Match Each Checkpoint With The Action It Checks For
Onlines
Mar 16, 2025 · 6 min read
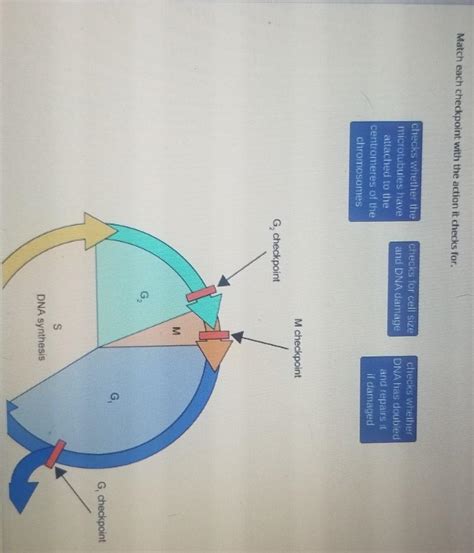
Table of Contents
Match Each Checkpoint With the Action It Checks For: A Comprehensive Guide to Checkpoint Security
Checkpoints, whether physical or digital, are crucial for ensuring security and control. Understanding what each checkpoint checks for is vital for maintaining effective security measures. This comprehensive guide delves into various types of checkpoints, detailing the specific actions and procedures they verify. We'll explore the logic behind these checks and how they contribute to overall security.
Understanding the Purpose of Checkpoints
Before diving into specific examples, it's essential to grasp the overarching purpose of checkpoints. They serve as gatekeepers, strategically placed to:
- Prevent unauthorized access: This is the primary function, blocking individuals or entities lacking proper authorization.
- Identify threats: Checkpoints act as a first line of defense in identifying potential risks, including weapons, contraband, or malicious actors.
- Enforce regulations: They ensure adherence to rules and regulations, whether related to security, health, or other compliance requirements.
- Monitor activity: Checkpoints provide a record of who or what passed through, aiding in investigations and accountability.
Types of Checkpoints and Their Corresponding Actions
Checkpoints vary significantly depending on their context. Let's examine several common types and the specific actions they perform:
1. Airport Security Checkpoints
Airport security checkpoints are arguably the most familiar type. Their primary goal is to prevent terrorism and other threats to aviation safety. The actions checked for include:
- Identity Verification: Passengers must present valid identification, usually a passport or driver's license, to confirm their identity and match it to their boarding pass.
- Baggage Screening: Both carry-on and checked baggage undergo rigorous screening using X-ray machines and potentially manual searches to detect prohibited items like weapons, explosives, and flammable materials. This is a critical checkpoint to ensure no dangerous items are brought on board the aircraft. The process aims to mitigate risks associated with both intentional and unintentional introduction of hazardous substances.
- Metal Detection: Passengers walk through metal detectors to screen for metallic objects that could be used as weapons. This is a swift and efficient method for detecting metallic threats. Those triggering the alarm undergo further screening.
- Liquid Restrictions: Passengers are subject to regulations regarding the type and quantity of liquids they can carry in their carry-on luggage. This limits the potential for liquid explosives to be brought on board.
- Explosive Trace Detection: This process involves swabbing passengers' hands and baggage to detect traces of explosives. This is a supplementary check that increases the probability of detecting explosives, even if they are hidden.
2. Border Control Checkpoints
Border control checkpoints are critical for national security and immigration enforcement. The actions checked for often include:
- Passport and Visa Checks: Travelers must present valid passports and visas, if required, to prove their identity and legal right to enter the country. This involves verifying the authenticity of documents and checking for any outstanding issues.
- Customs Declaration: Travelers must declare any goods they are carrying that may be subject to import duties, taxes, or restrictions. This process aims to control the flow of goods and prevent smuggling.
- Immigration Status: Officers verify the traveler's immigration status, ensuring compliance with immigration laws and regulations. This includes checking for any overstays or violations.
- Criminal Background Checks: In some cases, border control agents may conduct criminal background checks to identify individuals with a history of criminal activity who pose a threat to national security.
- Biometric Screening: Increasingly, biometric screening, such as fingerprint or facial recognition, is used to verify identity and detect potential imposters.
