Pn Learning System Medical Surgical Endocrine Practice Quiz
Onlines
Mar 30, 2025 · 6 min read
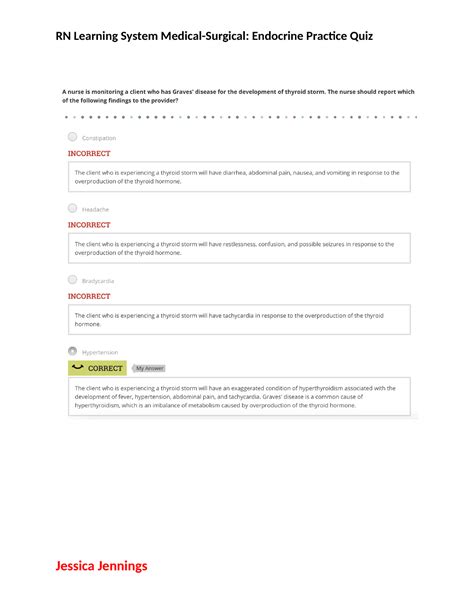
Table of Contents
PN Learning System Medical-Surgical Endocrine Practice Quiz: A Comprehensive Guide
The medical-surgical endocrine system is a complex and crucial area of nursing practice. A thorough understanding of endocrine disorders, their treatments, and associated nursing implications is vital for providing safe and effective patient care. This article serves as a comprehensive guide to preparing for a PN (Practical Nurse) learning system medical-surgical endocrine practice quiz, covering key concepts, common disorders, and nursing interventions. We’ll delve into the essential knowledge you need to succeed.
Understanding the Endocrine System
Before tackling specific disorders, it's essential to establish a firm grasp of the endocrine system's fundamental functions. The endocrine system is a network of glands that produce and secrete hormones, chemical messengers that regulate various bodily functions. These functions include:
- Metabolism: Hormones influence how the body uses energy from food.
- Growth and Development: Hormones are crucial for growth during childhood and adolescence.
- Reproduction: Hormones regulate sexual function and reproduction.
- Mood: Hormones play a significant role in emotional well-being.
- Sleep: Hormones regulate sleep-wake cycles.
Understanding the interplay between different glands (pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pancreas, ovaries, and testes) and their respective hormone production is paramount. This understanding forms the basis for comprehending endocrine disorders.
Key Hormones and Their Functions:
- Insulin (Pancreas): Regulates blood glucose levels.
- Glucagon (Pancreas): Raises blood glucose levels.
- Thyroxine (T4) and Triiodothyronine (T3) (Thyroid): Regulate metabolism.
- Calcitonin (Thyroid): Lowers blood calcium levels.
- Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) (Parathyroid): Raises blood calcium levels.
- Cortisol (Adrenal): Regulates stress response and metabolism.
- Aldosterone (Adrenal): Regulates sodium and potassium balance.
- Epinephrine and Norepinephrine (Adrenal): "Fight-or-flight" response hormones.
- Growth Hormone (Pituitary): Stimulates growth and cell reproduction.
- Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) (Pituitary): Regulates water balance.
Mastering these hormones and their functions is crucial for understanding the pathophysiology of endocrine disorders.
Common Endocrine Disorders: A Nursing Perspective
The following sections cover some of the most frequently encountered endocrine disorders in a medical-surgical setting. For each disorder, we'll discuss key characteristics, nursing assessments, and interventions.
1. Diabetes Mellitus:
Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune disease where the body destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Nursing care focuses on insulin administration, blood glucose monitoring, patient education on self-management, and recognizing signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia. Key Assessment Parameters: Blood glucose levels, urine ketones, signs of dehydration, and neurological changes.
Type 2 Diabetes: Characterized by insulin resistance and impaired insulin secretion. Nursing care emphasizes lifestyle modifications (diet, exercise), medication administration (oral hypoglycemics, insulin), and patient education on self-management. Key Assessment Parameters: Blood glucose levels, HbA1c levels, weight, and cardiovascular risk factors.
Gestational Diabetes: Diabetes that develops during pregnancy. Nursing care includes blood glucose monitoring, dietary management, and potential insulin therapy. Key Assessment Parameters: Blood glucose levels, fetal growth, and maternal well-being.
2. Thyroid Disorders:
Hypothyroidism: Underactive thyroid gland resulting in decreased production of thyroid hormones. Symptoms include fatigue, weight gain, constipation, and cold intolerance. Nursing care focuses on medication administration (levothyroxine), patient education on medication adherence, and monitoring for adverse effects. Key Assessment Parameters: Thyroid hormone levels (TSH, T3, T4), vital signs, and neurological status.
