025
-
Things Fall Apart Summary Chapter 1
Mar 31, 2025
-
Chapter 8 Summary Of The Hobbit
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of These Is An Ergonomic Guideline To Technology Use . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
