Which Patient Has The Lowest Risk For Developing Schizophrenia
Onlines
Apr 02, 2025 · 5 min read
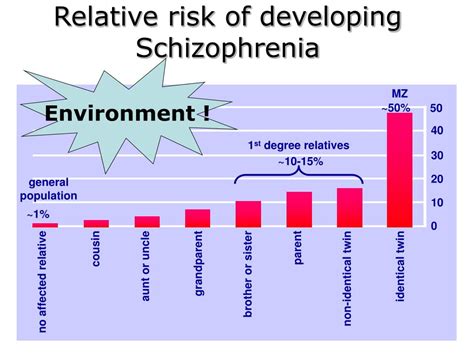
Table of Contents
Which Patient Has the Lowest Risk for Developing Schizophrenia?
Schizophrenia, a chronic and severe mental illness, significantly impacts a person's ability to think, feel, and behave clearly. While its exact cause remains unknown, research has identified several factors influencing an individual's risk of developing this debilitating condition. Understanding these factors allows us to identify those with the lowest risk, which is crucial for preventative strategies and early intervention. This comprehensive article will delve into the complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors that contribute to schizophrenia risk, ultimately highlighting the patient profile with the lowest probability of developing the disorder.
Genetic Predisposition: The Hereditary Component
A strong family history of schizophrenia is a major risk factor. The closer the biological relationship to an affected individual, the higher the risk. This points to a significant genetic component. However, it's crucial to understand that inheriting genes associated with schizophrenia doesn't guarantee the development of the illness. The presence of these genes simply increases susceptibility. This isn't a deterministic relationship; it's probabilistic.
Specific Genes and Polygenic Risk
While no single "schizophrenia gene" exists, research has identified numerous genes associated with an increased risk. These genes often influence neurodevelopment, neurotransmission, and immune function. The influence of these genes is often complex and polygenic, meaning multiple genes interact to influence the risk. The cumulative effect of these genetic variations can significantly impact an individual's susceptibility.
Epigenetics: Environmental Influences on Gene Expression
Epigenetics plays a critical role, illustrating how environmental factors can alter gene expression without changing the DNA sequence itself. Stressful life events, exposure to toxins, and nutritional deficiencies during critical developmental periods can modify gene activity, potentially increasing the risk of schizophrenia in genetically vulnerable individuals.
Environmental Factors: Beyond Genetics
Beyond genetics, various environmental factors contribute to the risk of schizophrenia. These factors often interact with genetic predisposition, exacerbating the risk in vulnerable individuals.
Prenatal and Perinatal Complications
Several prenatal and perinatal factors have been linked to an increased risk of schizophrenia. These include:
- Maternal infections during pregnancy: Exposure to certain viral or bacterial infections during pregnancy can increase the risk.
- Maternal malnutrition: Nutritional deficiencies during pregnancy, particularly deficiencies in certain vitamins and minerals, can also elevate the risk.
- Obstetric complications: Difficulties during labor and delivery, such as hypoxia (oxygen deprivation), can increase susceptibility.
- Low birth weight: Babies born with low birth weight are at a higher risk.
Childhood Trauma and Abuse
Experiences of trauma and abuse during childhood significantly impact mental health. Childhood trauma can lead to dysregulation of the stress response system, altering brain development and increasing vulnerability to psychiatric disorders, including schizophrenia. Neglect, physical abuse, and emotional abuse are all associated with heightened risk.
Substance Abuse
Substance abuse, especially cannabis use, particularly during adolescence, has been linked to an increased risk of developing schizophrenia, especially in individuals with a genetic predisposition. The effect of cannabis may be amplified by its interaction with genetic factors.
Lifestyle Factors and Protective Measures
While not directly causing schizophrenia, certain lifestyle factors can influence the risk. Adopting healthy lifestyles can potentially mitigate some of the risk factors and promote mental well-being.
Healthy Diet and Nutrition
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids supports brain health. Adequate nutrition during development is especially important. A diet deficient in essential nutrients may increase vulnerability.
Regular Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular physical activity reduces stress, improves mood, and promotes overall physical and mental health. Exercise is a crucial aspect of maintaining good mental well-being, potentially reducing the risk of developing mental illness.
Stress Management Techniques
Effective stress management techniques, such as mindfulness, yoga, and meditation, can help individuals cope with stress and improve resilience. Chronic stress can exacerbate mental health vulnerabilities. Learning healthy coping mechanisms is crucial.
Social Support and Strong Relationships
Strong social support networks and healthy relationships are protective factors against mental illness. Feeling connected and supported reduces the impact of stressors and promotes overall well-being.
Identifying the Patient with the Lowest Risk
Based on the factors discussed, the patient with the lowest risk for developing schizophrenia would possess the following characteristics:
- No family history of schizophrenia: A family history free of schizophrenia significantly lowers the risk.
- Uncomplicated pregnancy and birth: A healthy pregnancy and uncomplicated delivery further decrease the risk.
- No childhood trauma or abuse: Absence of significant childhood trauma is a key protective factor.
- Healthy lifestyle: A lifestyle characterized by a balanced diet, regular exercise, and effective stress management significantly reduces overall risk.
- Absence of substance abuse: Avoiding substance use, particularly cannabis, especially during adolescence, is crucial.
Conclusion: A Complex Interaction of Factors
The development of schizophrenia is a complex interplay of genetic susceptibility and environmental influences. While genetic predisposition plays a significant role, environmental factors can act as either risk factors or protective factors. Individuals with no family history, healthy prenatal development, positive childhood experiences, healthy lifestyles, and the absence of substance abuse exhibit the lowest risk for developing schizophrenia. However, it's vital to remember that even with minimal risk factors, the possibility of developing schizophrenia cannot be entirely eliminated. Promoting mental wellness and seeking professional help at the earliest signs of mental health concerns are crucial in mitigating risks and improving outcomes.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. If you have concerns about schizophrenia or any mental health issue, consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized assessment and guidance.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Texas Has A Reputation Of Being A State
Apr 03, 2025
-
Thompson Simone Biles And The Most Human Meaning Of Courage
Apr 03, 2025
-
Why Is Take 5 So Expensive
Apr 03, 2025
-
Nursing Care Plan For Neonatal Jaundice
Apr 03, 2025
-
Famous Forensic Christmas Mystery Picture Answer Key
Apr 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Patient Has The Lowest Risk For Developing Schizophrenia . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
