Wave On A String Phet Answer Key
Onlines
Mar 17, 2025 · 6 min read
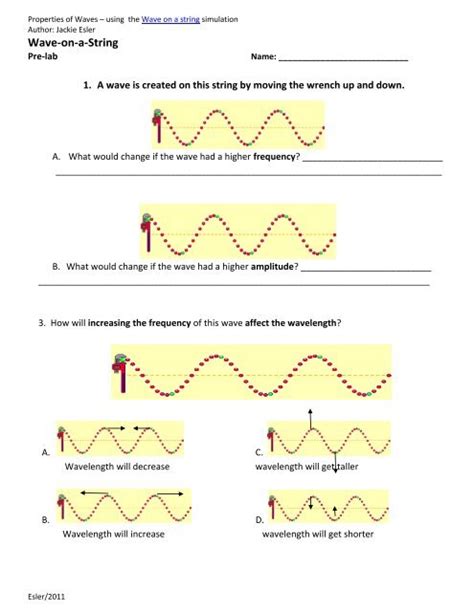
Table of Contents
Wave on a String PhET Simulation: A Comprehensive Guide
The PhET Interactive Simulations project offers a fantastic tool for exploring physics concepts, including wave behavior. Their "Wave on a String" simulation provides a dynamic and engaging way to understand various properties of transverse waves. This detailed guide will dissect the simulation, explaining its features and answering common questions, essentially acting as your comprehensive Wave on a String PhET answer key.
Understanding the Wave on a String Simulation
The simulation allows you to manipulate several parameters to observe their effects on wave propagation. Key features include:
-
Oscillator: This controls the wave generation. You can adjust the frequency, amplitude, and damping. Understanding how these affect the wave's properties is crucial.
-
String Tension: Altering the tension directly impacts the wave speed. Higher tension leads to faster waves. This connection is fundamental to understanding the wave equation.
-
Damping: This simulates energy loss in a real-world system. Higher damping leads to waves that decay more quickly.
-
Wave Properties: The simulation visually displays key wave characteristics like wavelength, frequency, and amplitude.
-
Fixed End vs. Loose End: You can choose between a fixed end (where the wave reflects inverted) and a loose end (where it reflects upright). This demonstrates the principle of boundary conditions.
Exploring Key Concepts with the Simulation
Let's dive into specific concepts and how the simulation helps you grasp them.
1. Relationship between Frequency, Wavelength, and Wave Speed
The simulation is excellent for demonstrating the fundamental wave equation: v = fλ, where:
- v represents wave speed
- f represents frequency
- λ represents wavelength
By adjusting the oscillator's frequency and observing the resulting wavelength, you can directly verify this relationship. Increasing the frequency while keeping tension constant will decrease the wavelength, and vice versa. This reinforces the inverse relationship between frequency and wavelength at a constant speed. The tension setting here acts as a constant influencing the wave speed (v).
2. The Effect of Tension on Wave Speed
The simulation clearly shows that increasing string tension increases the wave speed. This is because a tighter string offers greater resistance to displacement, allowing the wave to propagate faster. This directly relates to the mathematical expression for wave speed in a string, which involves the square root of the tension.
3. Amplitude and Energy
The amplitude of a wave represents the maximum displacement from equilibrium. The simulation demonstrates that a larger amplitude corresponds to a wave carrying more energy. This is intuitive; a larger wave visibly carries more 'oomph'. The simulation doesn't directly quantify energy, but the visual representation allows for a clear qualitative understanding.
4. Damping and Energy Dissipation
Damping simulates the loss of energy due to friction and other resistive forces. By increasing the damping, you'll observe the wave's amplitude gradually decreasing over time. This visually represents energy dissipation, showcasing how real-world waves don't propagate indefinitely.
5. Superposition and Interference
The simulation allows you to generate multiple waves simultaneously. When waves overlap, they interfere, demonstrating the principle of superposition. You can observe constructive interference (waves adding up to create a larger amplitude) and destructive interference (waves canceling each other out). This is a powerful visual demonstration of a complex wave phenomenon.
