Worksheet Triangle Sum And Exterior Angle Theorem
Onlines
Mar 20, 2025 · 7 min read
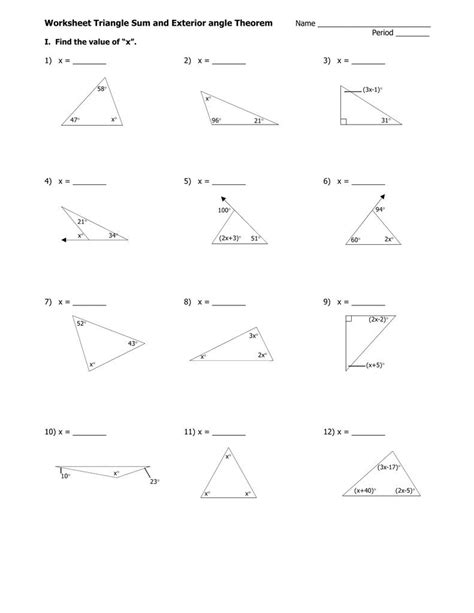
Table of Contents
Delving Deep into Triangle Sum and Exterior Angle Theorems: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the fundamental theorems governing triangles is crucial for mastering geometry. This comprehensive guide will delve deep into the Triangle Sum Theorem and the Exterior Angle Theorem, exploring their proofs, applications, and how to effectively utilize them in problem-solving. We'll also examine practical examples and explore related concepts to build a solid understanding of these essential geometric principles.
The Triangle Sum Theorem: The Foundation of Triangle Angle Relationships
The Triangle Sum Theorem states that the sum of the interior angles of any triangle always equals 180 degrees. This seemingly simple theorem forms the bedrock of many geometric proofs and problem-solving techniques. Let's explore its proof and then examine some practical applications.
Proof of the Triangle Sum Theorem
Several methods exist to prove the Triangle Sum Theorem. Here's a common approach using parallel lines:
-
Draw a Triangle: Start with any triangle, labeling its vertices A, B, and C.
-
Draw a Parallel Line: Draw a line through vertex A parallel to side BC.
-
Identify Alternate Interior Angles: This parallel line creates two alternate interior angles. Angle 1 is equal to angle B (because they are alternate interior angles formed by a transversal intersecting parallel lines), and angle 2 is equal to angle C (for the same reason).
-
Sum of Angles on a Straight Line: Angles 1, A, and 2 together form a straight line, and the sum of angles on a straight line is always 180 degrees.
-
Conclusion: Therefore, angle B + angle A + angle C = 180 degrees, proving the Triangle Sum Theorem.
Applications of the Triangle Sum Theorem
The Triangle Sum Theorem finds applications in various geometrical problems. Here are a few examples:
-
Finding Missing Angles: If you know two angles of a triangle, you can easily find the third angle using the theorem. For example, if two angles are 60° and 80°, the third angle is 180° - 60° - 80° = 40°.
-
Classifying Triangles: The theorem helps classify triangles based on their angles. An acute triangle has all angles less than 90°, a right triangle has one 90° angle, and an obtuse triangle has one angle greater than 90°.
-
Solving Geometric Problems: The theorem is instrumental in solving more complex geometric problems, often used in conjunction with other theorems and postulates. For instance, it can be used to find unknown angles in multi-triangle configurations or to prove congruence of triangles.
The Exterior Angle Theorem: Exploring External Angle Relationships
The Exterior Angle Theorem states that the measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the measures of the two non-adjacent interior angles. This theorem offers another powerful tool for solving problems involving triangles.
Proof of the Exterior Angle Theorem
The proof of the Exterior Angle Theorem is relatively straightforward and builds upon the Triangle Sum Theorem:
-
Identify Interior and Exterior Angles: Consider a triangle ABC. Extend side BC to create an exterior angle at C, which we'll call angle D.
-
Triangle Sum: We know from the Triangle Sum Theorem that angle A + angle B + angle C = 180°.
-
Supplementary Angles: Angles C and D are supplementary angles (they form a straight line), so angle C + angle D = 180°.
-
Substitution: Substitute 180° for (angle A + angle B + angle C) in the equation angle C + angle D = 180°. This gives angle A + angle B + angle C = angle C + angle D.
-
Simplification: Subtract angle C from both sides to obtain angle A + angle B = angle D.
-
Conclusion: This proves the Exterior Angle Theorem: the exterior angle (angle D) is equal to the sum of the two non-adjacent interior angles (angle A and angle B).
