8.1 Intro To Insurance Answer Key
Onlines
Apr 04, 2025 · 7 min read
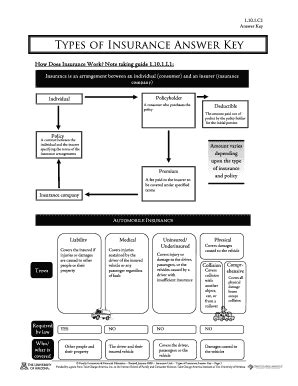
Table of Contents
8.1 Intro to Insurance: A Comprehensive Guide and Answer Key
Understanding insurance can feel like navigating a dense jungle of jargon and fine print. But grasping the core concepts is crucial for protecting yourself and your assets. This comprehensive guide will break down the fundamentals of insurance, providing explanations and addressing common questions, essentially acting as your own personal 8.1 Intro to Insurance answer key. We'll cover everything from the basic principles to different types of insurance, helping you become a more informed and confident consumer.
What is Insurance?
At its heart, insurance is a risk management tool. It's a contract (a policy) where an individual or entity (the insured) pays a fee (a premium) to an insurance company (the insurer) in exchange for financial protection against potential losses. The insurer agrees to compensate the insured for specified losses if a covered event (an insured peril) occurs. This transfer of risk from the individual to the company is the fundamental principle underpinning the entire insurance industry.
Think of it like this: you pay a small, predictable amount (the premium) to avoid the possibility of a large, unpredictable loss (an accident, illness, or other covered event). This predictability allows for financial planning and peace of mind.
Key Terms to Understand:
- Insured: The individual or entity who is covered by the insurance policy.
- Insurer: The insurance company providing the coverage.
- Premium: The periodic payment made by the insured to the insurer.
- Policy: The legal contract outlining the terms and conditions of the insurance coverage.
- Claim: A formal request made by the insured to the insurer for compensation following a covered loss.
- Deductible: The amount the insured must pay out-of-pocket before the insurer begins to cover expenses.
- Co-pay: A fixed amount an insured pays for a covered health care service.
- Co-insurance: The percentage of costs of a covered healthcare service that an insured pays after meeting their deductible.
- Peril: The cause of a possible loss (e.g., fire, theft, illness).
- Hazard: A condition that increases the chance of a peril occurring (e.g., faulty wiring increasing the risk of a fire).
- Risk: The chance or probability of a loss occurring.
Types of Insurance:
Insurance is a vast field encompassing numerous types of coverage. Here are some of the most common:
-
Auto Insurance: Protects against financial losses resulting from car accidents, including damage to your vehicle, injuries to yourself or others, and legal liability. This often includes liability coverage, collision coverage, comprehensive coverage, and uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage.
-
Homeowners/Renters Insurance: Protects your dwelling and belongings from various perils like fire, theft, and vandalism. Renters insurance is crucial even if you don't own your home, as it covers your personal belongings.
-
Health Insurance: Covers medical expenses, including doctor visits, hospital stays, and prescription drugs. Different plans offer varying levels of coverage and cost-sharing responsibilities.
-
Life Insurance: Provides financial protection for your beneficiaries in the event of your death. This can help cover funeral expenses, outstanding debts, and ongoing living expenses for your family.
-
Disability Insurance: Provides income replacement if you become unable to work due to illness or injury. This can help maintain your financial stability during a time of vulnerability.
-
Business Insurance: Protects businesses from a wide range of risks, including property damage, liability claims, and business interruption. This can include general liability, professional liability (errors and omissions), and workers' compensation.
How Insurance Works: A Step-by-Step Guide
-
Assessment of Risk: Insurance companies carefully assess the risk associated with insuring you. Factors like age, health, driving record, and location influence premiums.
-
Policy Purchase: You select a policy that meets your needs and budget. This involves choosing coverage levels and paying the premium.
-
Covered Event: An insured peril (e.g., a car accident, a house fire, a medical emergency) occurs.
-
Filing a Claim: You report the incident to your insurer and provide necessary documentation.
-
Investigation and Assessment: The insurer investigates the claim to determine the extent of the loss and whether it's covered by the policy.
-
Compensation: If the claim is approved, the insurer pays compensation according to the policy terms. This may involve paying for repairs, medical expenses, or other losses.
