Tina Jones Respiratory Shadow Health Documentation
Onlines
Mar 17, 2025 · 6 min read
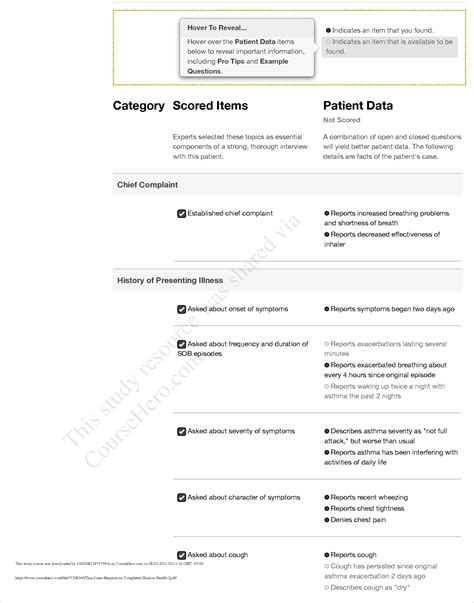
Table of Contents
Tina Jones Respiratory Shadow Health Documentation: A Comprehensive Guide
Shadow Health Tina Jones respiratory assessment provides a valuable simulated clinical experience for nursing students. Mastering this simulation requires a thorough understanding of respiratory assessment techniques, accurate documentation, and the ability to interpret findings within the context of the patient's overall health. This comprehensive guide delves into Tina Jones's case, providing insights into her respiratory system, potential diagnoses, and crucial documentation points. We'll explore how to effectively utilize the Shadow Health platform to improve your assessment skills and enhance your understanding of respiratory conditions.
Understanding Tina Jones's Respiratory Status
Tina Jones presents with a complex history and several factors contributing to her respiratory status. Successfully navigating her case requires attention to detail and a systematic approach. Her symptoms, past medical history, and physical examination findings are interconnected and crucial for formulating a comprehensive diagnosis.
Key Symptoms and Presenting Complaints
Tina Jones's initial complaints typically revolve around:
- Cough: Note the character of the cough – productive or non-productive, the consistency of sputum (if any), frequency, and duration. Documenting these details is vital for differentiating between various respiratory conditions.
- Shortness of Breath (Dyspnea): Assess the severity of dyspnea using appropriate scales (e.g., Borg Dyspnea Scale). Note when the dyspnea occurs (at rest, with exertion), and any associated factors.
- Chest Pain: If present, characterize the pain (location, quality, radiation, exacerbating/relieving factors). Differentiate between pleuritic chest pain (sharp, worsened by breathing) and other types of chest pain.
- Wheezing: Document the presence, location, and character of wheezing (inspiratory, expiratory, or both). Note if the wheezing is continuous or intermittent.
- Fatigue: Assess the severity and impact of fatigue on Tina's daily activities.
Past Medical History and Risk Factors
Consider the following aspects of Tina Jones's past medical history and risk factors that impact her respiratory system:
- Smoking History (pack-years): A significant risk factor for various respiratory illnesses, including COPD and lung cancer. Accurately calculating pack-years is crucial.
- Allergies: Document any known allergies (environmental, medication) that might contribute to respiratory symptoms.
- Family History: Inquire about family history of respiratory diseases like asthma, COPD, cystic fibrosis, or lung cancer.
- Occupational Exposures: Exposure to dust, chemicals, or other irritants in the workplace can significantly impact lung health.
Performing a Comprehensive Respiratory Assessment
The Shadow Health simulation allows for a detailed assessment of Tina Jones’s respiratory system. Accurately performing and documenting each aspect is essential.
Inspection
- Respiratory Rate and Rhythm: Observe the rate, depth, and rhythm of breathing. Document any irregularities (tachypnea, bradypnea, apnea, Kussmaul respirations, Cheyne-Stokes respirations).
- Respiratory Effort: Note the use of accessory muscles (sternocleidomastoids, intercostals, abdominal muscles). Increased effort suggests respiratory distress.
- Skin Color: Assess for cyanosis (bluish discoloration) or pallor, indicating potential hypoxia.
- Cough: Observe the presence of a cough and its characteristics (productive or non-productive, type of sputum).
- Posture: Note the patient's posture. Patients with respiratory distress may adopt a tripod position.
Palpation
- Thoracic Expansion: Assess the symmetry of chest expansion during breathing. Unequal expansion may indicate underlying pathology.
- Tactile Fremitus: Palpate for vibrations felt on the chest wall during spoken words. Increased or decreased fremitus can indicate consolidation or air trapping.
