Shadow Health Tina Jones Comprehensive Assessment Subjective Data
Onlines
Mar 31, 2025 · 7 min read
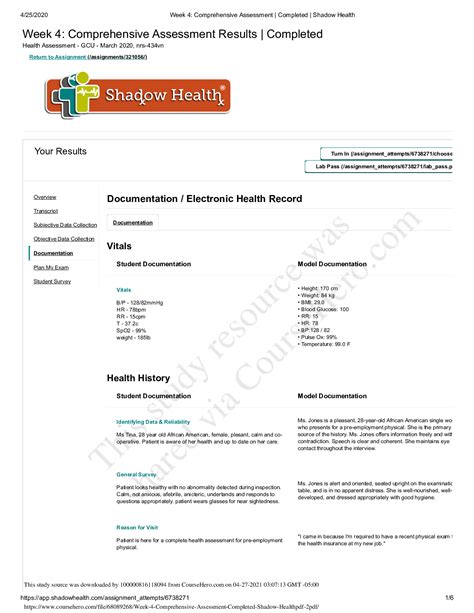
Table of Contents
Shadow Health Tina Jones Comprehensive Assessment: Subjective Data Deep Dive
Keywords: Shadow Health, Tina Jones, comprehensive assessment, subjective data, nursing assessment, health history, patient interview, virtual patient simulator, clinical skills, medical terminology, review of systems, chief complaint, history of present illness, past medical history, family history, social history, patient education.
This in-depth guide provides a thorough exploration of the subjective data gathered during a comprehensive assessment of Tina Jones within the Shadow Health virtual patient simulator. We will meticulously dissect each component of the subjective data, highlighting crucial information and its clinical significance. Understanding Tina Jones' subjective data is vital for developing a comprehensive care plan and accurately diagnosing her condition. This guide is intended for nursing students and healthcare professionals seeking to improve their patient assessment and clinical reasoning skills.
Understanding the Subjective Data Gathering Process
Before diving into Tina Jones' specific details, let's establish the fundamental principles of collecting subjective data. Subjective data encompasses information reported by the patient, their family, or caregivers. This is in contrast to objective data, which is gathered through observation and examination. Collecting reliable subjective data relies heavily on effective communication, active listening, and the ability to ask open-ended and focused questions. In the Shadow Health simulation, this involves skillfully navigating the virtual interview to elicit relevant information from Tina Jones.
Tina Jones' Chief Complaint and History of Present Illness (HPI)
Tina Jones' chief complaint usually revolves around symptoms related to her specific scenario in the simulation. This is the primary reason she has sought medical attention. For instance, she might present with chest pain, shortness of breath, abdominal pain, or other significant symptoms. The HPI then delves deeper into the onset, character, location, duration, severity, pattern, associated symptoms, alleviating factors, and aggravating factors of her chief complaint.
Analyzing the HPI is crucial because it:
- Identifies the primary problem: It pinpoints the main issue requiring medical attention.
- Provides context: It paints a picture of how the problem has developed over time.
- Guides further assessment: It informs the direction of the physical exam and diagnostic testing.
- Supports diagnosis: It helps build a differential diagnosis and ultimately guide treatment.
For example, if Tina Jones presents with chest pain, the HPI will explore whether the pain is sharp, dull, aching, or crushing; its location (e.g., substernal, radiating to the arm); the duration of the pain; its relationship to activity; and any associated symptoms like shortness of breath, diaphoresis, or nausea. This detailed information is crucial in differentiating between, for example, angina, a myocardial infarction, or musculoskeletal pain.
Review of Systems (ROS) in Tina Jones' Assessment
The review of systems (ROS) is a systematic inquiry into each body system to uncover additional symptoms or concerns the patient may not have volunteered during the HPI. The ROS is crucial for identifying potential comorbidities and clues that might otherwise be missed. A comprehensive ROS in the Shadow Health Tina Jones simulation typically covers:
- General: Overall health, weight changes, fatigue, fever, chills.
- Skin: Rashes, lesions, changes in skin color or texture.
- HEENT: Headaches, vision changes, hearing loss, ear pain, nasal congestion, sore throat, mouth sores.
- Respiratory: Cough, shortness of breath, wheezing, chest pain.
- Cardiovascular: Chest pain, palpitations, shortness of breath, edema.
- Gastrointestinal: Abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, changes in bowel habits.
- Neurological: Headaches, dizziness, weakness, numbness, tingling, seizures, changes in mental status.
- Musculoskeletal: Joint pain, muscle weakness, stiffness, back pain.
- Endocrine: Changes in weight, thirst, urination, heat or cold intolerance.
- Hematologic/Lymphatic: Easy bruising or bleeding, swollen lymph nodes.
- Renal/Urologic: Changes in urination, pain with urination, kidney pain.