Factors Affecting Insurance Premiums:
Several factors influence the cost of your insurance premiums:
-
Risk Profile: Higher-risk individuals (e.g., those with poor driving records or pre-existing health conditions) typically pay higher premiums.
-
Coverage Amount: More extensive coverage usually results in higher premiums.
-
Deductible: A higher deductible generally leads to lower premiums, as you're accepting more financial responsibility for smaller losses.
-
Location: Insurance costs can vary significantly based on location, due to factors like crime rates and natural disaster frequency.
-
Credit Score (in some cases): In certain jurisdictions, your credit score can impact your insurance premiums.
8.1 Intro to Insurance: Sample Questions & Answers
Let's address some common questions to solidify your understanding. This section serves as a practical answer key for the fundamental concepts covered in a typical 8.1 introduction to insurance module.
Q1: What is the primary purpose of insurance?
A1: The primary purpose of insurance is to transfer risk from an individual or entity to an insurance company, providing financial protection against potential losses. It allows for managing unpredictable costs and maintaining financial stability.
Q2: Explain the difference between a peril and a hazard.
A2: A peril is the cause of a potential loss (e.g., fire, theft, illness), while a hazard is a condition that increases the likelihood of a peril occurring (e.g., faulty wiring increases the risk of a fire, poor health increases risk of illness).
Q3: What is a deductible? How does it affect your insurance premium?
A3: A deductible is the amount you must pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. A higher deductible typically leads to lower insurance premiums, as you are accepting more financial responsibility for smaller losses.
Q4: Describe the concept of "risk pooling" in insurance.
A4: Risk pooling is the fundamental principle where many individuals pay premiums into a common pool, allowing the insurer to pay for the losses of a few. This spreads the risk and makes insurance affordable.
Q5: Explain the difference between liability and collision coverage in auto insurance.
A5: Liability coverage protects you financially if you cause an accident that injures someone or damages their property. Collision coverage protects your vehicle if it's damaged in an accident, regardless of fault.
Q6: Why is it important to understand your insurance policy thoroughly?
A6: Understanding your policy is crucial to ensure you are adequately protected and to avoid surprises when you need to file a claim. Knowing your coverage limits, deductibles, exclusions, and other terms will prevent misunderstandings and potential disputes with your insurer.
Q7: What factors influence insurance premiums?
A7: Many factors influence premiums, including your risk profile (age, health, driving record), the amount of coverage you choose, your deductible, your location, and in some cases, your credit score.
Q8: What should you do if you're involved in an accident that requires filing an insurance claim?
A8: Immediately contact the authorities (police) if necessary, document the accident scene (take photos if safe), obtain contact information from involved parties, and promptly report the incident to your insurance company, following their instructions on how to file a claim. Provide all necessary documentation as requested.
Q9: What types of insurance are recommended for young adults just starting out?
A9: Young adults typically benefit from auto insurance, renters insurance (even if living with parents), and health insurance. Depending on their circumstances, life insurance can be a consideration as well.
Q10: How can I find affordable insurance?
A10: Shop around and compare quotes from multiple insurers. Consider increasing your deductible to lower your premiums, maintaining a good driving and credit record (where applicable), bundling insurance policies, and exploring different coverage options to find the best balance between cost and protection.
Conclusion:
Insurance can seem complex, but by understanding the core principles, common terms, and various types of insurance available, you can make informed decisions to protect yourself and your assets. Remember, this guide provides a foundation for your understanding; always consult with a professional insurance agent or broker for personalized advice tailored to your specific needs and circumstances. This guide serves as a valuable resource, acting as your comprehensive 8.1 Intro to Insurance answer key, empowering you to navigate the world of insurance with confidence. Remember to regularly review your policies to ensure they continue to meet your evolving needs. Proper insurance planning is a crucial component of responsible financial management.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Ap Computer Science Principles 2021 Practice Exam Mcq
Apr 04, 2025
-
Graphing Skill 1 What Type Of Graph Is It
Apr 04, 2025
-
The Axial Skeleton Review Sheet 8
Apr 04, 2025
-
Lesson 4 Homework Practice Powers Of Monomials Answer Key
Apr 04, 2025
-
Which Is A False Statement Of Electronic Records
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 8.1 Intro To Insurance Answer Key . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
