The Figure Shows The Supply And Demand For Online Music
Onlines
Mar 16, 2025 · 6 min read
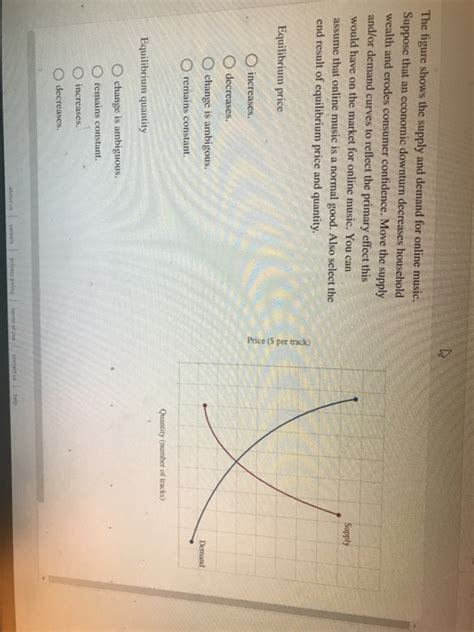
Table of Contents
Decoding the Digital Soundscape: A Deep Dive into the Supply and Demand of Online Music
The vibrant world of online music presents a fascinating case study in the interplay of supply and demand. Understanding this dynamic is crucial for artists, labels, streaming services, and even listeners themselves. This article will delve into the complexities of this market, exploring the factors that shape supply, the forces driving demand, and the resulting equilibrium (or lack thereof) that defines the online music landscape.
The Supply Side: A Symphony of Sources
The supply of online music is surprisingly multifaceted. It's not simply a matter of artists uploading their tracks; it involves a complex ecosystem of players, each contributing to the overall availability of music online.
1. Independent Artists: The rise of digital distribution platforms has empowered independent artists like never before. They can bypass traditional record labels, directly uploading their music to services like Spotify, Apple Music, Bandcamp, and YouTube Music. This democratization of music distribution has significantly increased the supply of online music, offering consumers a vast array of genres, styles, and artistic expressions often overlooked by major labels. The key advantage for independent artists is complete control over their creative vision and revenue streams. However, the challenge lies in marketing and promotion, a significant hurdle that often requires considerable investment in time, effort, and possibly funds.
2. Major Record Labels: While their dominance might seem challenged by the indie surge, major labels still control a substantial portion of the music supply. They possess the resources for extensive marketing campaigns, artist development, and global distribution networks, ensuring their artists reach a wider audience. However, their business model, often focused on a small number of high-profile acts, can lead to a less diverse catalog compared to the indie sector. Their involvement often comes with strict contracts that can limit artistic freedom for the sake of maximizing profits.
3. Music Publishers: Beyond the recording itself, the musical composition (the song itself) is a separate entity with its own commercial value. Music publishers manage the copyright and licensing of musical works, making them a crucial part of the music supply chain. They handle synchronization licenses for use in film, television, and advertising, representing an essential income stream for songwriters and composers.
4. Streaming Services Themselves: Platforms like Spotify and Apple Music are not passive conduits; they actively curate playlists, recommend music, and even commission original content, impacting the overall supply. Their algorithms and editorial decisions effectively shape the music landscape, influencing listener exposure and the visibility of different artists and genres.
The Demand Side: A Chorus of Consumers
The demand for online music is undeniably robust, fuelled by several key factors:
1. Convenience and Accessibility: The ease of access to millions of songs via streaming services is a major driver of demand. Consumers can listen to music anytime, anywhere, with minimal friction. This convenience has replaced physical media and even illegal downloading for many. This ease of access fosters discovery. Users are more likely to explore new artists and genres when the barrier to entry is so low.
2. Price Point: The subscription model of most major streaming platforms represents a significant value proposition for consumers. For a relatively low monthly fee, users gain access to a vast library of music, making it more affordable than purchasing individual albums or songs. This accessibility broadens the consumer base to those who might not have been able to afford significant music purchases previously.