- Tenderness: Palpate for any tenderness over the chest wall.
Percussion
- Percuss the chest: Percuss systematically over different lung fields to assess for resonance (normal lung sound), hyperresonance (increased air), or dullness (consolidation or fluid).
Auscultation
- Lung Sounds: Systematically auscultate all lung fields, listening for normal breath sounds (vesicular, bronchovesicular, bronchial), as well as adventitious sounds like wheezes, crackles, rhonchi, and pleural rubs. Document the location, characteristics, and intensity of any abnormal sounds.
- Heart Sounds: Assess heart sounds for rate, rhythm, and presence of murmurs. Cardiac issues can indirectly affect respiratory function.
Interpreting Findings and Differential Diagnoses
Based on Tina Jones's assessment findings, several differential diagnoses should be considered:
- Asthma: Characterized by wheezing, cough, shortness of breath, and variable airflow obstruction.
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): A progressive lung disease involving chronic bronchitis and/or emphysema, typically associated with a history of smoking.
- Pneumonia: Infection of the lung parenchyma, often presenting with cough, fever, sputum production, and crackles on auscultation.
- Acute Bronchitis: Inflammation of the bronchi, often caused by viral or bacterial infection, characterized by cough, sputum production, and wheezing.
- Pulmonary Embolism (PE): Blood clot in the pulmonary artery, often presenting with sudden onset shortness of breath, chest pain, and tachypnea. This is a life-threatening condition requiring immediate attention.
- Pleurisy: Inflammation of the pleura, causing sharp chest pain worsened by breathing.
- Lung Cancer: A serious condition with a range of potential symptoms, including cough, hemoptysis (coughing up blood), weight loss, and chest pain.
Crucial Documentation in Shadow Health
Accurate and thorough documentation is paramount in the Shadow Health simulation. Here are key aspects to focus on:
- Subjective Data: Thoroughly document Tina Jones's reported symptoms, including their onset, duration, severity, and any associated factors.
- Objective Data: Record all findings from the physical examination, including vital signs (respiratory rate, heart rate, blood pressure, temperature, oxygen saturation), auscultation findings, and percussion notes. Be specific and detailed. Use precise medical terminology.
- Assessment: Formulate a differential diagnosis based on the collected data. Prioritize the most likely diagnoses based on the evidence.
- Plan: Outline your plan of care, including diagnostic tests (e.g., chest x-ray, pulmonary function tests, arterial blood gas analysis), treatments (e.g., bronchodilators, antibiotics, oxygen therapy), and patient education. Justify your choices based on your assessment.
- Medication Reconciliation: If Tina is taking any medications, document them accurately, including dosage, frequency, and route of administration. Be aware of potential drug interactions.
- Follow-up Plans: Outline your plan for follow-up, including any needed referrals or further diagnostic testing.
Enhancing Your Performance in Shadow Health
To excel in the Tina Jones respiratory assessment, consider these strategies:
- Review Respiratory Anatomy and Physiology: A solid understanding of the respiratory system is crucial for accurate interpretation of findings.
- Practice Auscultation Techniques: Practice listening to lung sounds on real patients (if possible) or using audio recordings to refine your skills.
- Familiarize Yourself with Common Respiratory Conditions: Review the symptoms, diagnostic criteria, and treatment options for various respiratory diseases.
- Utilize Shadow Health Resources: Take advantage of the built-in resources within the Shadow Health platform, such as hints and feedback.
- Seek Feedback from Instructors: Discuss your assessments with your instructors to identify areas for improvement.
Conclusion
Mastering the Tina Jones respiratory assessment in Shadow Health requires meticulous attention to detail, a systematic approach, and a strong understanding of respiratory physiology and pathology. By carefully documenting your findings, formulating a differential diagnosis, and outlining a comprehensive plan of care, you will not only excel in the simulation but also develop crucial clinical skills for effective patient care. Remember to continuously review respiratory assessment techniques and utilize the platform's resources to refine your diagnostic reasoning and documentation skills. The more you practice, the more confident and competent you will become in managing patients with respiratory conditions.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Participant Motivation Is Usually The Result Of
Mar 17, 2025
-
All Flags Such As Porn And Upsetting Offensive Are Query Independent
Mar 17, 2025
-
An Electrical Motor Provides 0 50 W Of Mechanical Power
Mar 17, 2025
-
Studying Marketing Should Help You To Blank
Mar 17, 2025
-
Shaping Clay On A Rapidly Turning Wheel Is Called
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Tina Jones Respiratory Shadow Health Documentation . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