- Psychiatric: Mood changes, anxiety, depression, suicidal ideation.
Each system needs careful questioning to unearth relevant details. For example, within the cardiovascular ROS, understanding the character, location, radiation, and associated symptoms of chest pain, alongside any history of cardiac issues, provides invaluable insights.
Past Medical History (PMH) and Medication Reconciliation
The PMH section provides critical background information on Tina Jones' previous health conditions, surgeries, hospitalizations, and allergies. This information helps contextualize her current symptoms and assess potential interactions between her present condition and past medical history. A complete PMH will include dates, details of treatment received, and the outcome of each condition or procedure.
Medication reconciliation is an essential part of the PMH. This involves carefully reviewing all medications Tina Jones is currently taking, including prescription drugs, over-the-counter medications, herbal remedies, and supplements. This is crucial for identifying potential drug interactions, adverse effects, and adherence issues.
Family History (FH) Significance
The family history explores the health status of Tina Jones' immediate family members (parents, siblings, children). This is important because certain diseases have a genetic predisposition. Identifying a family history of conditions like heart disease, cancer, diabetes, or mental health disorders can help assess Tina Jones' risk factors and inform preventative strategies.
Social History (SH) - Lifestyle Factors
The social history provides information about Tina Jones' lifestyle factors that may influence her health. This includes:
- Occupation: This can reveal exposure to occupational hazards.
- Lifestyle: Diet, exercise, smoking, alcohol consumption, recreational drug use.
- Living Situation: This influences social support and access to resources.
- Marital Status: This affects social support and emotional well-being.
- Safety: Assessing risk for domestic violence, abuse, or neglect.
- Cultural beliefs: This influences health practices and perceptions of illness.
Gathering a thorough social history is paramount because these lifestyle factors significantly influence overall health and contribute to many chronic conditions. For instance, a history of smoking heavily increases the risk of lung cancer and cardiovascular disease.
Mental Health Assessment
A crucial component often overlooked is a thorough mental health assessment. This includes:
- Mood: Assessing current mood, including feelings of sadness, anxiety, or irritability.
- Affect: Observing the patient's emotional expression.
- Thought Processes: Evaluating the organization and coherence of their thoughts.
- Cognitive Function: Assessing memory, concentration, and orientation.
- Suicidal/Homicidal Ideation: Directly inquiring about thoughts of self-harm or harming others.
This is particularly important in cases where mental health issues may contribute to or exacerbate physical symptoms.
Spiritual and Cultural Considerations
Respecting Tina Jones' spiritual and cultural background is vital. This involves:
- Religious beliefs: Understanding how their beliefs may influence their healthcare decisions.
- Cultural practices: Acknowledging any cultural practices relevant to their health.
- Support system: Identifying family and community resources that provide support.
This demonstrates respect and helps establish rapport, leading to more accurate and effective healthcare delivery.
Synthesizing Subjective Data for Clinical Reasoning
After collecting all the subjective data, the crucial step is synthesizing it to form a coherent picture of Tina Jones' health status. This involves identifying patterns, inconsistencies, and potential connections between different pieces of information. This process forms the basis for developing a differential diagnosis and forming a comprehensive plan of care.
For example: If Tina Jones reports chest pain, shortness of breath, and a family history of heart disease, coupled with a lifestyle that includes smoking and lack of exercise, it significantly increases the probability of cardiovascular issues. This synthesis of subjective data informs the subsequent objective examination and diagnostic testing.
The Importance of Documentation
Accurate and thorough documentation of all subjective data is crucial. This forms a permanent record of the patient's encounter and ensures continuity of care. Effective documentation includes clear, concise language, using appropriate medical terminology, and avoiding subjective opinions or interpretations. Proper documentation is vital for legal and ethical reasons.
Conclusion: Mastering Subjective Data Collection with Shadow Health Tina Jones
The Shadow Health Tina Jones simulation provides an invaluable opportunity to practice collecting and interpreting subjective data. By meticulously focusing on the chief complaint, history of present illness, review of systems, past medical history, family history, social history, and incorporating essential mental health and cultural considerations, you'll develop the critical skills necessary for conducting effective patient interviews and making accurate clinical judgments. Through consistent practice and thoughtful analysis of the information gathered, you'll build confidence in your assessment skills and contribute to providing the highest quality patient care. Remember, a strong foundation in subjective data collection is essential for providing holistic and effective patient care.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Amoeba Sisters Video Recap Dihybrid Crosses
Apr 02, 2025
-
Family Furniture Corporation Incurred The Following Costs
Apr 02, 2025
-
For Which Client Is Hair Molding The Best Setting Technique
Apr 02, 2025
-
Catcher In The Rye Summary Chapter 6
Apr 02, 2025
-
Angle Of Elevation And Depression Trig Worksheet
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Shadow Health Tina Jones Comprehensive Assessment Subjective Data . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