Hyperthyroidism: Overactive thyroid gland resulting in excessive production of thyroid hormones. Symptoms include weight loss, nervousness, palpitations, and heat intolerance. Nursing care focuses on medication administration (antithyroid drugs, radioactive iodine), patient education, and monitoring for adverse effects. Key Assessment Parameters: Thyroid hormone levels (TSH, T3, T4), vital signs, and cardiac rhythm.
3. Adrenal Disorders:
Addison's Disease (Adrenal Insufficiency): A condition where the adrenal glands don't produce enough cortisol and aldosterone. Nursing care focuses on hormone replacement therapy (cortisol and aldosterone), monitoring for electrolyte imbalances, and educating patients about the importance of medication adherence and stress management. Key Assessment Parameters: Electrolyte levels (sodium, potassium), blood pressure, and signs of dehydration.
Cushing's Syndrome: A condition caused by prolonged exposure to high levels of cortisol. Nursing care focuses on managing symptoms (hyperglycemia, hypertension, weight gain, muscle weakness), providing emotional support, and collaborating with the healthcare team on treatment strategies. Key Assessment Parameters: Blood glucose levels, blood pressure, weight, and signs of muscle wasting.
4. Parathyroid Disorders:
Hypoparathyroidism: Characterized by low levels of parathyroid hormone, leading to low blood calcium levels. Nursing care focuses on calcium and vitamin D supplementation, monitoring for tetany (muscle spasms), and promoting safety measures to prevent falls. Key Assessment Parameters: Calcium levels, phosphorus levels, and neurological status.
Hyperparathyroidism: Characterized by high levels of parathyroid hormone, leading to high blood calcium levels. Nursing care focuses on monitoring for kidney stones, bone pain, and gastrointestinal issues. Key Assessment Parameters: Calcium levels, phosphorus levels, and kidney function tests.
Nursing Interventions and Patient Education: A Holistic Approach
Effective nursing care for patients with endocrine disorders requires a comprehensive approach encompassing:
- Medication Administration: Accurate and timely administration of prescribed medications is crucial. This includes understanding the mechanisms of action, potential side effects, and proper administration techniques.
- Blood Glucose Monitoring: Regular blood glucose monitoring is essential for managing diabetes. Nurses must be proficient in performing blood glucose testing and interpreting the results.
- Dietary Management: Nutrition plays a critical role in managing many endocrine disorders. Nurses should provide dietary counseling and support to patients.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise and weight management, are crucial for managing many endocrine disorders. Nurses should encourage and support patients in adopting healthy lifestyle choices.
- Patient Education: Educating patients and their families about their condition, medication, and self-management strategies is crucial for achieving optimal outcomes. This includes teaching patients how to monitor their blood glucose levels, recognize signs and symptoms of complications, and adjust their treatment plan as needed.
- Psychosocial Support: Endocrine disorders can have a significant impact on a patient's emotional well-being. Nurses should provide emotional support and refer patients to mental health professionals if needed.
Preparing for Your PN Learning System Medical-Surgical Endocrine Practice Quiz
To effectively prepare for your practice quiz, consider the following strategies:
- Review Class Materials: Thoroughly review all course materials, including textbooks, lecture notes, and handouts. Pay particular attention to areas where you feel less confident.
- Practice Questions: Utilize practice quizzes and questions available in your learning system or from other reputable resources. This will help identify areas needing further study and improve test-taking skills.
- Focus on Key Concepts: Concentrate on understanding the fundamental principles of endocrine physiology, common endocrine disorders, and associated nursing interventions.
- Create Flashcards: Develop flashcards to aid in memorizing key concepts, hormones, and disorders.
- Study Groups: Collaborate with fellow students to review materials and quiz each other. This approach enhances learning and helps solidify understanding through discussion.
- Prioritize Sleep and Nutrition: Ensure you get adequate rest and maintain a healthy diet in the days leading up to the quiz. This will enhance cognitive function and reduce stress.
- Time Management: Develop a realistic study schedule that allows you to cover all the necessary material without feeling overwhelmed.
By diligently reviewing these key concepts and employing effective study strategies, you can significantly enhance your readiness for your PN learning system medical-surgical endocrine practice quiz. Remember, consistent effort and a comprehensive understanding of the material are your best assets for success. Good luck!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Block Initially At Rest Is Given A Quick Push
Apr 01, 2025
-
Ms Jensen Has Heard About Original
Apr 01, 2025
-
Experiment 13 The Geometrical Structure Of Molecules Answers
Apr 01, 2025
-
You Completed Your Ati Capstone Assessment And Want To Contact
Apr 01, 2025
-
Paralytic Medications Exert Their Effect By
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Pn Learning System Medical Surgical Endocrine Practice Quiz . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
