Centroamérica Es Una Zona De Pocos Volcanes.
Onlines
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
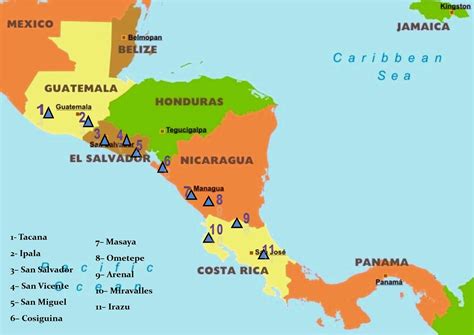
Table of Contents
Central America: A Region of Few Volcanoes? Debunking the Myth
The statement "Central America is a region of few volcanoes" is demonstrably false. In reality, Central America boasts a remarkably high density of volcanoes, forming a significant part of the geologically active Pacific Ring of Fire. This volcanic activity has profoundly shaped the region's landscape, culture, and even its climate. Understanding the reality of Central America's volcanism requires a deeper dive into its geological history, the types of volcanoes present, and the ongoing risks and benefits associated with this fiery landscape.
The Myth of Scarcity: Why the Misconception Exists
The misconception that Central America has few volcanoes might stem from a few factors. Firstly, the sheer size of the continent might lead to a relative perception of low density. Compared to the vast expanse of North or South America, the relatively narrow isthmus of Central America may seem to have a smaller number of volcanoes. Secondly, many people may be unaware of the extent of submerged or inactive volcanic features, which contribute significantly to the overall volcanic count. Finally, the dramatic visual impact of major volcanic eruptions in other parts of the world could overshadow the less frequent, yet still significant, volcanic activity in Central America.
The Ring of Fire Reality: A Tectonic Hotspot
Central America sits squarely on the Ring of Fire, a zone of intense seismic and volcanic activity circling the Pacific Ocean. This geological phenomenon is caused by the subduction of the Cocos and Nazca tectonic plates beneath the Caribbean plate. As these plates collide, immense pressure builds up, melting rock and creating magma that rises to the surface, forming volcanoes. This continuous process results in a chain of volcanoes running along the western edge of Central America, forming a dramatic and visually stunning landscape.
Types of Volcanoes in Central America: A Diverse Landscape
Central America is home to a variety of volcanic types, each with unique characteristics. These include:
-
Stratovolcanoes: These are the most common type in Central America, characterized by their steep slopes and layered structure of alternating lava flows, ash, and tephra. Famous examples include Volcán de Fuego in Guatemala and Arenal Volcano in Costa Rica. These volcanoes are often associated with explosive eruptions.
-
Shield Volcanoes: While less common than stratovolcanoes, shield volcanoes are also present. These are characterized by their broad, gently sloping sides formed by the accumulation of fluid lava flows.
-
Calderas: These large, basin-shaped depressions are formed by the collapse of a volcano after a massive eruption. They can be filled with water, creating stunning crater lakes, as seen in the case of Laguna de Apoyo in Nicaragua.
-
Lava Domes: These smaller, dome-shaped features are formed by the slow extrusion of viscous lava. They can often be found within or on the flanks of larger volcanoes.
Key Volcanic Regions: A Detailed Overview
The distribution of volcanoes isn't uniform across Central America. Certain regions concentrate a higher density of these impressive features:
-
Guatemala: This country boasts a significant number of volcanoes, including the highly active Volcán de Fuego and Pacaya, which frequently erupt, offering a dramatic display of nature's power. The landscape is punctuated by volcanic peaks that shape the country's geography and influence its fertile agricultural lands.
-
El Salvador: El Salvador also possesses a notable concentration of volcanoes along its Pacific coast, with some showing signs of recent activity. These volcanoes contribute to the nation's unique topography.
-
Nicaragua: Nicaragua features several prominent volcanoes, some of which are located near large lakes, adding to the picturesque landscape. Momotombo and Masaya are amongst the most well-known active volcanoes in this region.
-
Costa Rica: While having fewer active volcanoes compared to its northern neighbors, Costa Rica possesses iconic volcanoes like Arenal, a classic cone-shaped stratovolcano known for its dramatic lava flows (historically) and breathtaking scenery. Poás Volcano, with its impressive crater lake, further illustrates the region's rich volcanic history.
-
Panama: While Panama has fewer active volcanoes than the other countries, its volcanic history is still evident in the geological formations and the presence of extinct volcanoes.
The Impact of Volcanoes: Beyond the Spectacle
The impact of volcanoes in Central America extends far beyond the visually stunning landscapes they create. Their influence permeates various aspects of life in the region:
-
Fertile Soil: Volcanic eruptions deposit nutrient-rich ash and minerals into the soil, creating exceptionally fertile land ideal for agriculture. This volcanic soil contributes significantly to the region's agricultural production and supports diverse ecosystems.
-
Geothermal Energy: The heat generated by volcanic activity can be harnessed to produce geothermal energy, a renewable and sustainable source of power. This is a growing area of development in Central America.
-
Tourism: The dramatic beauty of Central America's volcanoes attracts a significant number of tourists annually, boosting the regional economy. Volcano hiking, exploration of crater lakes, and observation of volcanic activity are popular tourist activities.
-
Natural Hazards: While beneficial in many ways, volcanoes also pose significant hazards. Volcanic eruptions can release devastating pyroclastic flows, lahars (volcanic mudflows), and ash clouds, posing risks to human life, infrastructure, and agriculture. Regular monitoring and disaster preparedness are crucial for mitigating these risks.
Volcanic Monitoring and Risk Mitigation
Given the significant volcanic activity in Central America, robust monitoring systems are essential. Specialized institutions utilize a range of tools and techniques to track seismic activity, gas emissions, and ground deformation, allowing for early warning systems that help protect populations and infrastructure. This proactive approach minimizes the impacts of potential eruptions and promotes community resilience. Educational programs also play a crucial role in raising awareness about volcanic hazards and promoting preparedness among the local populations.
Conclusion: A Region Shaped by Fire
The statement that Central America has few volcanoes is a profound misunderstanding. The region's volcanic landscape is a defining feature, shaping its geography, supporting its agriculture, driving its economy, and posing ongoing challenges to its inhabitants. By understanding the dynamic interplay of geological forces, acknowledging the risks, and embracing the benefits, Central America can continue to thrive in its unique, volcanic environment. The region's story is one of coexistence with nature’s power, where the spectacular beauty of its volcanoes is intricately woven into the fabric of its history and future. The volcanoes are not just a feature of the landscape; they are the heart of Central America's identity. Further research and ongoing monitoring remain crucial in understanding this complex relationship and ensuring the safety and prosperity of its people.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
You Have Just Been Hired As The Assistant Manager
Mar 17, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Linux File Systems Support Journaling
Mar 17, 2025
-
Medical Surgical Lpn Rn Assessment 1 Shiftkey Answers
Mar 17, 2025
-
Project Stem 7 4 Code Practice Question 1
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Type Of Pay Is Modeled Below
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Centroamérica Es Una Zona De Pocos Volcanes. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