3. Military Checkpoints
Military checkpoints, often found in conflict zones or areas with heightened security concerns, have a primary focus on safety and security of military personnel and installations. The actions checked for include:
- Identification and Authorization: Personnel must present valid military identification and authorization to access restricted areas. This confirms their identity and clearance level.
- Vehicle Inspection: Vehicles are often thoroughly inspected for weapons, explosives, or contraband. This is crucial for preventing the introduction of unauthorized materials into sensitive areas.
- Security Clearance Verification: Access to specific areas within a military base may require more stringent security clearance verification beyond basic identification.
- Weapons and Equipment Checks: Military personnel are subject to checks of their weapons and equipment to ensure they are properly secured and accounted for.
- Suspicious Activity Monitoring: Military personnel at checkpoints are trained to identify and report any suspicious activity, such as unusual behavior or suspicious packages.
4. Cybersecurity Checkpoints (Network Security)
In the digital realm, cybersecurity checkpoints play a vital role in protecting computer networks and systems. These checkpoints, often implemented through firewalls and intrusion detection systems, check for:
- Unauthorized Access Attempts: These checkpoints monitor network traffic for attempts to access systems or data without proper authorization. This is crucial for preventing unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Malware and Virus Detection: Checkpoints scan incoming traffic for malicious software like viruses, worms, and Trojans, preventing their entry into the network.
- Data Integrity Checks: Checkpoints verify the integrity of data transmitted across the network, ensuring it hasn't been tampered with or corrupted.
- Intrusion Detection: These checkpoints monitor network activity for patterns indicative of intrusion attempts, such as unauthorized login attempts or unusual network traffic.
- Authentication and Authorization: These checkpoints verify the identity of users and devices attempting to access the network, ensuring only authorized entities gain access.
5. Building Security Checkpoints
Building security checkpoints, commonly found in office buildings, government facilities, or other high-security locations, prioritize the safety and security of the building’s occupants and assets. The actions checked for typically include:
- Access Card or Key Verification: Employees or visitors may need to present an access card or key to gain entry. This verifies their authorization to enter the building or specific areas within it.
- Visitor Registration: Visitors typically need to register at a reception desk, providing their identification and the purpose of their visit. This allows for tracking and accountability.
- Baggage Screening: Depending on the security level, bags may be subject to visual inspection or screening using X-ray machines.
- Metal Detection: Similar to airport security, metal detectors may be used to screen individuals for weapons.
- Security Camera Monitoring: Checkpoints often involve security cameras that monitor activity, providing a visual record of who entered and when.
The Importance of Effective Checkpoint Procedures
The effectiveness of checkpoints relies heavily on well-defined procedures and adequately trained personnel. Key aspects include:
- Clear and Consistent Procedures: Standardized procedures ensure that all checkpoints operate consistently, minimizing the risk of errors or inconsistencies.
- Trained Personnel: Personnel at checkpoints need thorough training on procedures, security protocols, and how to identify potential threats.
- Regular Audits and Reviews: Regular audits and reviews of checkpoint procedures help identify weaknesses and improve effectiveness.
- Technology Integration: The integration of technology, such as biometric scanners or advanced screening equipment, can significantly enhance the effectiveness of checkpoints.
- Adaptability to Evolving Threats: Checkpoints need to be adaptable to evolving threats and security challenges, incorporating new technologies and techniques as needed.
Conclusion
Checkpoints are an essential part of maintaining security across various domains. Understanding the specific actions each checkpoint checks for is critical for maximizing their effectiveness. From airport security to cybersecurity, effective checkpoints, coupled with well-trained personnel and adaptable procedures, form a critical layer of defense against unauthorized access, threats, and breaches. The continuous evaluation and improvement of checkpoint procedures remain crucial in maintaining a secure and controlled environment.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Participant Motivation Is Usually The Result Of
Mar 17, 2025
-
All Flags Such As Porn And Upsetting Offensive Are Query Independent
Mar 17, 2025
-
An Electrical Motor Provides 0 50 W Of Mechanical Power
Mar 17, 2025
-
Studying Marketing Should Help You To Blank
Mar 17, 2025
-
Shaping Clay On A Rapidly Turning Wheel Is Called
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Match Each Checkpoint With The Action It Checks For . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