6. Reflection and Boundary Conditions
The choice between a fixed end and a loose end highlights the impact of boundary conditions on wave reflection. At a fixed end, the wave reflects inverted, while at a loose end, it reflects upright. This directly demonstrates how the boundary conditions determine the phase change upon reflection.
7. Standing Waves and Resonance
By carefully adjusting the frequency, you can create standing waves. These are stationary wave patterns formed by the superposition of two waves traveling in opposite directions. Specific frequencies, called resonant frequencies, will produce stable standing waves with distinct nodes (points of zero displacement) and antinodes (points of maximum displacement). The simulation helps visualize these patterns and understand the concept of resonance.
Advanced Exploration and Problem Solving
Beyond the basic observations, the simulation encourages deeper exploration. Consider these advanced applications:
-
Quantitative Analysis: Use the simulation's measurements (wavelength, frequency, amplitude) to perform calculations and verify the wave equation under various conditions.
-
Predictive Modeling: Based on your understanding of the relationships between different parameters, try to predict the outcome of changing a specific parameter before actually changing it in the simulation.
-
Comparative Studies: Systematically vary one parameter while keeping others constant to isolate its impact on wave properties. This methodical approach enhances your understanding of cause and effect.
-
Real-world Applications: Relate the concepts observed in the simulation to real-world examples like musical instruments, seismic waves, or light waves.
Addressing Common Questions (Your Wave on a String PhET Answer Key)
Here are some frequently asked questions and answers based on the simulation:
Q: Why does the wave speed change when I adjust the tension?
A: The speed of a wave on a string is directly proportional to the square root of the tension. Higher tension means the string resists displacement more strongly, leading to faster wave propagation.
Q: How can I create a standing wave?
A: Adjust the frequency of the oscillator until you observe a stable wave pattern with nodes and antinodes. These are standing waves, resulting from the superposition of incident and reflected waves. Resonant frequencies are key to producing them.
Q: What is the difference between a fixed end and a loose end?
A: A fixed end reflects the wave with a 180-degree phase shift (inverted), while a loose end reflects the wave without a phase shift (upright). This difference stems from the boundary conditions at each end.
Q: What does damping represent?
A: Damping simulates energy loss due to friction and other resistive forces. Higher damping causes the wave amplitude to decay faster over time.
Q: How does amplitude relate to energy?
A: A larger amplitude means the wave carries more energy. Although the simulation doesn't directly show energy, the visual representation of amplitude allows a clear qualitative understanding of this relationship.
Q: Can I use this simulation to study longitudinal waves?
A: No, this specific simulation focuses on transverse waves, where the wave's displacement is perpendicular to its direction of propagation. Longitudinal waves (like sound) require a different simulation.
Q: How does this simulation relate to real-world phenomena?
A: This simulation provides a foundation for understanding many real-world wave phenomena, including sound waves in musical instruments, seismic waves, and even light waves (although light waves are electromagnetic, the principles of superposition and interference still apply).
Conclusion: Mastering Wave Phenomena with the PhET Simulation
The "Wave on a String" PhET simulation is an invaluable tool for grasping fundamental concepts related to wave mechanics. By actively experimenting with different parameters and observing their effects, you can develop a deeper intuitive understanding of wave behavior. This guide serves as a thorough Wave on a String PhET answer key, guiding you through the simulation’s features and providing answers to common questions. Remember to use the simulation actively, exploring beyond the basics and applying your knowledge to real-world situations to truly master the subject. Through careful observation and experimentation, you'll be well on your way to becoming proficient in the fascinating world of wave physics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Medical Surgical Lpn Rn Assessment 1 Shiftkey Answers
Mar 17, 2025
-
Project Stem 7 4 Code Practice Question 1
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Type Of Pay Is Modeled Below
Mar 17, 2025
-
Which Statement Describes The Greek Philosopher Socrates
Mar 17, 2025
-
The Far Prohibits All Of The Following Except
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Wave On A String Phet Answer Key . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
