Satellites Can Be Used To Study Faults By ______.
Onlines
Mar 17, 2025 · 7 min read
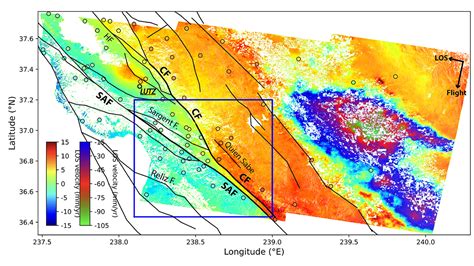
Table of Contents
Satellites Can Be Used to Study Faults by Remote Sensing Techniques
Earth's surface is a tapestry of geological features, many of which hold clues to the planet's dynamic history. Faults, fractures in the Earth's crust where tectonic plates meet and move, are among the most significant of these features. Understanding faults is crucial for predicting earthquakes, managing geological hazards, and unraveling the complexities of plate tectonics. Traditionally, fault studies relied heavily on ground-based surveys, which are time-consuming, expensive, and often limited in scope. However, the advent of satellite technology has revolutionized this field, offering a powerful new tool for investigating faults across vast areas with unprecedented detail. Satellites can be used to study faults by employing a range of remote sensing techniques, providing invaluable data for geological research and hazard assessment.
The Power of Remote Sensing in Fault Studies
Remote sensing, the acquisition of information about an object or phenomenon without making physical contact, harnesses the power of electromagnetic radiation to observe the Earth's surface. Satellites, orbiting high above, act as sophisticated sensors, capturing data across diverse wavelengths, from visible light to infrared and radar. This diverse data allows geologists to detect subtle surface features indicative of fault activity, analyze deformation patterns, and monitor changes over time, yielding a comprehensive understanding of fault characteristics.
1. Optical Imagery: Unveiling Surface Expressions
Optical imagery, obtained from satellites equipped with multispectral and hyperspectral sensors, provides valuable insights into surface features associated with faults. These sensors capture images in various wavelengths of visible and near-infrared light, revealing subtle variations in color and tone that reflect differences in rock type, vegetation, and soil moisture.
- Lineaments: Faults often manifest as linear features, known as lineaments, on the Earth's surface. Optical imagery, with its high spatial resolution, allows geologists to identify these lineaments, even in heavily vegetated or sparsely populated areas. The analysis of lineament patterns helps to map fault zones, delineate their extent, and understand their geometry.
- Displacement Features: Faults can cause distinct offsets in surface features, such as streams, roads, or geological formations. Optical imagery facilitates the precise measurement of these displacements, providing quantitative data about fault slip and movement. This analysis is especially critical for assessing the potential for future seismic activity.
- Geomorphic Indicators: Faults often create characteristic landforms, such as scarps (steep slopes), fault valleys, and sag ponds. Optical imagery allows geologists to identify and map these geomorphic indicators, helping to delineate fault traces and understand their evolution.
2. Radar Imagery: Piercing Through the Clouds and Vegetation
Unlike optical imagery, which relies on sunlight for illumination, radar (Radio Detection and Ranging) imagery can penetrate clouds, vegetation, and even some types of soil. This makes radar a valuable tool for studying faults in areas with persistent cloud cover or dense vegetation, providing invaluable data where optical imagery is limited.
- InSAR (Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar): InSAR is a particularly powerful technique that uses radar data from multiple satellite passes to measure ground deformation with millimeter-level accuracy. By comparing images acquired at different times, InSAR can detect subtle ground movement associated with fault creep, slow slip events, or the build-up of strain before an earthquake. This is crucial for monitoring active faults and assessing seismic hazard.
- Polarimetric Radar: This advanced technique uses different polarizations of radar waves to gather information about the surface roughness and scattering properties of the terrain. This information can help to identify subtle changes in surface characteristics related to faulting, such as changes in soil moisture or vegetation density, which may precede or accompany fault activity.
3. Thermal Infrared Imagery: Detecting Heat Anomalies
Thermal infrared imagery captures the heat emitted by the Earth's surface. Faults can generate thermal anomalies due to various processes, including friction during fault movement, hydrothermal activity, or changes in subsurface heat flow. Analyzing thermal infrared data can help to identify active faults and understand the underlying processes driving fault activity.
