Algebra Nation Section 7 Exponential Functions Answers
Onlines
Mar 10, 2025 · 5 min read
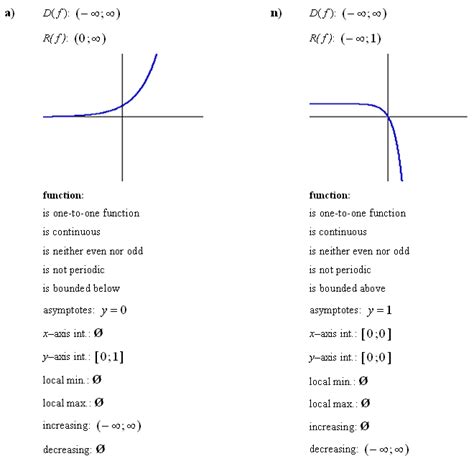
Table of Contents
Algebra Nation Section 7: Exponential Functions – A Comprehensive Guide
Algebra Nation's Section 7 on exponential functions is a crucial stepping stone in mastering algebra. This comprehensive guide will delve into the key concepts, providing detailed explanations, examples, and strategies to help you conquer this section. We'll explore the core ideas, tackle common problem types, and offer tips for improving your understanding and problem-solving skills.
Understanding Exponential Functions: The Fundamentals
An exponential function is a function where the independent variable (usually x) appears as an exponent. Its general form is f(x) = abˣ, where:
- 'a' represents the initial value or y-intercept (the value of the function when x=0).
- 'b' represents the base, which determines the rate of growth or decay. If b > 1, the function represents exponential growth; if 0 < b < 1, it represents exponential decay.
- 'x' is the independent variable (exponent).
Key Characteristics of Exponential Functions:
-
Growth/Decay Rate: The base 'b' dictates the rate at which the function grows or decays. A larger 'b' (greater than 1) indicates faster growth, while a smaller 'b' (between 0 and 1) signifies faster decay.
-
Asymptotes: Exponential functions have a horizontal asymptote. For exponential growth, the asymptote is the x-axis (y=0). For exponential decay, the asymptote is also the x-axis. The function approaches but never touches the asymptote.
-
Domain and Range: The domain of an exponential function is typically all real numbers (-∞, ∞). The range, however, depends on whether it's growth or decay and the value of 'a'. For growth functions with a > 0, the range is (0, ∞). For decay functions with a > 0, the range is also (0, ∞).
Types of Exponential Function Problems in Algebra Nation Section 7
Section 7 likely covers various problem types, including:
1. Evaluating Exponential Functions:
This involves substituting a value for x into the function f(x) = abˣ and calculating the corresponding output, f(x).
Example: Find f(2) if f(x) = 3(2ˣ).
Solution: Substitute x = 2 into the equation: f(2) = 3(2²) = 3(4) = 12
2. Graphing Exponential Functions:
Understanding how to graph exponential functions is essential. You'll need to identify key points, such as the y-intercept and a few other points to sketch an accurate graph.
Example: Graph the function f(x) = 2ˣ.
Solution: Start by finding the y-intercept: when x = 0, f(0) = 2⁰ = 1. So, (0, 1) is a point on the graph. Then find a few more points: When x = 1, f(1) = 2¹ = 2 (1, 2) When x = 2, f(2) = 2² = 4 (2, 4) When x = -1, f(-1) = 2⁻¹ = 1/2 (-1, 1/2) Plot these points and draw a smooth curve that approaches the x-axis (asymptote) as x becomes more negative.
3. Solving Exponential Equations:
Solving exponential equations involves finding the value of x that satisfies the equation. Often, this requires using properties of exponents or logarithms.
Example: Solve 2ˣ = 8.
Solution: Rewrite 8 as a power of 2: 8 = 2³. Therefore, 2ˣ = 2³, which means x = 3.
More complex example: Solve 3ˣ = 10.
Solution: Since we can't easily rewrite 10 as a power of 3, we use logarithms. Take the logarithm of both sides (base 10 or natural logarithm): log(3ˣ) = log(10). Using the logarithm property, we get x log(3) = 1. Solving for x, we have x = 1/log(3). Use a calculator to find the approximate value of x.
4. Word Problems Involving Exponential Functions:
Many real-world situations can be modeled using exponential functions. These problems might involve compound interest, population growth, radioactive decay, or other applications.
Example: A population of bacteria doubles every hour. If the initial population is 1000, what will the population be after 3 hours?
Solution: This is an exponential growth problem. The formula is P(t) = P₀ * 2ᵗ, where P(t) is the population after t hours, P₀ is the initial population, and t is the time in hours. P(3) = 1000 * 2³ = 1000 * 8 = 8000. The population will be 8000 after 3 hours.
5. Understanding Exponential Growth and Decay Models:**
These problems focus on identifying whether a situation represents exponential growth or decay and then applying the appropriate formula to solve the problem. Common formulas include:
- Exponential Growth: A = P(1 + r)ᵗ (A = final amount, P = principal amount, r = growth rate, t = time)
- Exponential Decay: A = P(1 - r)ᵗ (A = final amount, P = initial amount, r = decay rate, t = time)
Strategies for Mastering Algebra Nation Section 7
-
Practice Regularly: Consistent practice is key to mastering exponential functions. Work through numerous examples and problems.
-
Understand the Concepts: Don't just memorize formulas; understand the underlying principles behind exponential growth and decay.
-
Use Visual Aids: Graphs can significantly aid in understanding the behavior of exponential functions.
-
Seek Help When Needed: Don't hesitate to ask for help from teachers, tutors, or classmates if you're struggling with specific concepts.
-
Break Down Complex Problems: Divide complex problems into smaller, manageable steps.
-
Review Your Mistakes: Analyze your errors to understand where you went wrong and avoid repeating those mistakes.
Advanced Concepts and Extensions (Potentially Covered in Later Sections)
Algebra Nation might also introduce more advanced topics related to exponential functions in subsequent sections, such as:
-
Logarithmic Functions: These are inverse functions of exponential functions, and understanding them is crucial for solving more complex exponential equations.
-
Natural Exponential Function (eˣ): The base e (Euler's number) is a special constant used in many applications involving continuous growth or decay.
-
Applications in Calculus: Exponential functions play a vital role in calculus, particularly in differential and integral calculus, for modeling rates of change and accumulation.
Conclusion
Algebra Nation Section 7 on exponential functions provides a strong foundation for further studies in algebra and beyond. By understanding the core concepts, practicing regularly, and utilizing the strategies outlined above, you can successfully navigate this section and develop a solid grasp of exponential functions and their applications. Remember, consistent effort and a deep understanding of the underlying principles are essential for achieving mastery. Good luck!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Correctly Label The Following Tissues Of The Digestive Tract
Mar 10, 2025
-
Book 2 Questiosn V For Vendetta
Mar 10, 2025
-
Primary Claims Submission Includes A Patient Who Has Coverage By
Mar 10, 2025
-
Ojala Qu4e Las Fabricas Dejen De
Mar 10, 2025
-
Moles And Chemical Formulas Report Sheet Answers
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Algebra Nation Section 7 Exponential Functions Answers . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