Applications of the Exterior Angle Theorem
The Exterior Angle Theorem offers a powerful shortcut in many geometric calculations:
-
Finding Missing Angles: If you know an exterior angle and one of the non-adjacent interior angles, you can immediately find the other interior angle.
-
Simplifying Calculations: It often simplifies calculations compared to using the Triangle Sum Theorem directly, particularly in more complex geometric diagrams.
-
Proofs and Problem Solving: The theorem plays a significant role in more advanced geometric proofs and problem-solving scenarios. It can be used to establish relationships between angles in various geometric shapes.
Combining Theorems for Advanced Problem Solving
Many challenging geometry problems require the combined application of both the Triangle Sum Theorem and the Exterior Angle Theorem. Let's explore a few examples:
Example 1:
A triangle has angles measuring 2x, 3x, and 4x. Find the value of x and the measure of each angle.
- Solution: Using the Triangle Sum Theorem: 2x + 3x + 4x = 180°. This simplifies to 9x = 180°, so x = 20°. Therefore, the angles measure 40°, 60°, and 80°.
Example 2:
An exterior angle of a triangle measures 110°. One of the non-adjacent interior angles measures 50°. Find the measure of the other non-adjacent interior angle.
- Solution: Using the Exterior Angle Theorem: 110° = 50° + y, where y is the measure of the other non-adjacent interior angle. Therefore, y = 110° - 50° = 60°.
Example 3: A more complex scenario
Imagine a triangle with an exterior angle and two interior angles unknown. We know the exterior angle is twice the value of one of the interior angles, and the remaining interior angle is 30 degrees greater than the first. How do we solve this?
First, let's define our variables: Let the first interior angle be 'x'. The exterior angle is then '2x', and the second interior angle is 'x + 30'.
Using the Exterior Angle Theorem: 2x = x + (x + 30) This simplifies to 2x = 2x + 30. This equation leads to a contradiction, indicating there's no solution that satisfies these conditions. This highlights how these theorems can also be used to prove the impossibility of certain geometric configurations.
Beyond the Theorems: Exploring Related Concepts
The Triangle Sum and Exterior Angle Theorems are interconnected with several other important geometric concepts:
-
Isosceles Triangles: In an isosceles triangle (two sides are equal), the two angles opposite the equal sides are also equal. The Triangle Sum Theorem can then be used to determine the measure of all three angles.
-
Equilateral Triangles: In an equilateral triangle (all three sides are equal), all three angles are equal and measure 60° (due to the Triangle Sum Theorem).
-
Congruent Triangles: The theorems aid in proving triangle congruence using various postulates (like ASA, SAS, SSS). Equal angles often play a crucial role in establishing congruence.
-
Similar Triangles: While not directly used in the proof, the angle relationships defined by these theorems are fundamental to understanding similar triangles (triangles with proportional sides and equal angles).
Practical Applications and Real-World Examples
The principles discussed here extend far beyond theoretical geometry. They find applications in various fields:
-
Architecture and Engineering: Understanding angles is crucial for building stable structures, calculating slopes, and designing effective architectural features.
-
Cartography and Surveying: Precise angle measurements are fundamental for creating accurate maps and surveying land.
-
Computer Graphics and Game Development: These theorems are essential for creating realistic 3D models and simulations, determining the orientation and perspective of objects.
-
Navigation and Aviation: Calculations involving angles are crucial for navigation, flight planning, and determining courses.
Conclusion: Mastering Triangle Geometry
The Triangle Sum and Exterior Angle Theorems represent foundational concepts in geometry. Understanding their proofs, applications, and relationships with other geometric principles is key to successfully solving a wide range of geometrical problems. By mastering these theorems, you'll strengthen your problem-solving skills and gain a deeper appreciation for the elegance and power of geometric reasoning. Remember to practice regularly, working through diverse problems to build your confidence and expertise in applying these crucial theorems. Continuous practice is the key to truly mastering the intricacies of triangle geometry.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Only Cloud Type Forecast In Taf Reports Is
Mar 21, 2025
-
The Scarlet Letter Summary Chapter 1
Mar 21, 2025
-
Core Curriculum Introductory Craft Skills Module 4 Answer Key
Mar 21, 2025
-
This Metamorphic Melange Is Formed Due To
Mar 21, 2025
-
Hesi Case Study Heart Failure With Atrial Fibrillation
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Worksheet Triangle Sum And Exterior Angle Theorem . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