- Identifying Geothermal Activity: Faults often act as conduits for geothermal fluids, leading to elevated temperatures at the surface. Thermal infrared imagery can identify these thermal anomalies, providing clues to the location and activity of geothermal systems associated with faults.
- Monitoring Volcanic Activity: Faults play a significant role in volcanic activity, often acting as pathways for magma ascent. Thermal infrared imagery is instrumental in monitoring volcanic activity, detecting changes in heat flux, and assessing the potential for eruptions, particularly in areas with obscured surface features.
Applications of Satellite Fault Studies
The data obtained through satellite remote sensing has a wide array of practical applications in various fields:
- Earthquake Hazard Assessment: By mapping active faults and monitoring their movement, satellite data is crucial for assessing earthquake hazard. This information is vital for land-use planning, building codes, and emergency response strategies. InSAR, in particular, provides real-time monitoring capabilities, allowing scientists to detect precursory signals before earthquakes.
- Oil and Gas Exploration: Faults often act as pathways for hydrocarbon migration, making them important targets for oil and gas exploration. Satellite imagery helps geologists identify and characterize faults, guiding exploration efforts and reducing exploration risks.
- Geotechnical Engineering: Understanding the location and characteristics of faults is essential for geotechnical engineering projects, such as dam construction, tunnel excavation, and infrastructure development. Satellite data assists engineers in identifying potential geological hazards and designing safer and more sustainable structures.
- Landslide Hazard Assessment: Faults can destabilize slopes, increasing the risk of landslides. Satellite imagery helps to identify areas prone to landslides, facilitating mitigation efforts and minimizing risks to life and property.
- Mineral Exploration: Some ore deposits are associated with faults, making fault mapping crucial for mineral exploration. Satellite imagery helps to identify potential mineralized zones, guiding exploration and reducing exploration costs.
Limitations and Challenges
While satellite remote sensing offers numerous advantages, it's essential to acknowledge its limitations:
- Resolution Limitations: The resolution of satellite imagery can limit the detection of smaller faults or subtle deformation features. Higher-resolution data is often more expensive and may not be available for all areas.
- Data Processing and Interpretation: Analyzing satellite data requires specialized expertise and software. Interpreting the data correctly and avoiding misinterpretations is crucial for accurate fault characterization.
- Atmospheric Effects: Atmospheric conditions, such as cloud cover, can affect the quality of satellite imagery. In areas with persistent cloud cover, radar imagery is a more suitable option, but it also has its limitations.
- Ground Truthing: While satellite data provides a broad overview, it's essential to validate the findings through ground-based surveys (ground truthing). This helps to ensure the accuracy of the interpretations and provides a more complete understanding of the fault system.
The Future of Satellite Fault Studies
Satellite technology continues to advance, with higher-resolution sensors, improved data processing techniques, and the development of new remote sensing methods emerging constantly. This progress will further enhance the capabilities of satellite remote sensing in fault studies, leading to:
- More accurate fault mapping: Higher-resolution imagery and advanced processing techniques will allow for more precise mapping of faults, even in complex geological settings.
- Improved earthquake prediction: Real-time monitoring using InSAR and other techniques will provide more accurate insights into fault behavior and improve our ability to predict earthquakes.
- Better understanding of fault processes: Combining different remote sensing techniques and integrating them with other datasets will provide a more holistic understanding of the processes driving fault activity.
- Enhanced geological hazard assessment: This improved understanding will lead to more effective strategies for managing geological hazards and mitigating their impacts.
In conclusion, satellite remote sensing has revolutionized fault studies, providing a powerful tool for investigating these critical geological features. By employing a range of techniques, from optical and radar imagery to thermal infrared sensing, geologists can map faults, monitor their movement, and assess associated hazards with unprecedented detail. While challenges remain, ongoing technological advancements promise even greater accuracy and insights into the dynamic processes shaping our planet, ultimately contributing to improved hazard mitigation and a better understanding of Earth's complex geological history. The future of fault studies is undeniably linked to the continued advancements and wider applications of satellite remote sensing technology.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
You Have Just Been Hired As The Assistant Manager
Mar 17, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Linux File Systems Support Journaling
Mar 17, 2025
-
Medical Surgical Lpn Rn Assessment 1 Shiftkey Answers
Mar 17, 2025
-
Project Stem 7 4 Code Practice Question 1
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Type Of Pay Is Modeled Below
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Satellites Can Be Used To Study Faults By ______. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