3. Social Influence: Music is deeply intertwined with social identity and cultural trends. Streaming services often incorporate social features, allowing users to share their listening habits with friends and engage in discussions about music. This social aspect fuels demand by creating a sense of community and encouraging music discovery through shared experiences.
4. Personalization and Recommendation Algorithms: Streaming platforms leverage sophisticated algorithms to suggest music tailored to individual user preferences. This personalized experience enhances user satisfaction and encourages continued engagement, further driving demand. The algorithms, while not perfect, help users discover artists and songs they may never have encountered otherwise, ultimately expanding their musical tastes.
5. Technological Advancements: Improved mobile technology, high-quality headphones and speakers, and advancements in audio compression have all enhanced the listening experience. Better sound quality enhances the overall consumption experience, making the demand for premium listening experiences more desirable.
The Equilibrium Point: Where Supply Meets Demand
The intersection of supply and demand shapes the pricing and availability of online music. However, it's not a simple, static equilibrium. Several factors complicate the relationship:
1. Pricing Strategies: Streaming services utilize various pricing models, including free (ad-supported) and paid (subscription-based) tiers. These strategies balance the need to attract users with the need to generate revenue to pay artists and other stakeholders. The pricing can directly impact demand. A higher price point would likely limit the number of subscribers, while a very low price point could potentially affect profitability and the ability to pay artists appropriately.
2. Royalties and Revenue Sharing: The distribution of revenue from streaming services to artists and labels is a complex and often debated topic. The payment structures often involve a complex calculation of streams, market share, and licensing agreements, making it difficult for artists to earn a substantial income. The relatively low royalty rates paid to artists per stream have been criticized as unfair, impacting the long-term supply of music.
3. Copyright and Licensing: The legal framework surrounding copyright and licensing is vital. Ensuring artists' rights are protected is crucial for fostering a sustainable music ecosystem. However, navigating this complex landscape can be challenging, and copyright disputes can create friction between artists, labels, and streaming platforms. The complexities can inhibit growth on both supply and demand sides.
4. Emerging Technologies: Technologies like AI-generated music and NFTs are beginning to alter the online music landscape. These innovations can impact both supply and demand, potentially creating new revenue streams for artists but also raising ethical and legal questions. The long-term impact on the market is not yet fully understood.
The Future of Online Music: Harmonizing Supply and Demand
The future of the online music industry hinges on addressing the challenges and capitalizing on the opportunities present.
-
Fairer compensation for artists: Finding a sustainable model for paying artists fairly while ensuring the viability of streaming services is paramount. This could involve exploring different royalty structures, innovative payment models, and greater transparency in revenue sharing.
-
Improving artist discovery: While algorithms assist with music discovery, human curation remains essential. Support for emerging and independent artists is crucial for promoting diversity and creativity.
-
Strengthening copyright protection: Robust copyright laws are needed to protect artists' intellectual property, preventing unauthorized use and ensuring fair compensation.
-
Embracing new technologies responsibly: Leveraging technologies like AI and NFTs responsibly requires careful consideration of their ethical and legal implications, ensuring they benefit both creators and consumers.
-
Focus on user experience: Continuing to improve the user experience, personalization, and overall ease of use of streaming services is crucial for maintaining high demand.
The supply and demand of online music is a dynamic and ever-evolving system. Understanding its complexities is essential for all stakeholders involved. By working collaboratively towards fair compensation, improved discoverability, and a sustainable model, the industry can ensure a vibrant and flourishing future for artists and listeners alike. The digital soundscape is rich and full of potential – let's ensure it's a harmonious one for everyone involved.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
When Responding To Litigation Holds Foia Requests Investigations Or Inquiries
Mar 17, 2025
-
Participant Motivation Is Usually The Result Of
Mar 17, 2025
-
All Flags Such As Porn And Upsetting Offensive Are Query Independent
Mar 17, 2025
-
An Electrical Motor Provides 0 50 W Of Mechanical Power
Mar 17, 2025
-
Studying Marketing Should Help You To Blank
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Figure Shows The Supply And Demand For Online Music . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
