What Are Two Types Of Ipv6 Unicast Addresses Choose Two
Onlines
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
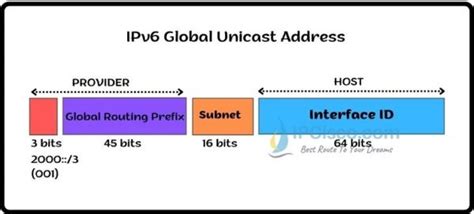
Table of Contents
Two Types of IPv6 Unicast Addresses: A Deep Dive into Global Unicast and Unique Local Addresses
The transition to IPv6, the next-generation internet protocol, is crucial for addressing the ever-growing demand for IP addresses. Unlike its predecessor, IPv4, IPv6 boasts a vastly larger address space, effectively eliminating the IP address exhaustion problem. Within this expansive address space lie several address types, each serving a unique purpose. This article will delve into two prominent types of IPv6 unicast addresses: Global Unicast Addresses and Unique Local Addresses (ULA). We'll explore their structure, functionality, and practical applications, highlighting their key differences and when to use each.
Understanding IPv6 Unicast Addresses
Before diving into specific address types, let's establish a foundational understanding of IPv6 unicast addresses. A unicast address, in both IPv4 and IPv6, uniquely identifies a single interface on a network. When a packet is sent to a unicast address, it's delivered specifically to the device with that address. This contrasts with multicast and broadcast addresses, which deliver packets to multiple interfaces.
IPv6 addresses are 128 bits long, represented as eight groups of four hexadecimal digits separated by colons (:). For example, 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334 is a valid IPv6 address. Leading zeros within each group can be omitted for brevity (e.g., 2001:db8:85a3::8a2e:370:7334). Furthermore, consecutive groups of zeros can be replaced with a single double colon (::), but only once per address.
Global Unicast Addresses: Your Gateway to the Global Internet
Global Unicast Addresses (GUA) are the workhorses of IPv6, providing globally routable addresses that can be reached from anywhere on the internet. These addresses are assigned by Internet service providers (ISPs) and are essential for communication between devices across different networks. Think of them as the IPv6 equivalent of public IPv4 addresses.
Structure of Global Unicast Addresses
GUAs follow a specific hierarchical structure, reflecting the organization of the internet's routing infrastructure. The structure typically consists of:
-
Global Routing Prefix (GRP): This is the most significant part of the address, assigned by regional internet registries (RIRs) to ISPs. It identifies the network or organization that owns the address space.
-
Subnet ID: This portion identifies a specific subnet within the larger network assigned to the ISP.
-
Interface ID: This is the least significant part of the address, uniquely identifying a specific interface on a device within the subnet. This is usually derived from the device's MAC address using a process called EUI-64.
Key Features of Global Unicast Addresses
-
Global Reachability: The defining characteristic of GUAs is their ability to be reached from any point on the internet.
-
Hierarchical Routing: Their structured design allows for efficient routing of packets across the internet.
-
Assigned by ISPs: ISPs assign these addresses to their customers, enabling them to connect to the internet.
-
Unique Identification: Each GUA is unique globally, preventing address conflicts.
Practical Applications of Global Unicast Addresses
GUAs are used in a multitude of internet applications, including:
-
Web browsing: Accessing websites requires a globally routable address.
-
Email communication: Sending and receiving emails relies on globally unique addresses.
-
Online gaming: Multiplayer games depend on GUAs for communication between players.
-
Cloud services: Accessing cloud resources often utilizes GUAs.
-
IoT devices: Many internet-connected devices rely on GUAs for communication.
Unique Local Addresses: Your Private IPv6 Network
Unique Local Addresses (ULA), also known as site-local addresses, are designed for private networks that don't require global routing. They are suitable for internal communication within an organization or home network and are not routable across the public internet. Think of them as the IPv6 equivalent of private IPv4 addresses (192.168.x.x, 10.x.x.x, 172.16.x.x).
Structure of Unique Local Addresses
ULAs are easily identifiable by their fixed prefix: fc00::/7. The remaining bits are used for identifying specific subnets and interfaces within the private network. This structure ensures that ULAs never overlap with global unicast addresses, preventing potential routing conflicts.
Key Features of Unique Local Addresses
-
No Global Routing: ULAs are not routable across the public internet. This enhances security and privacy.
-
Auto-configuration: ULAs can be auto-configured using a process called Stateless Address Autoconfiguration (SLAAC), simplifying network setup.
-
Private Network Use: ULAs are ideal for internal networks, such as home networks, office networks, or virtual private networks (VPNs).
-
Privacy Enhancement: Because ULAs aren't exposed to the public internet, they contribute to improved privacy.
-
No ISP Assignment: ULAs don't require assignment from an ISP, offering flexibility and autonomy.
Practical Applications of Unique Local Addresses
ULAs find use in several scenarios:
-
Home Networks: Connecting devices within a home network without the need for globally routable addresses.
-
Office Networks: Facilitating internal communication within an organization without exposing devices to the global internet.
-
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): Creating secure connections between devices across geographically dispersed locations.
-
Testing and Development Environments: Providing a safe and isolated environment for testing network applications.
-
Virtual Machines: Assigning private IP addresses to virtual machines running within a network.
Choosing Between Global Unicast and Unique Local Addresses
The choice between GUAs and ULAs depends heavily on your network's needs and connectivity requirements. Here's a simple guide:
| Feature | Global Unicast Address (GUA) | Unique Local Address (ULA) |
|---|---|---|
| Routing | Globally routable | Not routable on the public internet |
| Assignment | Assigned by ISP | Auto-configured or manually assigned locally |
| Purpose | Public internet communication | Private network communication |
| Security | Less secure (exposed to the internet) | More secure (not exposed to the internet) |
| Privacy | Less private (globally identifiable) | More private (not globally identifiable) |
| Complexity | More complex configuration | Simpler configuration |
Use Global Unicast Addresses (GUAs) when:
- You need to access resources on the public internet.
- Your devices need to be reachable from the outside world.
- Your application requires global communication.
Use Unique Local Addresses (ULAs) when:
- You only need communication within a private network.
- You want to enhance security and privacy.
- Simple network configuration is desired.
- You are creating a test or development environment.
Conclusion: Navigating the IPv6 Address Space
Understanding the differences between Global Unicast Addresses and Unique Local Addresses is crucial for effective IPv6 network management. By selecting the appropriate address type for each situation, you can optimize network performance, enhance security, and ensure seamless communication within and beyond your private network. The vast address space of IPv6, coupled with the diverse address types, provides the flexibility to address the evolving needs of the internet. Remember to carefully consider your specific requirements when choosing between GUAs and ULAs to maximize the benefits of IPv6. The transition to IPv6 is not merely a technical upgrade; it's a fundamental shift toward a more scalable, secure, and efficient internet. Mastering the intricacies of IPv6 addressing is key to navigating this new landscape successfully.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
When The Simcell Membrane In The Cell O Scope
Mar 20, 2025
-
What Is The Medial Border Of The Highlighted Region Called
Mar 20, 2025
-
The Number Of Accidents At A Manufacturing Facility
Mar 20, 2025
-
Continuous Monitors Are Run For Systems That Could
Mar 20, 2025
-
The First 100 Days Icivics Answer Key
Mar 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are Two Types Of Ipv6 Unicast Addresses Choose Two . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
